| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2125183
![]()
ELECTROMAGNETIC SOURCE OF ENERGY
The name of the inventor: Yurik Alexey Dmitrievich; Yurik Nelli Mihailovna
The name of the patent holder: Yurik Alexey Dmitrievich; Yurik Nelli Mihailovna
Address for correspondence: 350072 Krasnodar, ul.Moskovskaya 90-69, Yurik Alexey Dmitrievich
Date of commencement of the patent: 1996.12.14
The invention relates to the field of power engineering and makes it possible to simplify the design of autonomous power sources. The electromagnetic energy source comprises a frame on which a coupled synchronous motor and a synchronous generator are mounted, connected together by a single rotation shaft which is connected to an external drive device and an exciter. Each synchronous motor and generator contains a stator with multiphase windings connected in series with the consumer of electricity, a rotor in which electromagnets with excitation windings are placed.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the field of energy, namely to energy sources and can be used in various fields of the national economy, in aircraft building, transport, shipbuilding.
A synchronous machine consisting of a stationary part - a stator, in whose grooves a three-phase winding is placed, and a rotating part - of a rotor with electromagnets to the winding of which a direct current is applied is close to the claimed invention, with the help of contact rings and superimposed brushes . Its rotor is performed either with a pole pole (with protruding poles) or an implicit pole (cylindrical rotor).
And a DC machine is known, consisting of a stator yoke, inside which are placed electromagnetic poles with excitation windings, fed by a direct current. Inside the yoke of the stator with clearance is placed on the rotation shaft an armature with a winding connected to the collector. P.S. Sergeev. Electric machines "Gosenergoizdat", 1962, M. The disadvantage of known devices is low efficiency .
The closest to the claimed invention in terms of essential features is a gravitational energy source containing the frame on which the rotor is arranged in the form of at least two balls (see copyright certificate No. 2055235 Class F 03 G 3/00 of 27.02.96) - inductors connected to each other by one axis of rotation, with the axis of rotation connected to an external drive device; Each ball-inductor contains inside the frame of the planetary device installed with a gap, in the central part of which there is an additional spherical working chamber in which a ball-eccentric is installed with a clearance, at least two movable radial blades along the circumference of the planetary device frame, forming external working cavities in pairs The channels connected between the induction balls are MHD generator channels.
The known technical solution includes the following features similar to the prototype: the frame on which the rotor is arranged in the form of at least two inductor balls interconnected by one rotation axis, the axis of rotation being connected to an external drive device.
The known device is fundamentally different from the claimed one and has a number of drawbacks: high precision of manufacturing is required, since this device belongs to high-capacity hydraulic machines requiring special electrical insulating materials.
The technical problem to be solved by the claimed invention includes the creation of a coupled electromagnetic energy source: a synchronous motor and a synchronous generator, using the currents of the consumer connected through the multiphase windings of the synchronous motor to the multi-phase windings of the synchronous generator, which interact with the magnetic field of the synchronous motor create an electromagnetic force that on the shaft Rotation of the synchronous motor creates an additional torque.
And in a combined DC motor, when the consumer currents interact in the ring winding of the annular armature with the magnetic field of the pole electromagnets of the stator inner yoke, an electromagnetic force arises that creates an additional torque on the shaft of rotation of the annular armature. The technical problem is solved by the fact that a positive current connection is realized between the synchronous motor and the synchronous generator through their multiphase windings.
The technical problem is solved by the fact that the electromagnetic power source is equipped with: an electromagnetic control system, a frame on which are mounted coupled (at least two) synchronous motor and a synchronous generator (or coupled dc machines) connected together by a single rotation shaft, with the possibility of rotation around it Relative to each other within one revolution and connected to an external drive device containing a constant current source, in each of which a stator is placed inside the housing, in whose slots a multi-phase winding is placed, each phase winding of the multiphase winding of the synchronous generator, through each phase winding Multiphase winding of the synchronous motor, are connected in series with wires to the consumer of electric power. Inside each stator, with a gap and the possibility of moving around its own axis of rotation, a rotor is mounted on the rotational shaft, which contains electromagnets with excitation windings, and a collector connected by wires with excitation windings and an exciter is placed on the rotation shaft mounted on the radial bearings inside the stator.
