Bladder
The bladder, vesica urinaria, is a flat, round hollow muscular organ, located in the cavity of the pelvis , directly behind the pubic adhesion. The size and shape of the bladder varies depending on the filling of the urine. The filled bladder looks like a pear in shape. The wide part of it is turned upward and backward, and the narrow part is facing downwards and forwards. Empty bladder, when its walls fall off, saucer-like; The average capacity is 750 cc.
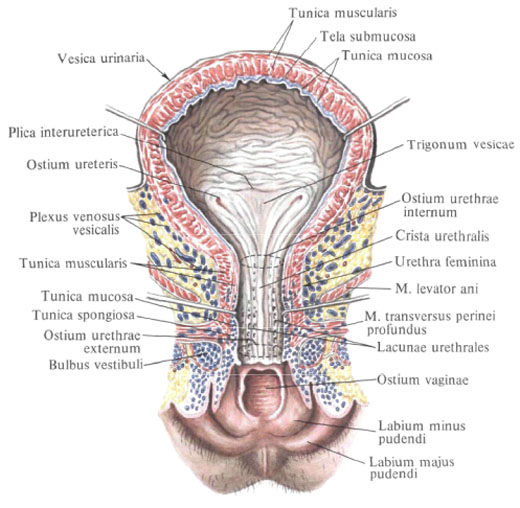
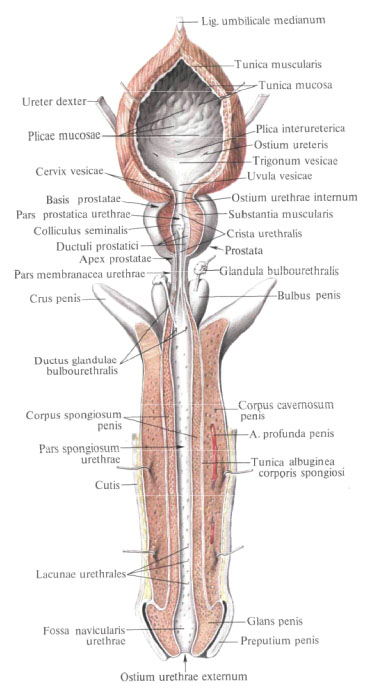
The bladder consists of several sections that move one into another. The main part is the body of the bladder , corpus vesicae. The uppermost part of the bladder forms its apex, apex vesicae, which is clearly discernible with a filled bladder; She goes up, towards the navel, into the middle umbilical ligament, lig. Umbilicale medianum, connecting the bladder with the navel; This ligament represents the overgrown urinary duct, the urachus. The posterior part of the bladder, directed towards the men in the direction of the rectum, and in women - towards the vagina, represents the bottom of the bladder, fundus vesicae; This is the least mobile part of the bladder. The anterior, elongated part of the bladder forms the neck of the bladder, cervix vesicae, in this part there is an internal opening of the urethra, ostium urethrae internum.
In the body of a filled bladder, the front, back and side walls are distinguished. The front wall corresponds to the area of the bladder between the tip and the neck; It is turned towards the pubic symphysis, and with a full bladder located behind the anterior abdominal muscles - the pyramidal and rectus abdominal muscles. The rear wall, facing upward, into the abdominal cavity, is the department covered with the peritoneum. The serous membrane present here, tunica serosa, fuses with the muscular membrane by means of a subserous base, tela subserosa.
The wall of the bladder consists of smooth muscle tissue, its lining is lined with a mucous membrane, it is covered partially by an adventitial membrane, partially - serous.
The muscular membrane, tunica muscularis, rather thick, consists of unsharply demarcated, transforming into one another three layers: outer, middle and inner.
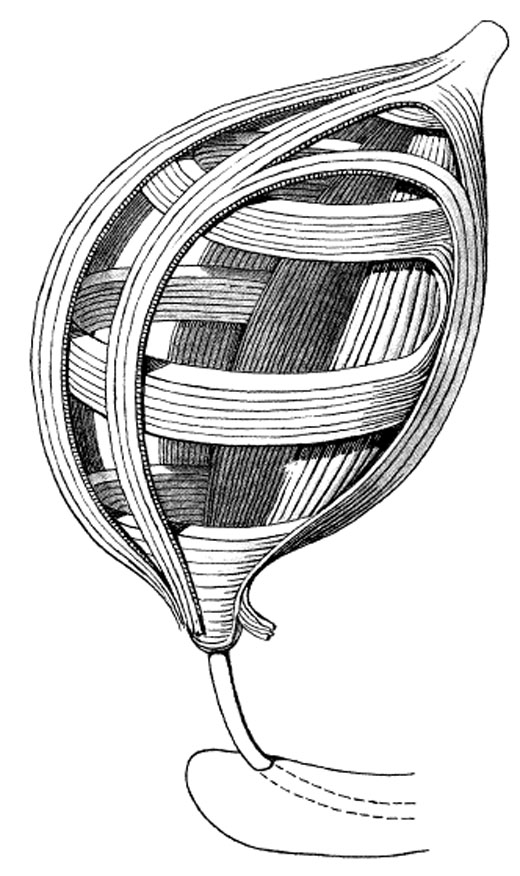
The outer longitudinal layer , stratum longitudinale externum, begins with each side of the pubic fusion from the lower branch of the pubic bone with pubescent muscle, m. Pubovesicalis, which goes back to the neck of the bladder and over the bottom, and then the posterior surface reaches the top of the bladder. Passing along the back wall of the bladder, the muscle gives the muscular layer of the rectum to the muscular layer of the rectum a twin rectum-vesicle muscle, m. Rectovesicalis, in women a similar muscle goes to the cervix, and from the posterior surface of it - to the lateral surfaces of the rectum and the sacrum - the rectum-uterine muscle, m. Rectouterinus.
