Bones of the wrist
The bones of the wrist , ossa carpi, are arranged in two rows. The upper, or proximal, row adjoins the distal part of the bones of the forearm, forming an elliptical articular surface convex towards the forearm; The other row is lower, or distal, facing the pastern. 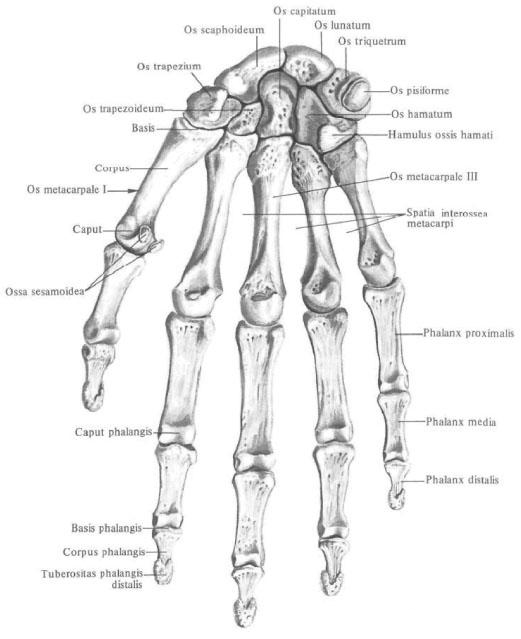
To the bones of the first row of the wrist, if we count from the ray edge of the hand to the ulnar bone, the following bones are included: scaphoid, semilunar, trihedral and pea-shaped.
The second row of bones of the wrist are respectively: bone-trapezium, trapezoid bone, capitate and hook-shaped bone.
Occasionally, the unstable central bone, os centrale, located between the scaphoid bone, trapezoid bone and the head bone is located on the back surface of the wrist.
Scaphoid
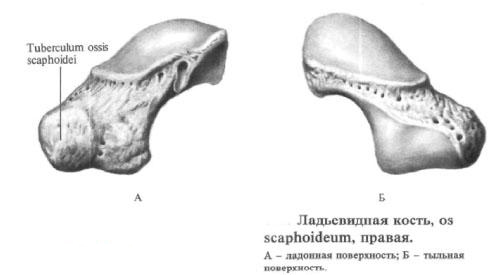
The scaphoid bone, os scaphoideum, occupies the most lateral position in the first row of the bones of the wrist. Its palmar surface is concave and extends in the external part to the tubercle of the scaphoid bone, tuberculum ossis scaphoidei.
The posterior surface of the bone is a narrow strip that extends proximally to the convex articular surface, which joins the carpal articular surface of the distal epiphysis of the radius. The lower medial bone section carries a concave articular surface, articulating with the head bone. Above it, on the medial side of the bone, is the articular surface for articulation with the semilunar bone. The lateral lower surface of the bone is articulated with a trapezoid bone and trapezoid bone.
Semilunar bone
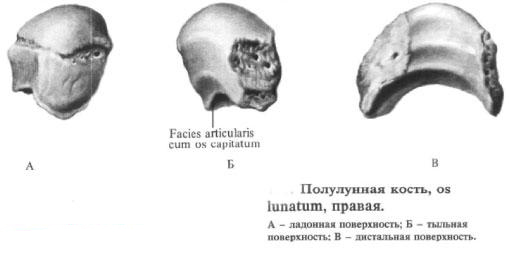
The semilunar bone, os lunatum, is medial to the navicular. The upper surface of the bone is convex. It articulates with the carpal joint surface of the radius. The lower surface of the bone is concave, in the lateral part of the bone there is an articular surface for articulation with the head bone, and in the medial surface there is an articular surface for articulation with a hooked bone.
The lateral side of the bone has an articular surface, articulating with the scaphoid bone. The medial surface of the bone is articulated with a trihedral bone.
Triangular bone
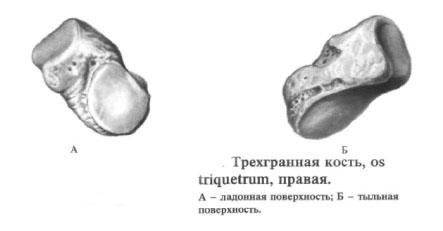
The trihedral bone, os triquetrum, occupies the most medial position in the first row of the bones of the wrist. The upper surface of the bone is convex, bearing the articular surface for articulation with the distal forearm.
The lateral part of the bone has a flat articular surface, articulating with the semilunar bone; The lower, slightly concave surface is articulated with a hook-shaped bone, and the palm surface - with a pea-bone.
