| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2024871
![]()
A METHOD FOR DETENDING DUODENOGASTRAL REFLUX
The name of the inventor: Tuev AV; Golovanova ES; Savina L.V.
The name of the patent holder: Tuev Alexander Vasilievich
Address for correspondence:
Date of commencement of the patent: 1991.04.01
Use: in medicine and biology, can be used for qualitative express diagnostics of duodenogastric reflux. Essence: drops of basal and stimulated contents of 0.01 - 0.03 ml each, applied to a slide, covered with a cover glass, dried at t = 35-38 ° C for 3-6 h, then examined in polarized light. And if there are optically active dendritic inclusions in the preparations, duodenogastric reflux is determined. The method is simple and allows increasing the accuracy of determining the presence of duodenogastric reflux.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to medicine and biology and can be used for qualitative express diagnostics of duodenogastric reflux (DGR).
A method of qualitative and quantitative detection of bile acids in gastric contents is known - thin-layer chromatography (prototype).
Gastric contents obtained on an empty stomach, or any portion of basal contents obtained in a fractional study, is filtered through gauze to remove lumps of mucus and undigested food, the pH of the juice is adjusted to 7.0-8.0 by adding a few drops of a saturated solution of sodium carbonate. To 1 ml of the thus prepared gastric contents, 5 ml of 96% ethanol are added, mixed and heated for 5 minutes in a water thermostat at 80 ° C. After centrifugation (3000 rpm, 5 min), the supernatant is poured into a wide-necked test tube ("Sugar cups") and evaporated in a boiling bath to dryness. The precipitate is washed twice with 5 ml of ether to remove cholesterol and dissolved in 0.2 ml of 96 ° alcohol for a qualitative reaction.
For qualitative detection of the LC micro-quantity of alcohol extract (10-20 ml) is applied to chromatographic plates. After drying, the plates are sprayed with a 10% alcohol solution of phosphomolybdic acid and placed in a drying cabinet at 105 ° C. If the concentration of LC is high enough in the gastric content, they are identified as separate spots on the chromatogram. In the case of a small concentration - in the form of a continuous line [1].
The disadvantage of the method is the complexity of the method of implementation during the preparation of the material and the qualitative detection of the LC, i.e. Preparing it for chromatography, namely: complete loss of the activity of the gastric contents by adding 96 o ethyl alcohol, heating for 5 minutes at 80 ° C, evaporation in a boiling water bath to dryness, rinsing in ether; The presence of chromatographic plates, which are produced abroad.
All of the above makes it difficult to use the chromatographic method for determining the LC in gastric contents, and this reduces the possibility of early diagnosis of GDR.
The purpose of the invention is to simplify the method and improve accuracy. This goal is achieved by performing a crystal-optical examination of the sample in the form of dried drops of gastric contents (the average portion of basal and stimulated contents) of the patient under study with subsequent study of its optical pattern in the crossed nicoles of a polarizing microscope.
In order to simplify the process and increase the accuracy of a drop of basal and pentagastrin-stimulated content, 0.01-0.03 ml each, is applied to a glass plate, covered with a cover slip, then dried at T = 35-38 ° C for 3-6 h , Microscopy in polarized light and in the presence of optically active dendritic inclusions in the preparation, a change in the composition of the gastric contents is recorded.
The method is carried out as follows. The average (2-3) portion of basal and stimulated (for example, pentagastrin) NLC in the form of drops (3-4), with a volume of 0.01-0.03 ml each, is applied separately on slides, covered with each cover glass and dried in a dry-air Cabinet at Т = 35-38 о С for 3-6 hours - to completely remove moisture.
The obtained preparation is microscopized in polarized light (for example, in a polarization microscope "MIN-8") and in the presence of optically active dendritic inclusions in it, the presence of LC, and hence the presence of DGR, is determined.
The crystal-optical study was performed by a polarizing microscope (MIN-8). With a high content of LC and NLC (basal and stimulated secrets), dendritic forms are present in the preparations.
All the patients under study were quantified in the LC content of the NLC.
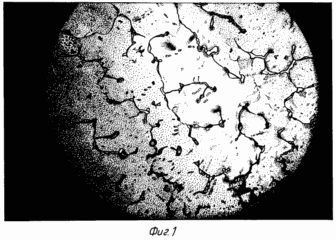
FIGS. 1-6 show a method of determining duodenogastric reflux.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Example 1 . Healthy S., 31, without a hereditary burden on the pathology of the gastrointestinal tract.
