| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2105407
![]()
METHOD FOR PRODUCING ELECTRICITY AND DEVICE FOR ITS IMPLEMENTATION
Name of the inventor: Vladimir Tokarev Omarovich; Timohin Alexander; Tigran G. Tsaturyan
The name of the patentee: Vladimir Tokarev Omarovich; Timohin Alexander; Tigran G. Tsaturyan
Address for correspondence:
Starting date of the patent: 1996.09.06
A method for producing electrical energy includes forming the electron beam 35 by heating the cathode 2 and the direction of the substrate 15 of the plasma-forming material. The electron beam passes through the screen in the form of two conjugate bases of smaller truncated cones 12, 13. The resulting plasma stream 37 concentrated in the cone 13 and twist it. At the same time by dividing the mass of the electrons and ions created by the potential difference between the cone surface 13 and the surface of the collector 14. In the cavity of the cone 12 form a standing wave that prevents the expanding plasma clot 34. The device comprises a cathode 2, an anode 4, the cathode heating system. The cathode 2 and the anode 4 are arranged in the housing 1. The housing 1 is installed in a glass enclosure 18. At one fixed lucheprovod a conical nozzle 8. Lucheprovod connected with chamber 10 through a screen with openings 11. The substrate 15 of the plasma-forming material is placed in the bottom of cup 18 . In the cavity of the cone 13, the collector 15 is set.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to electrical engineering and can be used to produce electricity by converting thermal energy into electrical energy plasma.
Known device implemented method for generating electrical energy, whereby the resulting in a fusion reactor plasma reported the channels rectilinear movement and perform conversion into electrical energy by installing in the path of the plasma several collector grids, made in the form of a "Venetian blinds" (see. US patent N 3816771 , Cl. 310-5, 1974).
The disadvantages of this technical solution is complex and expensive manufacturing equipment and of the process of significant size design, implementing the method, and the insufficient level of environmental safety, which is characteristic for the operation of nuclear reactors.
The closest to the proposed technical solution (method and apparatus) is a method for producing electrical energy, thermionic energy converter is implemented (US patent N 3300661, cl 310-4, 1967.) - Closest analog.
The apparatus comprises a housing mounted in the anode and cathode therein, intended for electron radiation, ionizing the portion in contact with the radiating surface, and the cathode heating system, and ionizing portion. The work function of the anode is less than the work function of the cathode.
Through the heating system is heated cathode that emits electrons. The cavity devices receive low-temperature plasma. During expiration electrons from cathode surface contact with the ionized metal vapor partial condensation on the surfaces of the anode and the cathode and conversion of thermal energy into electric energy.
The disadvantage of this invention is the low efficiency in conversion of thermal energy into electricity. It is not possible to use the invention for industrial purposes. The absence of ionizable flow control capabilities reduces the functionality of the device, increasing the likelihood of accidents, which adversely affects the ecological state of the environment. A significant disadvantage of the invention is the presence of backflow and vaporized material which condenses on the working surfaces of the cathode and anode, making it difficult to process the physical removal of the electrical energy emitted by the internal volume of the device.
The objectives of the present invention are to improve efficiency in the preparation of electrical energy, reduction of its production, but also the safety and environmental friendliness in the implementation of the present invention.
The problem is solved by a method for producing electrical energy, which includes the establishment of the flow of electrons by heating the cathode and the creation of a potential difference, the new is that the flow of electrons is formed in the electron beam and direct it to the substrate from the plasma of the material through the screen in the form of two conjugate smaller bases of truncated cones, with a conical cavity facing the substrate placed manifold being formed by a plasma flux is concentrated in the cavity of the cone and a second cone cavity form a standing wave, thus formed plasma clot twist providing creating a potential difference between cone collector and facing the substrate, by deposition of electrons on the collector surface, and - ions on the surface of the cone.
For realization of the proposed method, an apparatus comprising a cathode and an anode mounted in the housing, and a system of cathode heating, which according to the invention, the housing is set in the beaker, and the housing is secured lucheprovod as a conical nozzle, with lucheprovod through holes camera connected to screen, made in the form of two truncated cones joined by the smaller base, the vertex of the cone nozzle positioned in plane interfacing the small bases of the cones, and in the lower part of the glass substrate is placed plasma material and the cavity in the cone facing the substrate, the manifold is installed.
The device is characterized by the fact that the substrate is placed in a crucible made of a refractory material with the possibility of rotational and translational movement of the rotational-drive means. The cone angle of the cones of the screen is selected in the range of 16 - 48 degrees, and the collector and on the outer surfaces of the cones screen has electric coils. The glass housing is rallying, the body cavity is connected to the turbo-molecular pump and the cavity cup - with the backing pump.
Brief Description of the drawing, which shows a device for producing electric current, axial section.
