| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2121334
![]()
METHOD OF INFORMATION COLLECTION
BIOLOGICALLY ACTIVE SUBSTANCES ON THE MEDIA
The name of the inventor: Volkov E.E .; Egorochkin IV; Ermolaev MM; Nikolayev VP; Nakhabtsev VV; Pykhachev G.Yu .; Shamarin OV; Shabarov V.V.
The name of the patent holder: Legal Center "TIAN"
Address for correspondence:
Date of commencement of the patent: 1996.04.01
The invention relates to medicine, moreover, to reflexotherapy or therapy and allows to receive the means carrying information characteristics of biologically active substances (BAS). The method comprises forming a primary information carrier of the BAS on a photosensitive material with a helium-neon or helium-argon laser, placing this optical copy on a substrate connected to the input to the resonant circuit to the output of which is connected by a conductor to another plate on which the secondary carrier is mounted- Chemically inert to the body. After the circuit is turned on and the system is exposed, the information characteristics of the BAS are transferred from the primary medium to the secondary one.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to medicine, more specifically, to agents that can be used in reflexotherapy or therapy.
Methods for recording the wave characteristics of biologically active substances (BAS) used as test objects in the apparatus for reflexotherapy and diagnostics by R. Wall's method are known for carriers: wax, water and a microresonance circuit (see author N 1410313, 1993). G. A 61 H 39/00).
The essence of these technical solutions is that these carriers of information characteristics of testing BAS can replace native test objects in R. Wall's apparatus.
In addition, such storage media (see author's publication No. 1561253 A 61 H 39/00, 1992) may replace medicines in the treatment of patients. Thus, the prior art indicates the principal possibilities of transferring the information characteristics of BAS, including medicinal products, to different media and in different media.
The same optical capacity will also have an optical copy of the biologically active substance - this copy is obtained on the photosensitive material by irradiating BAS with a helium-neon or helium-argon laser.
Advantages of this information carrier of properties of BAS are before the above described - the photocopy is easy to transport and does not take up much space. It can be stored for a long time without losing its information properties. However, one of its drawbacks is the limited use for treatment, since this carrier can not be administered orally.
In connection with the above, we searched for ways to read information from a photocopy (primary media) and transfer it to a secondary medium that will have properties close to those of native BAS. For example, this secondary carrier can be a liquid that is easily dispensed, customary for use. Either this carrier is a homeopathic grist, which is easily used in treatment. The need for such a "rewrite" of information properties is due to the fact that the native BASs themselves have a certain shelf life, they require a lot of space and, therefore, are not always available. By creating a bank of information characteristics of BAS in the form of photocopies, it is possible at the given moment to obtain the required "overwriting" of these information properties on a suitable medium.
In the author. Svid. N 1561253 described already such a "rewrite". To this end, the information characteristics of the BAS are recorded on the primary medium, which is a microresonant circuit, and from this, these characteristics are transferred to a secondary medium-water. After the transfer, water, previously inert, acquires the medicinal properties of BAS without any side effects inherent in them.
As a result of numerous experiments, we found that the same effect can be obtained by using an optical copy of BAS.
With the help of the resonant circuit, information characteristics can be transferred from the primary medium to the secondary one. In this case, the secondary carrier will retain the therapeutic properties of BAS. This effect did not follow clearly from the known technical solutions, because In the author. Svid. N 1561253 primary information carrier is the resonant circuit itself.
As a prototype, we developed the above-described known method according to the author. Svid. N 1561253.
Common features of the claimed known method of transferring the information characteristics of BAS from the primary to the secondary carrier are as follows: the formation of a primary carrier of information characteristics of a biologically active substance and the transfer of these characteristics to a secondary carrier by means of a resonant circuit. In this case, chemically neutral compounds are used as a secondary carrier.
The difference between the claimed method and the known method lies in the fact that the optical medium on the photosensitive photographic material obtained by means of a laser is used as the primary carrier of the information characteristics of the BAS, and water, homeopathic grains, alcohol solutions, etc. can be used as secondary carriers.
