|
Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Electronics / Circuits / Home plans / |
|
Individual power station with own hands
Wind power unit
See also: |
Unconventional and environmentally friendly sources of electricity can serve you in the suburban or private plot for watering plants, watching TV, lighting and many other purposes.
Here you will find tips on choosing a location, construction and operation of wind turbines.
- Selecting wind turbine
- Choosing an electric generator
- Choice of the scheme of switching on the electric generator
- Selecting a drive
- Making propeller
- Calculation capacity wind power plant
- Selecting a location of a wind turbine
From the design of the device that converts wind energy into the kinetic energy of the rotating shaft, the design of the entire wind turbine depends. Currently, there are two most common types of wind turbines:
- wind wheel;
- propeller.
The wind wheel is much more complicated than the propeller and is a circular, three-dimensional lattice of blades, see Fig. 1.
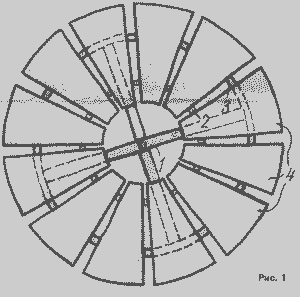
Picture 1
wind wheel blades are made of sheet steel, aluminum or duralumin sheets 1.5-2 mm thick.
The wind wheel is a slow-moving device. Since all electric generators without exception operate efficiently at a speed of 1000 rpm or higher, a multiplier with a ratio of 1:15, 1:20 must therefore be installed between the wind wheel and the generator.
The great advantage of the wind wheel is that it works almost silently and is able to rotate at a relatively low wind speed. The disadvantages are a complex structure, cumbersome and slow-moving.
Propeller-type device propeller aircraft. Structurally, the propeller is much simpler and easier propeller. The propeller rotates much faster and in certain conditions, eliminating the need multiplektora. See Fig. 2
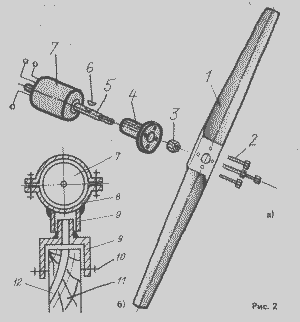
Figure 2
For wind farms it is more expedient to use two propellers simultaneously (.. See Figure 3), one of which is associated with power generator rotor rotates in one direction, the other - with the stator and rotates in the opposite direction. The use of such a design is similar to the use of a multiplier with a ratio of 1: 2.
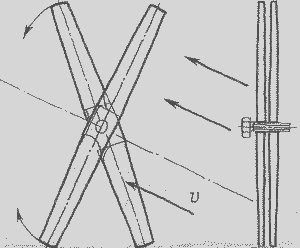
Figure 3
Choosing an electric generator
The first determining parameter is the rotational speed, which should be small. The second defining parameter is the power, the third - reliability.
If the power of wind turbines of 50-100 watts, it can be used generator, used in tractors of the brand G-31A, 60W power. This is a synchronous six-pole generator with rotating magnets and six fixed coils, see Fig. 4
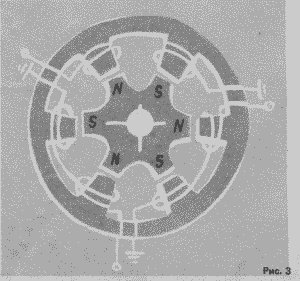
Figure 4
Electric generators of this type are good in that they require minimal maintenance: there are no coal brushes or a collector, which must be cleaned from time to time.
For a more powerful wind turbine, an electric generator suitable for buses, for example the G-2 power of 720 W, with a voltage of 12 V and a recoil current of 60 A, is suitable. Such a generator has a small diameter (0.25 m) and at a speed of 500-600 rpm can already Give a charging current. See. Figure 5
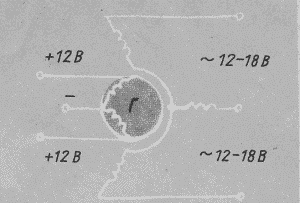
Figure 5
This generator is equipped with two coils of external excitation, which makes it possible to have power varying over a wide range. The excitation current is fed to the coils through three carbon brushes with three contact rings and can vary from ampere fractions to 1.5 A.
Since there are residual magnetisms in electromagnetic generators, it is possible to use this phenomenon with the help of diodes to self-excite the generator. self-excited generator allows the wind turbine is easy to get a move on and quickly gain momentum.
Choice of the scheme of switching on the electric generator
Battery charging circuit from the generator G-2 are shown in Figure 6.

