| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2078987
![]()
WAVE ENERGY INSTALLATION
The name of the inventor: Savchenko Anatoly Vasilyevich [UA]; Osadchuk Vladimir Aleksandrovich [UA]
The name of the patent holder: Ukrainian State Design, Design and Design Institute
Address for correspondence:
Date of commencement of the patent: 1994.02.01
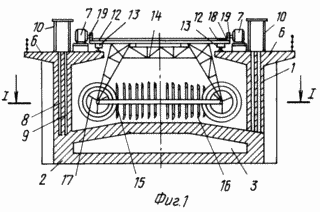
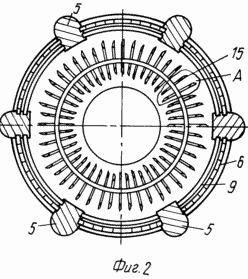
Use: The invention relates to hydropower and can be used in the creation of wave power plants. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION: A floating platform made as a casing 1 in the form of an open-topped cylindrical beaker with a bottom 2 provided with a cavity 3 made to be filled with water. The shell 1 is provided with wave-receiving holes in the form of through slits 4 in its side walls with the formation of sections between the slots of the struts 5 with the support areas 6 in the upper part on which the electric generators 7 are placed. The slits 4 are blocked by the shandors 8 and the flaps 9 regulated by the drives 10 that are located At the sites 6. The rotor of the wave power plant includes a support made in the form of a disk 11 mounted by the rollers 12 on a circular rail in the form of a rail 13 located on the support platforms 6 of the shell 2. The disk 11 by the truss 14 is rigidly connected to the annular support member 15, Which serves as a rotor shaft on which working blades 16 are fixed. The annular bearing element 15 is made in the form of a hollow torus, and the working blades 16 are in the form of annular grooves with convex surfaces oriented in one direction and connected to the hollow torus by hollow radial spokes 17. In this case The inner cavities of the torus and spokes are designed to be filled with water. The disc 11 is connected to the shafts of the electric generators 7 by means of a circular rack 18 fixed to the disc 11 and gears 19 placed on the rolls of the electric generators 7.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to hydropower, in particular to wave power plants.
A wave power plant is known that includes a floating platform, an electric generator and a rotor blade with a vertical axis of rotation, the platform being in the form of a shell with wave-receiving holes placed around the rotor along its periphery (US Patent No. 4,152,895, MKI F 03 B 13/12, 1979 G.).
The disadvantage of this wave power plant is the use of only the potential energy of the waves, as well as the pulse mode of operation, caused, as a rule, by the rupture of the jet in the shaft, the diameter of which is not regulated depending on the wave parameters. The constructive disadvantages include the complexity of manufacturing the spherical shell and ensuring its tightness, the location of the shaft of the turbine, the support part and the turbine itself in the mine filled with water, which excludes the possibility of its inspection and maintenance.
The construction of a wave power plant containing a platform with an adjustable buoyancy is also known. On the platform, an electric generator and a rotor with blades are mounted, having a vertical axis of rotation, the rotor being connected to the electric generator shaft and its blades being rotatable by the waves in one direction (GB patent No. 2081388, MKF 03/03/13/12, 1982).
The drawback of the construction of this wave power plant is the constant rotational motion of the blade, which complicates the design of the blade rotation assembly. In this design, it is necessary to use the energy of the wave flow to rotate the blade so that it can be placed in the working position. Only after the preliminary expenditure of wave energy to install the blades in the working position, the effect of the wave flow on the blade is useful and serves to move the impeller. A structural disadvantage is also the difficulty in achieving uniform tension of the cables fixing the support rings for different cable lengths, and also the unevenness of their elongation under variable loads, which can change the effect of the flow on the blade when the tension pulse of the cable coincides with the flow of the flow when it is applied to the blade.
The closest in technical essence and achieved result to the proposed design of a wave power plant is a wave power plant containing a floating platform, electric generators fixed to it and a rotor with a vertical axis of rotation, including a support and an annular supporting element with working blades fixed to it USSR N 1346845, MKI F 03 B 13/12, 1987, authors VM Lakhter, IS Kovalev and SM Skosareva).
