| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2091796
![]()
METHOD OF DIAGNOSTICS OF HELIKOBACTERIOSIS
The name of the inventor: Zhebrun AB; Safonova NV; Dovgal SG; Mileiko V.E .; Falovski
The name of the patentee: St. Petersburg Research Institute of Epidemiology and Microbiology named after Paster; Mixed partnership "Sintana Prozum"
Address for correspondence:
Date of commencement of the patent: 1993.05.28
The invention relates to the field of medicine, namely to the diagnosis of diseases caused by bacteria of the genus Helicobaster. The essence of the invention consists in the fact that ammonia is detected in the air of the patient's oral cavity with the help of indicator tubes, and at the concentration of it above 0.8 mg / m 3, infection is judged. In terms of sensitivity and specificity, the proposed method coincides with the prototype, but it surpasses it in safety for the examinee, in speed, simplicity of execution and economy. The method is ready for use: indicator tubes are produced in LLP "Sintana prosum".
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the field of medicine, namely to the diagnosis of diseases caused by bacteria of the genus Helicobacter.
In recent years, the etiological role of Helicobacter pylori has been proven in the occurrence of most gastritis and gastroduodenitis, and their etiopathogenetic value in peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum. Timely and reliable diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection is of primary importance for the selection of an effective method of treating patients.
In the diagnosis of Helicobacteriosis, biochemical tests are widely used to detect extracellular urease produced by Helicobacter and hydrolyzing urea to ammonia (urease tests).
The prototype of the invention is a method for diagnosing helicobacteriosis using a commercial CLO test (Delta West Ltd, Canning Vale, Western Australia). The CLO test is a gel-like tablet containing urea, phenolic red (pH indicator), and bacteriostatic agent. The material for the study is a biopsy of the gastric mucosa obtained by endoscopy. The biopsy is placed on the surface of the CLO-test tablet. When urea is present in the test material, urea is hydrolyzed to ammonia, increasing the pH of the medium and the indicator changes color from yellow to crimson. The results are recorded after 20 minutes, 3 and 24 hours. The total duration of the study, including the stage of taking the biopsy, is 1.5-24 hours. The disadvantage of the method is traumatism for the patient, the need to use imported expensive equipment (endoscope), the complexity of the execution (biopsy sampling stage ), The duration of the study.
The essence of the invention is that ammonia is detected in the air of the patient's oral cavity with the help of indicator tubes and at the concentration above 0.8 mg / m 3 it is judged about infection.
Indicator tubes made according to the recipe of SU 1458815 A1 are used. The indicator tube is a sciclode with an internal diameter of 2.0 ± 0.1 mm, filled with an indicator composition of a homogeneous yellow powder. When passing through the indicator composition of air containing ammonia, the powder is colored bright blue. The concentration of ammonia in mg / m 3 is determined from the scale of accounting for the value of the colored column. The indicator tube before use is opened, wiped with 70% alcohol. Air from the mouth of the patient is sucked through the tube with a device like PGA-VPM. Measurement time 15 min.
This method of diagnosing helikobakterioza according to our data is not inferior in sensitivity and specificity to the prototype, but it surpasses it in atraumatism and the rate of response.
Example 1 . Examine the proposed method of 3 groups of persons comparable in sex and age:
A) persons without complaints of discomfort in the epigastric region (not suffering from gastroduodenal diseases) 38,
B) persons with diagnoses of hyperacid gastritis, peptic ulcer of the stomach or duodenum 40,
C) persons with a diagnosis of anacid gastritis 6 (see table).
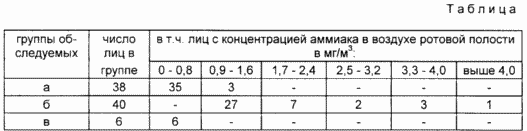
The concentration of ammonia in the control group (a and b) in most cases does not exceed 0.8 mg / m 3 (35 of 38 92.1% and 6 of 6 100%, respectively). In persons in group 6, this index for all 40 examined above 0.8 mg / m 3 . Consequently, the presence of ammonia in the oral cavity of the patient concentration above 0.8 mg / m 3 should be considered a diagnostic indicator of infection with Helicobacter pylori.
Example 2 . It differs from Example 1 in that 12 gastritis patients with peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum are examined simultaneously by two methods using a CLO test (biopsy specimens of the gastric mucosa and duodenum) and the proposed method (oral cavity air). Of 12 patients, the CLO test is negative in 2 and only in them the concentration of ammonia in the oral cavity is lower than the diagnostic value. The remaining 10 patients with a positive CLO test have an ammonia concentration in the range of 1.0-4.0 mg / m 3 .
Example 3 . It differs from Example 2 in that in patient C. the concentration of ammonia in the oral cavity is determined twice before and after the operation. The presence of Helicobacter pylori is documented by a CLO test and bacteriologically in the antrum and body of the stomach. The concentration of ammonia in the air of the mouth before the operation is 4 mg / m 3 , in the postoperative 0.4 mg / m 3 , i.е. After resection of infected tissue, there was a 10-fold decrease in the formation of ammonia to the level determined in the control group.
Thus, for sensitivity and specificity, the proposed method coincides with the prototype, but it surpasses its safety for the subject, speed, simplicity of execution and economy. The method is ready for use: indicator tubes are produced in LLP "Sintana prosum"
CLAIM
A method for diagnosing Helicobacteriosis, comprising sampling a biological material, followed by express analysis for ammonia, characterized in that express analysis is performed in the oral cavity of the patient in vivo and an infection is detected at a concentration of ammonia in the exhaled air above 0.8 mg / m 3 .
print version
Date of publication 29.03.2007gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.