| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2293452
![]()
METHOD OF PRODUCING ELECTRIC ENERGY FROM THE IONOSPHERE OF THE EARTH
The name of the inventor: Novikov Vasily Vasilyevich (KZ)
The name of the patent holder: Novikov Vasily Vasilyevich (KZ)
Address for correspondence: 101401 , Kazakhstan, Temirtau, Karaganda region, Prospect Komsomolsky, 55/1, ap. 8, V.V. Novikovu
The effective date of the patent: 2002.11.05
The invention relates to devices using natural sources of electricity, namely to devices using the energy of the Earth's ionosphere. The problem is solved using a plane-polarized laser beam obtained from gadolinium of scandium-halide garnet with chromium and niodime (GSGG-C3 3- No 3- ), devoid of divergence, i.e. Ray, transformed into a needle. The essence of the invention lies in the fact that a laser beam devoid of divergence, being a "conductor" of electric charges, passing the Earth's ionosphere and reflecting from a geostationary satellite, produces a stable electric current in the magnetohydrodynamic generator.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to devices using natural sources of electricity, namely to devices using the energy of the Earth's ionosphere.
A method for producing electric energy based on a laser beam in a power plant using atmospheric electricity in the regime of pulsed energy extraction at an electric field of the Earth is known (RU Patent No. 2076470, C1, H 05 F 7/00, 1997).
The disadvantage of this method is inefficiency, difficulty in practical use, not manageable.
The technical problem for solving this invention is the economical, controlled and stable generation of electrical energy from the Earth's ionosphere.
In this method, a laser beam is used, devoid of divergence in order to stably and maximally receive electrical energy, using its properties when it is repeatedly reflected through a geostationary satellite to Earth. To eliminate divergence, the property of rotating the plane of polarization of the laser beam as it passes through a quarter-wave plate is used (see the journal Nauka i Zhizn, No. 8, p.110, 1984) [1]. I quote this property from the Physical encyclopaedic dictionary edited by AM Prokhorov, p.325, 1983: "In crystals of certain symmetry classes, two electrically polarized waves (with opposite directions of detour) can propagate along each direction-both with their refractive indices . In the direction of the optical axis, the polarization of the waves turns out to be circular, which leads to a rotation of the plane of polarization of the linearly polarized light incident on the crystal. "
Further, proceeding from the inventive level, we place this crystal, i.e. Quarter-wave plate into a moving magnetic field created by a three-phase current that will interact with a laser beam passing through it (plate) as follows.
From the state of the art, by its nature light is both a particle and a wave (transverse with the electric and magnetic component of the field).
Let's analyze our case when the optical axis of an individual photon does not coincide with the direction of propagation of the laser beam and forms with it some angle (called the divergence angle), and hence both the polarization plane and the electric and magnetic components of the field are located not at 90 ° to the direction of propagation of the laser Ray and these forces will act on the side of the moving magnetic field in the following way.
In the perpendicular arrangement of the plane of polarization of the photon and its electric and magnetic field component and when the plane of polarization is rotated in the direction of the optical axis, the same forces equalize the photon in the direction of motion to the positive and negative "shoulders" of the field (see Fig.
When the plane of polarization, and therefore the electric and magnetic components of the field are not located at an angle of 90 ° to the direction of propagation of the laser beam, when the plane of polarization around the optical axis rotates, the moving magnetic field will act with unequal force on the positive and negative "shoulders" of the field . On the "shoulder" (negative, relative to "0" in the coordinate system), which is located at an angle of less than 90 ° to the direction of the moving field, large forces will act due to the fact that two fields (a moving magnetic field and an electric component of the laser beam field) Meet at an angle to each other and per unit time intersect with a greater number of lines of force than the "shoulder", which is located at an angle of more than 90 ° to the direction of the moving field (two fields run at an angle relative to each other (see Fig.3 , B)). As a result, the polarization plane will unfold to a stable state (perpendicular to the direction of the moving magnetic field), when the forces acting on the positive and negative "shoulders" of the field are balanced (see Fig. 3, c). In FIG. 3, a points denote a magnetic field moving from us, perpendicular to the plane of the sheet.
Method for obtaining electrical energy in MGD. Generator is as follows:
 |
 |
 | |
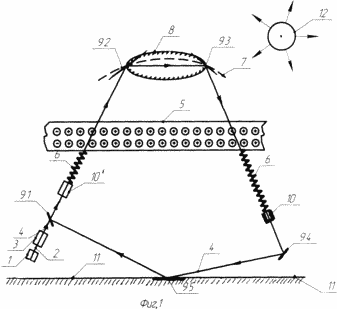
- FIG. 1 illustrates the principle of energy selection in the Earth's electric field,
- FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram of a collimator,
- FIG. 3 is a graphical diagram of the operation of the collimator.
On the ascending branch of the system (Fig. 1) we add MGD. Generator under №10 ', receiving stations are located at the latitude of Novosibirsk with a distance of 50 km from each other. Before the geostationary satellite will be ~ 45000 km (at the equator to the geostationary satellite will be 36000 km). As is known, the Earth's ionosphere is at altitudes of 65-220 km (the highest density of electric charges is 9.2 × 10 5 el / cm 3 ). The rate of formation of the streamer (ionization channel) in the atmosphere is 4000 km / sec (data of the physical encyclopedic dictionary edited by BA Vedensky, 1996). This means that a laser beam with a pulse of 0.05 sec and a repetition rate of 20 times per second is suitable for us.