The disadvantage of the design of this wave power plant is the inability to use the energy of vertical and other wave flows. The useful effect of horizontal flows is only on that part of the blades, which is placed by its leading edge along the normal to the flow. There is a constant occurrence of braking forces under the influence of multidirectional wave flows on the blade. The constructive shortcomings include the impossibility of concentrating the energy of the wave streams, but also the unreliability of the rotor rotation transfer unit through the rollers to the shaft due to friction and the possibility of slipping, and the placement of the generator near the wave surface.
The technical task of the invention is to improve the wave power plant, which provides the most complete use of the effect on the working blades of vertical flows and reflected waves, the elimination of the occurrence of braking forces under the influence of multidirectional wave flows on the blade, thereby increasing the power capacity of the installation.
The technical result is solved by the fact that in a known device of a wave power plant containing a floating platform, electric generators and a rotor with a vertical axis of rotation fixed thereon, including a support and an annular carrier with working blades fixed to it, according to the invention, the platform is made with an adjustable buoyancy in A shell arranged around the annular carrier element at its periphery and provided with through-going wave openings overlapped by the shutters, the rotor support is made in the form of a disk rigidly connected to the carrier element mounted by means of rollers on a circular rail fixed to the upper part of the shell, The working blades are made in the form of annular troughs oriented with convex surfaces in one direction.
In addition, the platform shell is made in the form of an open-topped cylindrical beaker with a bottom provided with a water-filled cavity.
In addition, the gates are provided with a drive with the possibility of independently overlapping through-going wave holes and are made in the form of a shedor and dampers.
In addition, the annular support member is formed as a hollow torus, and the working blades are in the form of annular grooves associated with the annular bearing member with hollow radial spokes, the inner cavities of the torus and spokes being made to be filled with water.
And the carrier element is connected to the support disc by means of trusses, the circular guide is made in the form of a rail, and the disk is connected to the shafts of the electric generators by means of a circular rack mounted on the disk and gears arranged on the shafts of the electric generators.
In addition, the figure formed by the envelope of the annular trough and its chord has the form of a symmetrical segment, the centers of the troughs lie on the axis of the torus, and their chords are vertical.
The features distinguishing the claimed technical solution are not revealed in other similar technical solutions when studying this and related fields of technology and, therefore, in the opinion of the applicant, the device meets the criterion of "novelty".
A comparative analysis of the claimed device with respect to the totality of its essential characteristics with the prototype shows that in the device of the wave power plant the construction of the platform in the form of an annular shell with wave-receiving apertures and its placement around the rotor, the shape of the blades in the form of annular grooves, the transmission of torque to the shafts of electric generators , The possibility of changing the position of the platform relative to the wave front, and the presence of a shutter.
Thus, the claimed device of the wave power plant corresponds to the criterion "inventive level".
The execution of the platform in the form of a shell with adjustable buoyancy and equipped with overlapping wave-receiving apertures makes it possible to fix the platform so that the horizontal axis of the carrier element coincides with the middle wave line with open apertures. In this case, the wave streams of any directivity passing through these openings interact with the working blades, creating aerodynamic forces directed always towards the convexity of the blade. Thus, the problem of using the energy of waves of any directivity is solved with the greatest efficiency.
For the secondary passage through the blades of the already reflected wave, the openings opposite the entrance of the wave to the installation are closed. The execution of blades in the form of annular troughs, oriented with convex surfaces in one direction, increases the area of interaction with them of the wave flow of any direction and excludes the possibility of occurrence of braking forces. In addition, the production of the spokes, the connecting blades with the supporting element, and the carrier element itself, hollow and water-filled, makes it possible to increase the rotor mass by filling the cavity of its shaft with an annular carrier element. This leads to an improvement in the uniformity of rotation of the rotor.
 |
 |
 |
 |
In Fig. 1 is a cross-sectional view along the axis of the wave power plant; FIG. 2 is a sectional view along 1-1, in FIG. 3, node A, in FIG. 4 section of 2-2.