The middle circular layer , stratum circulare, located deeper, is the most powerful muscle layer of the bladder, is the main one in the structure of the muscular wall. It is formed circularly (in the horizontal plane) by disposed beams.
In the region of the neck of the bladder, he passes into the sphincter of the urethra, m. Sphincter urethrae.
The inner longitudinal layer , stratum longitudinale internum, is the deepest and the weakest. It consists of bundles of muscles longitudinal, partially oblique, and is developed only in the region of the bottom of the bladder.
All three muscle layers are not equally developed in all parts of the bladder, and as a result of the presence of obliquely extending muscle beams passing from one layer to the other, the boundaries between them are not sufficiently expressed. Due to uneven development of muscle layers with a strong stretching of the bladder, some parts of its wall are thinned and the mucous membrane is stretched.
All three muscle layers are combined due to a common function - reducing the volume of the bladder in the muscle, pushing the urine, m. Detrusor vesicae.
The mucosa , tunica mucosa, is covered with transitional epithelium, has a submucosa, tela submucosa, rich in fibrous connective tissue and permeated with thinner and thicker elastic fibers, resulting in numerous folds; With a filled bladder, these folds stretch.
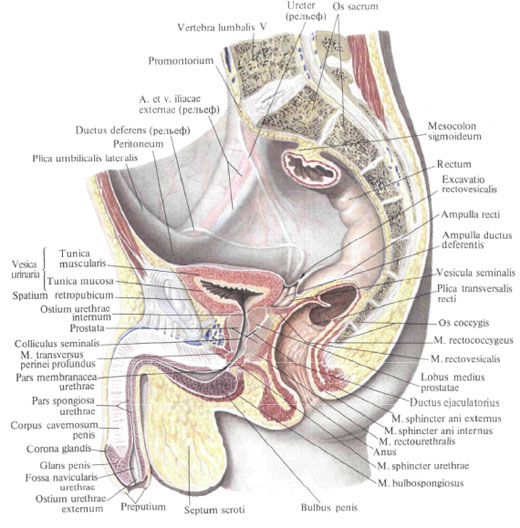
Upper posterior and partly lateral surfaces of the bladder are covered with the peritoneum; When the peritoneum passes from the bladder to the posterior surface of the anterior abdominal wall, a transverse pleural fold is formed, plica vesicalis transversa. Behind, at the level of the confluence of the ureters, the peritoneum passes from the bladder to the rectum, and in the womb - to the uterus. With its anterior, extraperitoneal surface, the bladder adjoins the pubic symphysis and the upper branches of the pubic bones and is separated from them by the visceral fascia; In a full state, the bubble comes out from behind the pubic symphysis upward, behind the rectus abdominal muscles.
In men, seminal vesicles, vas deferens and partly the prostate gland adhere to the bottom of the bladder; In the interval between the seminal vesicles, the front wall of the ampulla of the rectum adjoins the bottom of the bladder. In women, the cervix and the front wall of the vagina adhere to the bottom of the bladder. The anterior section of the bladder, its neck, is adjacent to the men in the posterior region of the upper part of the anterior surface of the prostate gland, in women to the urogenital diaphragm. The lower sections of the lateral walls of the urinary bladder, located retroperitoneally, are partly in contact with the pelvic floor, and in the filled state of the bladder - to the occlusal muscles; In men, the vas deferens adhere to these muscles, and the female has round ligament ligament.
Innervation: plexus hypogastrici superior et inferior (sympathetic innervation), nn. Splanchnici pelvini (parasympathetic), n. Pudendus from plexus sacralis (sensitive).
Blood supply: upper parts of the body and apex - a. Vesicalis superior (from a. Umbilicalis), lower divisions and the bottom of the bladder - a. Vesicalis inferior (from a. Iliaca interna), sometimes branches from a. Rectalis media, and for women -a. Uterina. Venous blood flows out by vv. Vesicales in plexus venosus vesicalis or directly in v. Iliaca interna. Lymphatic vessels carry lymph to the nodi lymphatici iliaci interni and paravesicularae (previsiculares, postvesiculares, vesicales laterales).
You will be interested to read this:









Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.