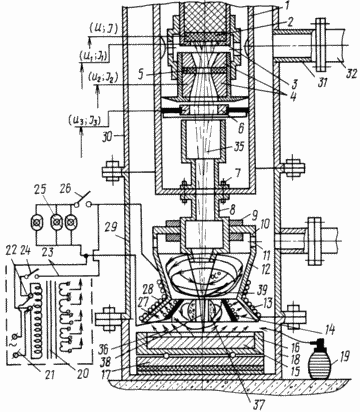 |
Device for producing electric energy consists of a housing 1, which houses the cathode 2 near-cathode electrode 3 and an anode 4 and 5 with the rings 6 and the magnetic lens. On the end surface of the housing 1 by means of fastening elements 7 installed lucheprovod formed as a conical nozzle 8. lucheprovode through nuts 9 fixed chamber 10 with holes 11 and the first electrode (screen) made in the form of interconnected smaller bases of truncated cones 12 and 13. In cone cavity 13 is situated the second electrode (collector) 14, and below the bottom of the glass, - the metal substrate 15. The substrate may be positioned in a crucible 16 made of a refractory material and set on the basis 17. The base 17 is placed on the bottom of the cup 18 and it is able to rotate and reciprocating driving means (not shown). Near the glass located source 19 of ionized vapor and a transformer 20 with connecting elements 21 to the electrical source and the elements 22 for the secondary connection to an electrical power source via leads 23 and switch 24 connected with the consumer 25 of generated electric power through a switch 26 connected to a single electrical circuit with the second electrode 14, which is placed on the electrical coil 27 and the outer surface of the truncated cones 12 and 13 (first electrode) 28 located electric coil. |
The glass 18 may be formed teams, as in the process of experiencing high temperatures and there is a need to replace the glass completely or its different parts. Therefore, the glass is composed of elements 29 and 30 attached to the base member 18. 30 glass tube 31 is attached, which is connected to turbomolecular pump 32 adapted to pump housing 33 and a conduit 34 connected backing pump designed for pumping cup cavity. (The diagram shows a fragmentary pumps).
METHOD FOR PRODUCING ELECTRICITY carried out as follows
Initially, depending on the melting temperature of the plasma substrate material 15 is mounted on the body 1 with conical nozzle 8 a desired angle ( ![]() ) At the top of the truncated cone. This relationship is shown in Table.
1 (prepared on the basis of experimental data).
) At the top of the truncated cone. This relationship is shown in Table.
1 (prepared on the basis of experimental data).
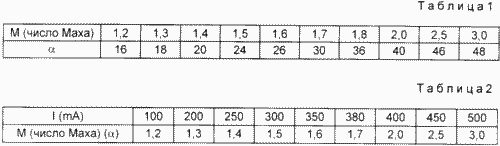
Before installation of the conical nozzle 8 is determined depending on the Mach number of the electric current generated by the cathode 2 (see. Table. 2).
In practice, the value of the Mach number a> 4 and thus not used in Table. 2 Mach number starts with M = 1,2.
In practice, the angle can not be more than 48 degrees.
, Since in this case the value of the Mach number must be greater than 3, which can not be ensured under the action of concentrated energy flux (electron beam). As shown by the experimental work with ![]() <16 degrees. the device has a very large size, which leads to disruption of the plasma clot formation. Therefore, the angle
<16 degrees. the device has a very large size, which leads to disruption of the plasma clot formation. Therefore, the angle ![]() determined within 16 degrees.
determined within 16 degrees. ![]() .
.
Further lucheprovod attached, which is mounted so that the top of the truncated cone of the nozzle was located 8 bases in plane interfacing the truncated cones 12 and 13 of the first electrode. Further, the device is connected consumer of electric power and a transformer 20. All connectors leak detector check. Includes backing pump 34, and after the establishment in a glass pressure 6.65 Pa include a turbo-molecular pump 32, which carries out the pumping cavity of the housing 1 to a pressure of 6.65 × 10 -3 Pa.
Then include a transformer 20 and heat the cathode 2 to a temperature of 1500 -1600 ° C, the in which an intensive outflow of electrons starts from its surface. Simultaneously, an appropriate voltage is applied to near-cathode electrode 3, the anode 4 and 6. The magnetic lens element 35 of the electron beam, moving at high speeds, falls on the substrate 15, whereby a substrate material is ionized and eventually the secondary and reflected electrons 36 towards the flock of the cone 13 forming a low-temperature plasma clot 37 with a channel 38 required for passage of the electron beam. Due to the fact that the flow path originating from the substrate 15 is mounted the truncated cone, the thread (as it is known from gas dynamics) "feels" cone top and decelerates, forming a standing wave. In this case the electron beam electrons themselves are generators of the spin move towards electrons and ions as "processed" their material (stored in the crucible) is moved, creating a temperature gradient between the crucible and the first electron. Due to the motion of electrons and the crucible and the temperature gradient created centrifugal forces that unwind electrons and ions. The electrons whose mass is much smaller than the mass of the ions, to spin closer to the electron beam axis, and the ions are at a far distance form their separate rotation.