The stated task is solved by the fact that a combined DC motor with a stator outer yoke is mounted on the frame, at least two pole electromagnets are placed on the inner surface of the radial plane with pole excitation windings connected by wires to the exciter; Inside the stator external armature, with a clearance and the possibility of movement around its own axis of rotation, is mounted on the rotation shaft, an annular armature containing a cylindrical frame fixed to the rotation shaft which is mounted on the radial thrust bearings inside the stator external yoke.
On the cylindrical frame there are: an outer annular magnetic circuit and an inner annular magnetic circuit, rigidly connected to each other and separated by an electromagnetic shield, the outer annular magnetic core together with the inner annular magnetic core, over the outer surface located in the grooves, is wound with a ring winding, On the shaft of rotation of the annular armature is connected by wires to the consumer of electricity, while inside the annular armature, with a gap and the possibility of rotation around its own axis of rotation within one revolution, a stator inner yoke is placed, along a circle in the radial plane on the outer surface of which are located, not less than Two, pole electromagnets with pole excitation windings connected by wires to the exciter; On the body and stator outer yoke there are removable covers. Comparison of the claimed invention with an analog shows that it corresponds to the criterion of "novelty". Comparable analysis with other technical solutions in this related field of science and technology did not allow us to identify the features that differentiate the claimed solution, which would make it possible to draw a conclusion, according to its criterion, "essential differences".
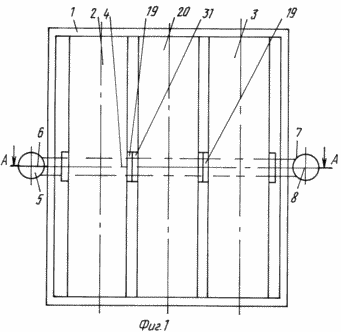 In Fig. 1 shows an electromagnetic energy source, its interior - a side view |
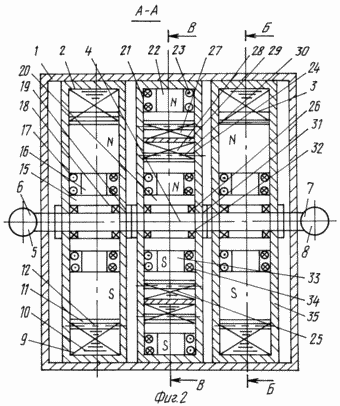 FIG. 2 shows a section A-A of FIG. 1 of the electromagnetic energy source by a horizontal plane along the axis of rotation, the top view |
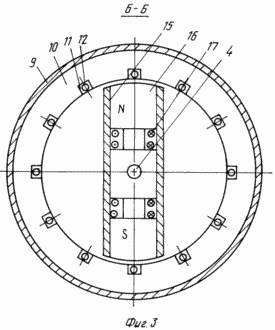 In Fig. 3 is a cross-sectional view taken along line B-B of FIG. 2 of the electromagnetic energy source by a vertical plane perpendicular to the axis of rotation - a side view along the axis of rotation of the synchronous motor |
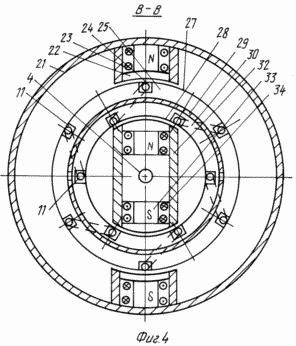 FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view taken along line B-B of FIG. 2 of the electromagnetic energy source by a vertical plane perpendicular to the axis of rotation - a side view along the axis of rotation for a combined DC motor |

In Fig. 5 shows a block diagram of an electromagnetic control system for devices of an electromagnetic power source from an electric power source
The electromagnetic energy source of FIG. 1 to 5 comprises a frame 1 on which twin synchronous engine 2 and synchronous generator 3 are mounted, connected to each other by a single rotation shaft 4, rotatable about it relative to each other within one revolution. Since DC machines are interchangeable, i.e. Can work as generators and motors, then instead of synchronous machines (synchronous motor and synchronous generator) it is possible to use DC coupled machines. The rotation shaft 4 is connected to an external drive device 5 comprising an electric power source 6 and an exciter 7 comprising a constant current