Pisiform bone
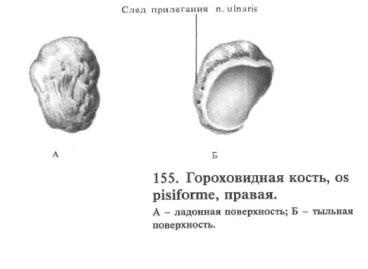
The bony bone, os pisiforme, is ovoid. It belongs to the sesamoid bones, ossa sesamoidea, and lies in the thickness of the tendon of the elbow flexor of the wrist. On the rear, back, side of the pea, there is a small flat articular surface, through which it joins with a trihedral bone.
Bone trapezoid
The bone trapezium, os trapezium, is distal to the scaphoid bone, occupying the most lateral position in the second row of the bones of the wrist. The upper surface of the bone carries an articulation pad for articulation with the scaphoid bone. The lower surface of the bone has a saddle articular surface, which articulates with the base of the metacarpal bone. On the medial part of the bone there are two concave articular surfaces: a large upper and a lower lower surface. The first serves for articulation with a trapezoid bone, the second - with the base of II metacarpal bone.
On the anterior (palmar) surface of the bone in the lateral section there is a small protrusion - a tubercle of bone-trapezium, tuberculum ossis trapezii. Inside of it is a furrow - a trace of the adjoining beam flexor of the hand, m. Flexor carpi radialis.
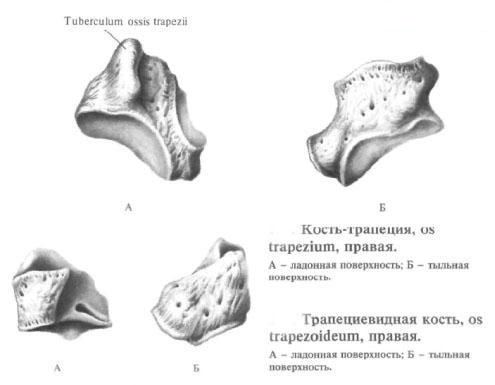
Trapezoidal bone
The trapezoid bone, os trapezoideum, is located next to the bone trapezoid. Its lower saddle articular surface is articulated with the second metacarpal bone.
The upper surface of the bone is concave and articulates with the scaphoid bone, lateral, somewhat convex, the surface - with a bone-trapezium and medial, concave, - with the head bone.
Head bone
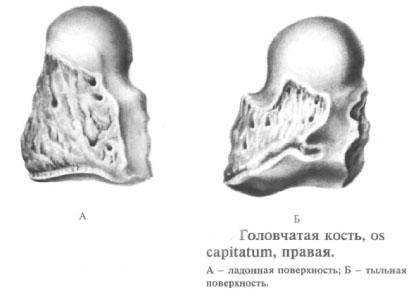
The head bone, os capitatum, is the largest of the bones of the wrist, in the proximal part has a globular head. The rest of the bone is somewhat thickened. The medial surface is articulated with a hooked bone, and the lateral, somewhat convex, with a trapezoid bone. The lower surface of the bone by means of a flat articular joint articulates with the base of the third metacarpal bone: the lateral surfaces of the bone have small articular surfaces for articulation with the bases of II and IV metacarpal bones.
Hook-shaped bone
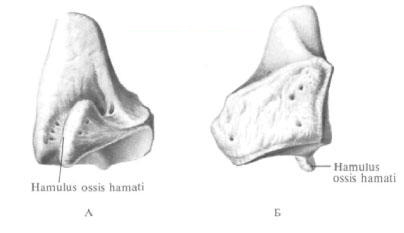
The hooked bone, os hamatum, is located next to the capitate bone, closing the second row of bones of the wrist with the medial, ulnar, side. On the anterior, palmar, bone surface is a well developed process, somewhat curved in the lateral, radial, side, - the hook of the hook-shaped bone, hamulus ossis hamati. The proximal bone surface is articulated with the semilunar bone, the lateral - with the head bone - medial, somewhat convex, - with a trihedral bone. On the distal bone surface, there are two joint articulations for articulation with IV and V metacarpal bones.
All wrist bones, ossa carpi, are joined by joints and ligaments.
The upper, or proximal, edge of the wrist, facing the bones of the forearm, convex more in the transverse direction.
Lower, or distal, the edge of the wrist is relatively even. Back, or back, the surface of the wrist is convex.
The front, palm, wrist surface is concave and is called the wrist groove, sulcus carpi. The lateral edges of the furrow are bounded by two elevations: from the lateral side - by the radial elevation of the wrist, formed by the scaphoid tubercles and the bone-trapezium, on the medial side - by the elbow erection of the wrist, formed by the pea-shaped bone and hook of the hook-shaped bone. A row of bones of the wrist is well probed through the skin. Thus, the scaphoid bone is felt somewhat downward and posteriorly from the styloid process of the radius bone; The semilunar bone is probed next to the previous one on the back of the hand; Pea - with partial flexion of the wrist in the wrist joint; Head - on the back of the hand, it is better when flexing it in the wrist joint.
You will be interested to read this:









Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.