The method is carried out as follows
An optical copy of BAS is obtained on the photosensitive photographic material with the aid of a helium-neon or helium-argon laser. For this, the BAS is placed between the radiation source and the photographic material, maintained and developed.
Then the received copy is established on a plate which is connected by a metal conductor with an input in a resonant circuit. The output of the resonance circuit is connected by a metallic conductor to another metal plate on which a container with a secondary carrier is mounted. The resonant circuit is turned on and maintained for a time sufficient to transfer information to the secondary medium.
An example of implementing the method
Patient B. with exacerbation of chronic otitis media of the middle ear according to the results of inoculation of the secreted, containing Streptococcus pyodenus, shows the antibiotic cephaloridine. However, the patient with the administration of this drug had allergic reactions in the form of reddening of the skin and rashes on it.
A solution of the antibiotic cephaloridine was prepared and placed in a glass vessel and installed between the photoplate and the helium-neon laser so that the entire volume of the antibiotic was captured by the light beam. The resulting optical copy of a 2 x 2 cephaloridine solution is mounted on a metal substrate that is connected by a conductor to the input of the resonant circuit. Its output is connected to another metal plate, on which is installed a glass container with distilled water. After exposure, the device was turned off. During the exposure information characteristics of the drug from the primary carrier - photocopies transferred to the secondary - distilled water.
The obtained preparation in an amount of 40 ml per day was used twice for 14 days. From the first reception of the drug positive dynamics of the process is observed. The pain subsided, the discharge gradually ceased, the hyperemia disappeared. Inspection of the otolaryngologist at the end of the course of treatment established a complete recovery.
Example 2
Patient N. 25 years old 6 d: follicular sore throat. With the help of the Voll apparatus, containing as a test agent p-ry various drugs selected etiopathogenetic treatment - ampicillin. At the same time, if the parameters of the device before the installation of the drug were 87 conventional units, then after the installation of ampicillin, they decreased by up to 52 conventional units. Instead of the native ampicillin p-test, a secondary carrier of its information was installed in the test cell-water treated according to the method described above. Indicators of the device were 54 units.
A total of about 50 patients with various inflammatory diseases were treated. In all cases, a high therapeutic effect of the prepared carriers of the information characteristics of BAS was found, adequate to the drugs themselves. In none of the cases did side effects of these carriers appear to be inherent in BAS.
The table shows the results of treatment of various diseases, conducted on the basis of the military hospital. Mandryko.
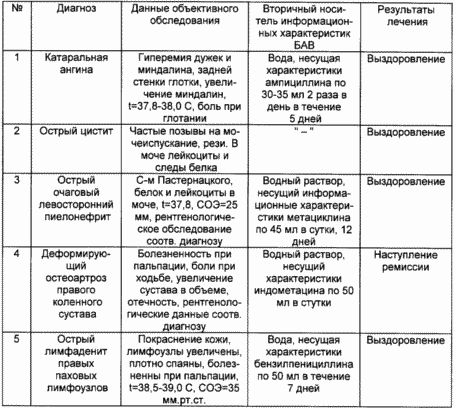
Thus, the claimed method allows replenishing the arsenal of medicines, making them cheaper to obtain and simplifying the diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
CLAIM
1. A method for transferring information characteristics of biologically active substances to carriers, comprising forming a primary information carrier for biologically active substances and subsequently transferring them to a secondary carrier by placing a secondary carrier, a chemically inert substance on the metal plate connected to the resonant circuit, The exposure of the system, characterized in that as an initial carrier of information characteristics of biologically active substances, an optical copy is used on the photosensitive material obtained with a helium-neon or helium-argon laser, which is placed on an additional metal plate connected to the input of the resonant circuit, and The plate with the secondary carrier is connected to the output of the resonant circuit.
2. A method according to claim 1, characterized in that water or saline is used as a secondary carrier of information characteristics of biologically active substances.
3. A method according to claims 1 and 2, characterized in that the homeopathic grit is used as a secondary carrier of information characteristics of biologically active substances.
print version
Date of publication 30.03.2007gg




Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.