source 8. In each synchronous motor 2 and a synchronous generator 3, a stator 10 is placed inside the housing 9, a multiphase winding 12, wherein each phase winding of the multi-phase winding 12 of the synchronous generator 3 through each phase winding of the multi-phase winding 12 of the synchronous motor 2 is connected in series by means of the wires 13 to the consumer of electricity 14. Within each stator 10, with a clearance and the possibility of movement around its own axis of rotation, A rotary shaft 4, a rotor 15 comprising electromagnets 16, with excitation windings 17, and a manifold 19 mounted on wires of rotation 4 mounted on radial bearings 18 inside stator 10 is connected to wires 13 with excitation windings 17 and exciter 7. and on the frame 1, a combined DC motor 20 is constructed containing a stator outer yoke 21, at least two pole electromagnets 22 with pole excitation windings 23 which are connected by wires 13 to exciter 7 are disposed in the radial plane on the inner surface of which. Inside the stator outer yoke 21, with a clearance and the possibility of movement around its own axis of rotation, an annular armature 24 is mounted on the rotation shaft 4, comprising a cylindrical frame 25 fixed to a rotation shaft 4 which is mounted on the radial thrust bearings 26 inside the stator outer yoke 21. On the cylindrical frame 25 there are placed: an outer annular magnetic circuit 27 and an inner annular magnetic circuit 28 rigidly connected to each other and separated by an electromagnetic shield 29. The outer annular magnetic circuit 27 together with the inner annular magnetic core 28 along the outer surface located in the slots 11 is entwined with a ring winding 30 The annular winding 30, through a manifold 31 mounted on the rotation shaft 4 of the annular armature 24, is connected by a wire 13 to the electric power consumer 14. Within the annular armature 24, with a clearance and rotation about its own axis of rotation within one revolution, a stator inner yoke 32, in a radial plane, on the outer surface of which there are at least two pole electromagnets 33, with pole excitation windings 34 connected by wires 13 to exciter 7. For access to the devices of the electromagnetic power source on the body 9, the stator outer yoke 21 Removable covers 35 are installed, and for controlling its electromagnetic control system 36.
The electromagnetic control system 36, its connection to the power source 6, the DC power source 8, and the connection circuit of the synchronous motor 2, the synchronous generator 3, the combined motor-generator 20, the external drive device 5, the driver 7 and the electric power consumer 14 is shown in the form The flowchart of FIG. 5.
The capacitor device 37 is shown in the flowchart of FIG. 5, its parallel connection in the disconnected position, where the marking of its connection to the multi-phase windings of the synchronous motor is shown. It is possible to connect the capacitor device in series with the multi-phase windings of the synchronous motor. The electromagnetic power source comprises a capacitor device 37 with the possibility of both parallel and serial connection of its wires 13 to the multi-phase windings 12 of the synchronous motor 2, which provides an increase in cos ![]() .
.
In the circuits of multi-phase windings 12, phase-shifting inverter devices 38 are installed between the synchronous generator 3 and the synchronous motor 2.