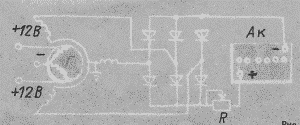
Figure 6
At low speed, the voltage generated by the generator may not be enough to charge the battery. Therefore, a step-up transformer is required, see Fig. 7.
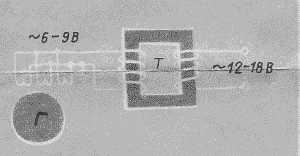
Figure 7
Drive SelectionWidely used was a hydraulic drive, which includes hydrotransmission. Hydraulic transmissions are used to transfer the torque from the windmill to the rotor shaft of the generator. In hydrotransfers, energy is transferred by the motion of a liquid under high pressure, see figure 8.
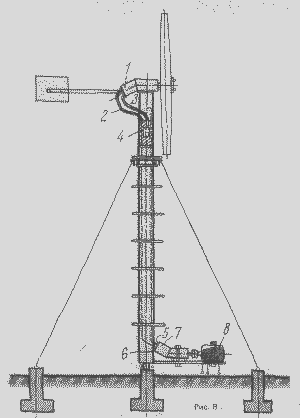
Figure 8
At the top of the mast is mounted a hydraulic pump 1 of a volumetric action (six-bar mark NSH-10U for pressure 10 MPa, or axial-piston grade 210.12 for pressure 16 MPa, etc.). Pressure line 2 from it in the form of a steel tube with a diameter of 1/2 "or flexible hose is lowered into the mast cavity, the same hose or tube 3 is lowered down from the pump suction hole to a depth of 0.5-0.7 m. Below, on a platform welded to A hydraulic motor 7 is mounted with an electric generator 8 , the shafts of which are connected by usual couplings.The pressure connection 6 of the hydraulic motor is connected to the pressure hose 2 of the hydraulic pump, and the discharge branch pipe 5 is connected to the internal cavity of the mast pipe which is filled with mineral oil 4. If the working volume of the hydraulic motor is less than the working volume Pump, then the speed of the hydraulic motor will be greater than the speed of the pump, that is, the propeller.
The system works like this. The propeller rotates the pump shaft, the pump draws mineral oil from the mast pipe cavity through the suction pipe and presses it through the pressure pipe to the pressure head of the hydraulic motor. From the hydraulic motor outlet, the oil flows again into the inner cavity of the mast. The hydraulic motor rotates and drives the generator. Because of the sensitivity to small particles, an oil filter is put in the system. The rotational speed of the units is regulated by the pressure or drain hose valve. The closed valve "turns off" the wind turbine in stormy weather. Hydraulic pumps and hydraulic pick from the tractor or aircraft.
Producing a propellerThe 1.5 m propeller is manufactured as follows. A pure fir, aspen or birch board is selected with a thickness of 25 mm, a width of 110-120 mm and is smoothly cut to a thickness of 20-23 mm. The center of the board is located and from it in both directions it measures 60-70 mm, is marked by risks see fig. 9. This is the central part of the board - the hub. To it four bolts fasten a metal flange which is put on an axis of a rotor of the generator or a multiplexer. Both halves of the board from the hub to the ends are stretched so that the truncated quadrangular pyramids have a cross section at the ends of 80x10mm (see sections 3-3, 4-4). Then the faces of the pyramids are shaved (half of their volume is removed), with one side being shackled on one side, on the other - the other. As a result, the whole front side looks like a propeller. On the back side, the right angle is smoothly rounded along the entire length of the board from the hub to the ends. The cross-section must have the shape of the cross-section of the aircraft wing (see sections 1-1, 2-2). The propeller is painted with oil paint.

Figure 9
The ends of the blades and its leading edge should be carefully lined with a thin aluminum sheet to avoid premature wear.
The speed of the propeller depends on the thickness of the board (the thickness of the hub). The thinner the hub (within reason), the speedboat propeller.
After installation, the propeller must be balanced.
Calculation of wind power plant
The power of the wind flow depends on its density and velocity, as well as the cross-sectional area of the air jet passing through the windmill.
In the case of a wind wheel, this is the active cross-sectional area:
F = p (D 2 - d 2) / 4
(Lvl)
Where: D - external diameter of the wind wheel (the distance between the outer ends of the two opposite blades);
D is the internal diameter of the wind wheel (the distance between the inner ends of the two opposite blades).
In the case of a propeller installation, the cross-sectional area is the area of the circle F, delimited by the propeller during its rotation, which is calculated by the formula:
F = pD 2/4
(Eq.2)
Where: D - the distance between the outermost points of the propeller blades.
The power of the air flow can be calculated using the kinetic energy equation for a body of mass m moving with velocity v,
E = mv 2/2
(Ur.3)
If in this equation instead of mass m substitute the mass of air flow passing through the cross section in one second, we obtain the power N of the air flow,
N = m 0 v / 2
(Lvl.4)
The unit mass can be expressed in terms of density and flow rate,
M 0 = pQ = pFv
(Eq.5)
Where: p - density of the air flow (1,3 / m 3 ); V is the airflow velocity.
Substituting equation 5 into equation 4, we obtain the formula
N = pFv 2/2
Selecting a location of a wind turbine
The best place for the installation of a wind turbine is a portion with lowest zatenyaemostyu from the wind by large trees and buildings with a minimum distance of their 25-30 m. Height it should exceed the height of nearby buildings by 3-5 m. Through the prevailing wind direction trees should not be.
Publication date 20.04.2003gg.




Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.