| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2200325
![]()
METHOD FOR PREDICTING THE COMPLICATIONS OF ULCERNAL DISEASE OF THE TWELFTH DIAGNOSTIC ACUTE ASSOCIATED WITH HELICOBACTER PYLORI
The name of the inventor: Ignatova GL; Sarsenbaeva AS; Sarsenbayev B.Kh.
The name of the patent holder: Ural State Medical Academy of Continuing Education
Address for correspondence: 454021, Chelyabinsk, pr. Pobedy, 287, UGMADO, library
Date of commencement of the patent: 2001.04.10
The invention relates to medicine, in particular to gastroenterology, surgery, and can be used in predicting complications of duodenal ulcer. The method is easy to use and allows you to evaluate the severity of morphological changes and using immunological methods to assess the nature and depth of shifts in the immune system and thereby provide the ability to predict complications of duodenal ulcer with high accuracy. A histological examination of duodenum mucosa biopsy specimens is made in the periulcerous zone, the level of immunoglobulins of class G in the blood serum is determined and in the presence of Helicobacter pylori, complete gastric metaplasia in the periulcerous zone and a decrease in immunoglobulins in serum below 6.62 ± 0.8 g / Development of complications.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to medicine, in particular to gastroenterology, surgery, and can be used in predicting complications of duodenal ulcer.
There is a known method for predicting the course of peptic ulcer disease [patent RU 2043635, G 01 N 33/50], where by the change in the concentration of free hydrochloric acid, pepsin, total, insoluble, soluble mucus in the histamine stimulated portion compared to basal (by the ratio ratio) Predict the course of duodenal ulcer and at the values of these factors equal to 0.98 ± 0.22 in the basal portion, 1.88 ± 1.20 in the stimulated histamine portion and / or 3.22 ± 1.44 and 6.54 ± 1.15, respectively, predict a favorable course of the disease with conservative treatment, with the coefficients equal to 2.74 ± 0.24 and 3.60 ± 0.42, and 3.62 ± 1.12 and 6.43 ± 0.85 In the corresponding portions of the gastric juice, a favorable course of the disease during surgery, and at values of the coefficients equal to 3.46 ± 1.29 and - 6.08 ± 2.3, respectively, predict an unfavorable course of the disease with conservative and surgical treatment.
Given the direct connection of duodenal ulcer with Helicobacter pylori infection, in this case, a method for predicting the course of duodenal ulcer taking into account histological and immunological criteria is proposed.
Histological method is one of the mandatory in the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection and morphological changes in the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum. The immunological method provides information on the depth of changes in the body's immune system for Helicobacter pylori infection. Determination of the level of immunoglobulins is an accessible and compulsory screening parameter for an immunological study.
Therefore, as a prototype, two methods are chosen:
- a method for predicting the course of gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer in patients with pyloric campylobacter [patent RU 2007728, G 01 N 33/68], where in patients with pyloric campylobacter, the content of cationic proteins in the integumentary epithelium of the duodenum is determined on the smears. At the content of cationic proteins in epithelium less than 0.8 and cationic proteins in granulocytes less than 1.0 in combination with bacterial contamination of more than 50 microns (+++), the decompensation of the bactericidal protection system of the mucosa and the threat of complications are judged. However, the disadvantage of the method is that it does not reflect the connection of the development of complications with the reaction of the duodenal mucosa to contamination by its infection with Helicobacter pylori;
- a method for predicting the course of peptic ulcer [RU 2006040, G 01 N 33/68], where the level of interleukin-1 in the spontaneous test is 0.34 ± 0.14 conv. Units , In the stimulated - 1.33 ± 0.2 conv. Ed. Determine an unfavorable prognosis during the course of the disease.