The wave power plant is a floating platform made as a shell 1 in the form of an open-topped cylindrical beaker with a bottom 2 provided with a cavity 3 made to be filled with water. The shell 1 is provided with wave-receiving holes in the form of through slits 4 in its side walls with the formation of sections between the slots of the struts 5 with the support areas 6 in the upper part on which the electric generators 7 are placed. The slits 4 are blocked by the shandors 8 and the flaps 9 regulated by the drives 10 that are located On the sites 6.
The rotor of the wave power plant includes a support made in the form of a disk 11 mounted by means of a roller 12 on a circular rail in the form of a rail 13 located on the support platforms 6 of the shell 1. The disk 11 is rigidly connected to the ring carrier 15 serving as a rotor shaft , On which the working blades 16 are fixed. The annular bearing element 15 is made in the form of a hollow torus, and the working blades 16 in the form of annular grooves with convex surfaces oriented in one direction and connected to the hollow torus by hollow radial spokes 17. In this case, the inner cavities of the torus and The spokes are designed to be filled with water.
The disc 11 is connected to the shafts of the electric generators 7 by means of a circular rack 18 fixed to the disc 11 and gears 19 placed on the shafts of the electric generators 7.
Operation is carried out as follows.
The platform with closed shandors 8 and shutters 9 is transported afloat to the installation site. When the cavity 3 is filled with water in the bottom 2 of the platform, it is placed on the ground or closes at anchors in such a way that the horizontal axis of the annular bearing element 15 coincides with the middle wave line with open shandors 8 and flaps 9 on the side of the wave movement. When the wave passes through the wave-receiving holes 4, the wave streams interact with the working blades 16 so that the wave streams having any direction of motion flow around the blades 16, thereby creating aerodynamic forces directed towards the convexity of the blade, which results in the movement of the carrier 15, Rotor shaft of the power plant. Through the molds 14, the movement of the shaft is transmitted to the disc 11, which by means of the rollers 12 moves along the circular guide rail 13. The shafts of the electric generators 7 are driven through the gear rails 18 and the gears 19 to rotate.
To increase the rotor mass, the cavity of its shaft of the annular bearing element 15 and the spokes 17 connecting it with the blades 16 are filled with water. This allows the use of mass increase as a flywheel to improve the uniformity of the rotor rotation.
When the wave passes through the installation, the gate opposite to the input can be closed, which allows the second reflected wave to pass through the blades 16 of the rotor shaft.
CLAIM
1. A wave power plant comprising a floating platform, electrogenerators and a rotor with a vertical axis of rotation fixed to it, a support and an annular carrier element with working lugs fixed thereon, characterized in that the platform is made with an adjustable buoyancy in the form of a shell arranged around the annular carrier Of the element along its periphery and provided with through-going wave-receiving apertures, overlapping gates, the rotor support is made in the form of a disk rigidly connected to the carrier element, mounted by means of guide rolls fixed in the upper part of the casing, the working blades fixed on the carrier element are made in the form of annular troughs, Oriented with convex surfaces in one direction.
2. The plant of claim 1, wherein the platform shell is in the form of an open-topped cylindrical beaker with a bottom provided with a water-filled cavity.
3. Installation according to claims 1 and 2, characterized in that the gates are provided with a drive with the possibility of independently overlapping through-hole holes and are designed in the form of a sundore and dampers.
4. An installation according to claims 1 to 3, characterized in that the annular support element is made in the form of a hollow torus, and the working blades are in the form of annular grooves associated with the annular bearing member with hollow radial spokes, the inner cavities of the torus and spokes being adapted to be Filling with water.
5. An installation according to claims 1 to 4, characterized in that the carrier element is connected to the support disc by means of trusses, the circular rail is made in the form of a rail, and the disk is connected to the shafts of the electric generators by means of a circular rack mounted on the disk and gears located on Shafts of power generators.
6. Installation according to. 4 and 5, characterized in that the figure formed by the envelope of the annular chute and its chord has the form of a symmetrical segment, the centers of the troughs lie on the axis of the hollow torus, and their chords are vertical.
print version
Date of publication 13.01.2007gg




Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.