From an external power source, for example a three-phase generator, voltage is applied to the pump device. Under the action of the pulse of the pump device, the laser generates radiation. The resulting laser beam passes through the laser beam transducer 3 (FIG. 1), hereinafter referred to as a collimator. Further, the transformed ray 4 (devoid of divergence, Figs. 2, 3) passes mirror 9.1, then MGD. Generator No. 10 'and goes to the ionosphere 5 (FIG. 1). On the path of the laser beam, an ionization channel (streamer) will be formed as a result of the interaction of laser radiation with the constituent gases of the atmosphere.
Ionization channel, i.e. The conductor for the electric charges of the Earth's ionosphere will be formed at a speed of 4000 km / sec, for this it needs 0.05 seconds to pass 200 km, the laser beam is also with a pulse of 0.05 sec.
As soon as the ionization channel reaches the ionosphere of the Earth, then on it to M.G.D. Generator number 10 'will go a portion of electric charges with the speed of light (this will require 0.0006 sec). The driving force of the process will be the equalization of the electrical potential between the ionosphere and the Earth (since the density of electric charges in the ionosphere is 9.2 × 10 5 el / cm 3 , and on the Earth ~ 0.1 e / cm 3 ). This process is confirmed by the patent No. 2076470 C1, H 05 F 7/00. Electric charges in MGD. Will be transformed into an electric current (see Polytechnical Dictionary edited by Artobolevsky II, Soviet Encyclopedia 1976, pp.269-270).
Because The laser radiation is pulsed, then after 0.05 seconds the pulse will be repeated, the ionization channel will be repeated, and electric charges on MGD will again go through it. Generator No. 10 'and it will produce a pulsating electric current of one direction, 20 pulses per 1 sec.
Then the laser beam, reflected in the mirrors of the geostationary satellite, passing through the Earth's ionosphere and MGD. Generator number 10, through the mirrors Nos. 9.4, 9.5 will return to the beginning, i.e. To mirror No. 9.1 (see Fig. 1).
The process of obtaining an electric current in MGD. Generator number 10 will be similar to the process of obtaining it in MGD. Generator number 10 '.
In the initial materials of the application it was stipulated that for the stable operation of the system two turns of the beam are made, ie 0.5 sec of the laser work. Because The distance to the geostationary satellite was 36,000 km, with the specified distance to the geostationary satellite being 45,000 km, this will take 0.6 sec of the laser work. Then the initial source of laser radiation is switched off.
In the process of work, there will be a loss of laser radiation power. In order for the system to be viable, the pumping of photons by the inclusion of laser radiation is necessary. In the initial materials of the application this fact is indicated. Following within the framework of these materials, we will clarify the operation of the system.
On each mirror there will be a loss of laser radiation power of 0.16%. Interest is taken from the physical encyclopaedic dictionary. We have 5 mirrors. The loss on the mirrors is 0.8%. For example, take a laser beam with a power of 1000 watts. It makes 2 turns, the power of the beam is 2000 W. With this power on the mirrors, we lose 16 watts. The loss of power will also be in ionization. These losses are 0.5%. So, on one turn, we lose 10 watts of ionization. Total loss of 26 watts, take ~ 25 watts. After 40 turns of the beam, the power in the system will decrease by 1000 W, i.е. To the power of the source of laser radiation, 1 revolution - 0.3 seconds, 40 revolutions = 12 seconds. This means that every 12 seconds we turn on the laser source for 0.3 seconds, raising the power to 2000 W. In support of what I have said, I quote the initial materials of the application p.3, the 8th line from the top: "Periodically, pumping the photons, we turn on the laser radiation". With the advent of an electric current in MGD. Generators the system switches to its own power supply.
Obtained in M.G.D. Generators in this way a stable constant electric current of a certain magnitude "A" and voltage "I" from both MGDs. Generators connected to each other, in parallel feeds an electric motor of direct current, which rotates the rotor of the generator producing a three-phase alternating current with a frequency of 50 Hz.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Other objects and advantages (from [2]) of the present invention will become apparent from the following attached drawings.
|
1 designate: 1 - source of laser beams 2 - laser beam 3 - collimator 4 - laser beam devoid of divergence 5 - ionosphere 6 - ions and electrons around the laser beam 7 - geostationary satellite orbit 8 - artificial Earth satellite 9.1-9.5 - reflecting mirrors 10,10 '- magnetohydrodynamic generators 11 - Earth 12 - the sun |
2 denote: 1 - incoming beam 2 - transformed ray 3 - quarter wave plate 4 - winding of three-phase current coils 5 - collimator 3 (a, b, c) denote: 1 - moving magnetic field 2 - E - electric component of the field 3 - H - magnetic field component 4 - x, y - coordinates 5 - angle of rotation 6 - angle of rotation |
[2] - Patent No. 2076470 C1, H 05 F 7/00, 1997.
Other purposes and advantages of [2] are the use of this application both in whole and in parts in various areas of science, technology, national economy, as well as armament and defense of the country.
CLAIM
A method for obtaining electric energy based on a device for pulsed energy extraction at an electric field of the Earth, performed by a laser beam with a pulse duration of a laser beam corresponding to the time of overlapping by a streamer of the ionosphere-earth space, characterized in that the generation of electric energy in a magnetohydrodynamic generator is based on the passage through Of its electric charges of the Earth's ionosphere when they are selected by means of a laser beam devoid of divergence with a pulse duration corresponding to the time of overlapping by the streamer of the space "Earth-Ionosphere" enclosed in mirrors in the system "Earth-geostationary satellite-earth", once obtained in a laser radiation source And its subsequent (source) trip with periodic pumping of photons by the inclusion of a source of laser radiation.
print version
Publication date 16.02.2007gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.