The disadvantage of this method is the high cost of reagents for determining interleukin-1 and the need for special equipment of an immunological laboratory
OBJECT OF THE PRESENT INVENTION:
- with the help of histological methods of investigation, to ensure the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection on the duodenal mucosa, to evaluate the severity of morphological changes (the presence of gastric metaplasia);
- Using immunological methods to assess the nature and depth of shifts in the immune system and thereby ensure the possibility of predicting complications of duodenal ulcer.
The technical result is the timely prevention of complications of duodenal ulcer.
This task is achieved by the fact that in the claimed method of predicting the likelihood of complications in duodenal ulcer by histological and immunological examination, according to the invention, a histological examination of duodenum mucosa biopsy specimens is made in the periulcerous zone, and the level of immunoglobulins of class G in the patient's serum is determined. If the infection of Helicobacter pylori, full gastric metaplasia in duodenum in the periulcerous zone is detected histologically, the level of immunoglobulin G in the blood serum is lower than 6.62 ± 0.8 g / l, determined by the immunological method (in the control group, the concentration of immunoglobulins of class G was 12, 4 ± 0,05 g / l, in patients with peptic ulcer of duodenum without complications 8.77 ± 0.77 g / l), predict the likelihood of complications of peptic ulcer disease of the duodenum.
Studies on patent and scientific and technical information sources have shown that the proposed method for predicting the risk of complications of duodenal ulcer is not known and should not be explicitly studied from the level of technology studied, that is, it meets the criteria of "novelty" and "inventive level."
The proposed method is carried out using known techniques:
- Diagnosis of infection of Helicobacter pylori in the duodenal mucosa by histological method using criteria Aruin LI With et al. (1993);
- Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection by the urinary respiratory method (Kornienko EA, Mileika VE, 1996);
- determination of the concentration of serum immunoglobulins by radial immunodiffusion in a gel (Manchini, 1966);
- Evaluation of morphological changes in the mucous membrane of the duodenum according to the visual analogue scale (Dixon MF et al, 1994).
55 patients with peptic ulcer of duodenum were examined. Of these, 33 patients had complications, 22 without complications. All patients underwent a comprehensive examination with mandatory inclusion for each of the above histological and immunological methods.
To build a mathematical model of individual forecasting, the computer program STATISTICA 5.0 for WINDOWS was used.
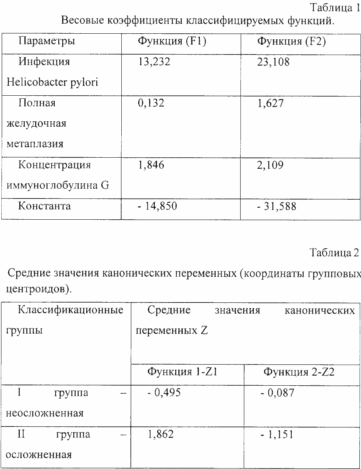
Using the module "Classification and single-factor analysis of variance", the most informative features were determined for the construction of the forecast model (with the probability of intergroup differences less than 0.05): detection of Helicobacter pylori infection with the probability of intergroup differences 0.01, total gastric metaplasia with the probability of intergroup differences 0 , 03, the concentration of immunoglobulins of class G with the probability of intergroup differences of 0.02. Further, using the "Dispersion Analysis" module, the value of Wilkes 0.317 was obtained, which indicated good discrimination.
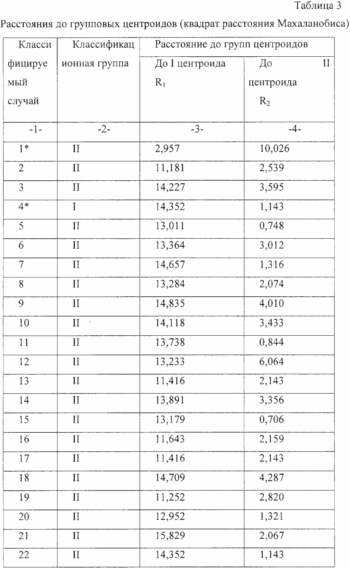
Then, using the discriminant analysis for each group, the coordinates of the group centroids were found, which are the eigenvalues of the canonical functions (see Table 1-3).