The electromagnetic energy source (Figures 1 - 5) works as follows. With the help of an external drive device 5, through the electromagnetic control system 36 powered by the power source 6, the synchronous motor 2, the synchronous generator 3, the combined motor-generator of the direct current 20, and the driver 7 mounted on the same rotation shaft 4 are brought into a constant Rotary motion. Simultaneously, from the DC power source 8 and the driver 7 are fed through the wires 13 through the field collector 19 of the excitation winding 17 of the synchronous motor 2 and the synchronous generator 3, the field excitation windings 23 and the pole field windings 34. When a DC current flows in the field windings 17, 23, 34, In electromagnets 16, pole electromagnets 22 and 33, a magnetic field that, when the rotor 15 of the synchronous generator 3 and the annular armature 24 of the combined generator-generator dc generator 20 rotates, in the multi-phase windings 12 of the synchronous generator 3, in the ring winding 30, the combined motor-generator of the constant Of current 20 induces (EMF) an electromotive force, under the influence of which an induction current flows in the closed circuit of the windings. The induction current flowing in the closed circuit of the multi-phase winding 12 of the synchronous generator 3, through the multi-phase winding 12 of the synchronous motor, via the wires 13 and through the electric power consumer 14, while the current flows in the multi-phase winding 12 of the synchronous motor 2, which interacts with the magnetic field of the electromagnets 16 The electromagnetic force driven into the rotary motion of the rotor 15, the torque under the action of the electromagnetic force is added together with the torque of the external drive device. The induction current flowing in the closed circuit of the ring winding 30 through the wires 13 through the collector 31 and the electric power consumer 14 interacts with the magnetic field of the pole electromagnets 33 causes the annular armature 24 rotationally actuated by the electromagnetic force, the torque being summable by the electromagnetic force to the moment External drive device, which contributes to the increment of energy. Practically energy is spent on losses, on friction and thermal losses in electrical circuits of the energy source.
CLAIM
- An electromagnetic energy source comprising a frame on which a rotor is arranged in the form of at least two inductor balls interconnected by one rotation axis, the rotation axis being connected to an external drive device, each ball-inductor comprising a planetary Device in the central part of which is placed an additional spherical working chamber in which a ball-eccentric is installed with a clearance, and at least two movable radial blades are installed along the circumference of the frame of the planetary device forming external working cavities pairwise connected between the induction balls by the channels of the MHD generator , Characterized in that it is equipped with an electromagnetic control system, a frame on which are mounted coupled (at least two) synchronous motor and a synchronous generator (or coupled DC machines), interconnected by a single rotation shaft with the possibility of rotating around it relative to each other in Within one revolution and connected to an external drive device containing a source of electric power and an exciter comprising a constant current source in each of which a stator is placed inside the housing in which the multi-phase winding is placed in the grooves, each phase winding of the multiphase winding of the synchronous generator through each phase The winding of the multiphase winding of the synchronous motor is connected in series by wires to the consumer of electric power, inside each stator with a clearance and the possibility of moving around its own axis of rotation, a rotor is mounted on the rotor shaft containing electromagnets with excitation windings, and a rotation shaft mounted on the radial bearings inside the stator Collectors connected by wires with excitation windings and exciter, and on the frame there is installed a combined DC motor containing a stator outer yoke, on the circle in the radial plane on the inner surface of which there are at least two pole electromagnets with pole excitation windings that are connected by wires With an exciter inside the stator external yoke with a gap and the possibility of movement around its own axis of rotation is mounted on the shaft of rotation an annular anchor containing a cylindrical frame fixed on the rotation shaft which is mounted on the radial thrust bearings inside the stator external yoke, A magnetic core and an inner annular magnetic conductor rigidly connected to each other and separated by an electromagnetic shield, the outer annular magnetic core together with the inner annular magnetic core along an outer surface located in the grooves, is wound with a ring winding which is connected to a collector mounted on the shaft of rotation of the annular armature Wires with the consumer of electricity, while inside the annular armature with a clearance and the possibility of rotation around its own axis within one revolution, a stator inner yoke is placed, along the circle in the radial plane, on the outer surface of which there are at least two pole electromagnets with pole excitation windings connected by wires to The driver, the body and the stator outer yoke have removable covers.
- The electromagnetic power source according to claim 1, characterized in that it comprises a capacitor device with the possibility of both parallel and series connection thereof to the multi-phase windings of the synchronous motor.
- The electromagnetic energy source according to claim 1, characterized in that phase-shifting inverter devices are installed in the circuits of multiphase windings between a synchronous generator and a synchronous motor.
print version
Date of publication 17.12.2006гг




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.