The standing wave 39, which consists of particles of the evaporated material particles inhibits vapor-gas stream moving at a speed of 10 3 - May 10 cm / s. Due to the fact that the electron beam itself is a twist generator, and the rotation speed of the flow depends on the magnitude of the concentrated electron beam current, the current is increased, studies have shown that the particle flow reaches the speed of rotation of 100 rev / sec or more. Since the electrons have a mass of 31 kg of 10, and the ions - 10 -27 kg, the radii of rotation vary dramatically. Electrons deposited on the surface of the second electrode. At the same time, if necessary, this medium is introduced into the stream of ionised source 19.
Is created between the electrodes is sufficiently large potential difference which is compared with a supply voltage of cathode 2 can be different from two and more times. Under appropriate conditions and the number of revolutions vapor stream particles potential difference can reach very high values corresponding to the difference in the electron and ion masses.
Next include the switches 24 and 26, is connected to a consumer of electrical energy 25 and the transformer 20 is disconnected from the power supply and the device starts to work at the expense of own generated energy. the transformer can be included if necessary.
In the process of plasmoid device 37 is constantly updated with the plasma generated by an electron beam, ion of substrate 15. The plasma clot held during working hours, which is determined by the need to replace the substrate. The separation of electrons and ions occurs almost instantly due to the influence of centrifugal forces. When this charging occurs evaporated material particles through interaction with ions orbiting plasma clot, which contributes to a potential difference between the first and second electrodes (300 - 400 V or more).
To create additional force facilitating retaining plasmoid can use electrical coils 27 and 28. This is necessary when the rotation speed of the plasma does not exceed about 100 / s.
Checking the industrial applicability of the invention was carried out on the device with the following parameters:
- The accelerating voltage (kV) - 15
- Operating Current (mA) - 200
- The plasma-forming material AMg - 6
- Plasma material moving speed (m / h) - 35
- The retention time of the plasmoid (h) - 0.5
- In a glass pressure (Pa) - 6.65
- Pressure in the housing with a cathode and an anode (Pa) - 6.65 · 10 -3
Vapor temperature of the material AlMg 6 is approximately equal to 2440 degrees. C. To register, plasmoid formation and retention of high-speed filming has been used in the plane of the device. For this the first and second electrodes are formed grooves through which the recording and implemented. At the same time we measured the potential difference between the collector walls and glass walls. The potential difference was 380, and the current is fixed at 10 A, the power - 4 kW.
Work carried out on the device, confirmed that the separation of electrons occurs from ions, and their rotation around a concentrated electron beam that precisely determines the conditions for obtaining an energy source.
To confirm the steam-gas stream was withdrawn rotating electrode 14 and the second baffle has been installed on the inner wall of the first manifold, after which the switch device was produced.
After the end of the inner cavity of the first electrode was photographed. The photograph clearly shows that the baffle with one hand net, and on the other - sprayed. This effect can be obtained only if the stream is rotated.
The present invention provides a cheap electric energy subject to the process of ecological purity, through the implementation of sustainable management of the plasma process. The device is simple to manufacture, reliable in operation. The method has wide technological possibilities, safe to implement and can be used in related areas of science and technology, in which the electron beam is used.
CLAIM
A method for producing electric energy, comprising forming the electron flux by heating the cathode and the creation of a potential difference, characterized in that the flow of electrons formed in the electron beam and direct it onto the substrate from the plasma of the material through a screen made of two conjugate smaller bases of truncated cones, with the in the cavity of the cone facing the substrate placed manifold being formed by a plasma flux is concentrated in the cavity of the cone and a second cone cavity form a standing wave, thus formed plasma clot twist, providing the establishment of the potential difference between the collector and the cone facing the substrate, by deposition of electrons on the collector surface, and ions on the surface of the cone.
A method according to claim 1, characterized in that the component is fed into the ionized plasma stream is formed.
Device for producing electric energy comprising a cathode and an anode mounted in the housing, and the cathode heating system, characterized in that the housing is set in the beaker, with the housing secured lucheprovod as a conical nozzle, with lucheprovod through holes chamber is connected with the screen, made in the form of two truncated cones joined by the smaller base, the vertex of the cone nozzle positioned in plane interfacing the small bases of the cones, and in the lower part of the glass substrate is placed plasma material and the cavity in the cone facing the substrate, the manifold is installed.
Apparatus according to claim 3, characterized in that the substrate is placed in a crucible made of a refractory material.
Apparatus according to claim 3, characterized in that the substrate has the capability of rotational and reciprocating movement of the drive means.
Apparatus according to claim 3, characterized in that the cone angle of the truncated cones 16 of the screen 48 o.
Apparatus according to claim 3, characterized in that the collector and on the outer surfaces of the cones screen has electric coils.
Apparatus according to claim 3, characterized in that a glass made teams.
Apparatus according to claim 3, wherein the body cavity is connected to a turbomolecular pump.
Apparatus according to claim 3, characterized in that the cavity is connected to the glass backing pump.
print version
Publication date 31.10.2006gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.