Technology: 4 portions of basal and 4 servings of pentagastrin-stimulated secret were obtained in the probe study of gastric contents. 3 droplets of the third portion of the basal secretions were applied to the slide, each with a volume of 0.01 ml, covered with coverslips and dried in a thermostat at T = 35 ° C for 3 hours, then microscopized. When studying preparations in polarized light, the microstructured surfaces of dried drops of NLC are optically inactive, since there are no optically active inclusions. Branching structures are visible (Fig. 1). In the study of the third portion of basal content by thin-layer chromatography, LCs are not determined, which indicates the absence of DGR.
3 drops of NLC of a second portion of pentagastrin-stimulated secret were applied to the slides, each volume of 0.03 ml, covered with coverslips, dried in a thermostat at T = 38 ° C. for 6 hours, then microscopized. When studying preparations in polarized light, the microstructured surfaces of dried drops of NLC are optically inactive. There are branching microtypes (Fig. 2). When studying the same portion of the stimulated secret by thin-layer chromatography, LCs are not determined, which indicates the absence of DGR.
A model composite prepared from standard LCD sets with a glycocholic acid content of 80 mmol / l. To prepare the preparation 3 drops of a standard solution of glycocholic acid, each volume of 0.01 ml, was applied to slide glasses, covered with slide glasses and dried for 3 hours at T = 35 ° C, then microscopized. When studying the preparation in polarized light, dendritic optically active structures are present (Fig. 3).
The second model composite prepared from a set of standard LCs, the content of which is 40 mmol / l, was applied in the form of 3 drops (each volume of 0.03 ml) on slides, covered with coverslips and dried for 6 hours at T = 38 ° C, Were microscopized in polarized light. The preparation contains dendritic optically active inclusions (Fig. 4).
Example 2 . Patient A., 35 years old. Diagnosis: peptic ulcer disease of the pyloroduodenal zone, subacute phase of relapse, with localization of the ulcerative defect in the bulb of the DPC. Functional duodenosis with the presence of GDR (radiographically and gastroduodenofibroscopically).
Technology: 3 drops of the third portion of the patient's basal secretion of the patient's basal secretion, 0.01 ml each, were applied to slide glasses, covered with coverslips and dried in a thermostat at T = 35 ° C for 3 hours, then microscopized in polarized light. In the crystallized drop there are dendritic optically active inclusions (FIG. 5). In the study of the third portion of basal content, the method described in the prototype increased the LC content to 31.2 mmol / l, which confirms the presence of DGR.
Example 3 . Patient I., 45 years old. Diagnosis: chronic antral gastritis, type B, with preserved secretory function, exacerbation phase. Functional bulboduodenosis with DGR.
Technology: 3 drops of the NLC of the second portion of the stimulated secretion of the patient were applied to slides, each with a volume of 0.03 ml, covered with coverslips, dried 6 hours in a thermostat at T = 38 ° C, then microscopized in polarized light. In the preparation, optically active dendritic inclusions were detected, which indicate the presence of LC, and consequently, DGR (Fig. 6). When the same portion of gastric secretion was tested by the method described in the prototype, the LC content was raised to 30.1 mmol / l, which confirms the presence of DGR.
The effectiveness of the crystallographic method of diagnostics of DGR in comparison with the prototype lies in the fact that, without conducting chromatographic and biochemical studies that require large technical and material costs, it is possible to carry out qualitative analysis of gastric contents according to the types of optically active inclusions and diagnose DGR (bulboduodenosis with pyloric insufficiency of stomach pulp ). The method is informative, simple in execution. The presence of LC is diagnosed by the presence of optically active dendritic forms.
CLAIM
METHOD FOR DETERMINING DUODENOGASTRAL REFLUX by detecting bile acids in gastric contents in vitro, characterized in that, in order to simplify and improve the accuracy of the method, a drop of basal and stimulated portions of native gastric contents is applied to a slide, covered with each cover glass and dried 3 to 6 hours In a thermostat at 35 - 38 o C, then it is examined in polarized light and if there are optically active dendritic inclusions in the preparation, the presence of duodenogastric reflux is determined.
print version
Date of publication 29.03.2007gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.