 |
 |
 |
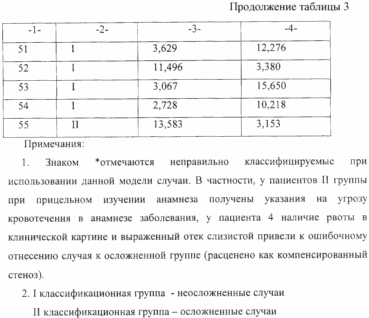 |
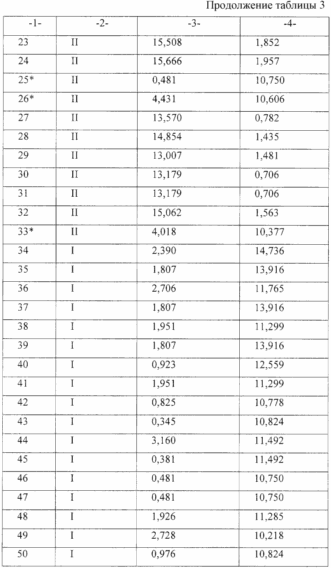
To predict complications and assign a patient to one or another group, it is necessary to calculate the values of both canonical functions and determine the Euclidean distance (the square of the Mahalanobis distance) from the obtained point to each of the centroids.
Interpretation of Table 3: the case belongs to the group with the minimum distance to the group centroid.
Results of calculation of the created mathematical model: probability of correct classification of patients of the I group 95.2%, Group II 88.2%. The total power of the model is 90.9%.
In order to determine which classification group the patient belongs to, it is necessary to calculate the classification marks (the case coordinates) that are the values of the functions F1 (x) and F2 (x), and then determine the distances from the obtained point to each of the group centroids. The minimum distance indicates the patient's belonging to a certain group.
F1 (x) = 13.232 h HP + 0.132 × M + 1.846 × IgG-1,850,
F2 (x) = 23.108 H HP + 1, 627 × M + 2.109 × IgG-3.588.
The distances to the group centroids (R1, R2) were calculated from the formula using the mean values of the canonical variables Z.
R = C (F1 (x) -Z1) 2 + (F2 (x) -Z2) 2 ,
R1 = C (F1 (x) + 0.495) 2 + (F2 (x) + 0.087) 2 ,
R2 = Ц (F1 (x) -1.862) 2 + (F2 (x) +1.151) 2 .
In the formulas:
HP is the coefficient corresponding to the degree of contamination of the duodenal mucosa (1 - poor degree of seeding (+), 2 - medium degree of seeding (++), 3 - high degree of seeding +++).
M - complete gastric metaplasia, corresponds to the classification code 2 in this model.
IgG is the concentration of class G immunoglobulins in serum, g / l.
Next, we determine the minimum distance and classify the patient into the appropriate group.
Clinical examples
1. The patient S., 60 years old. Case report 9319/797. Diagnosis: Duodenal ulcer with localization on the posterior wall of the bulb, associated with Helicobacter pylori. Chronic course. Active phase. Subcompensated stenosis of the pylorus. Resection of the stomach according to Hofmeister-Finsterer (6.09.00).
He suffers peptic ulcer of the duodenum since 1975, exacerbations are rare. Deterioration from the beginning of 2000 - pain in epigastrium, right hypochondrium, periodically vomiting, weight loss. Endoscopic examination revealed a deep ulcer of the back wall of the bulb of the duodenum with a diameter of 20 mm. A positive result was obtained for Helicobacter pylori (+++) by two methods of diagnosis.
Histology 18699-18701 - chronic duodenitis of high degree of activity with complete gastric metaplasia, Helicobacter pylori +++.
25302-25308 - chronic atrophic high degree of pangastritis with focal incomplete intestinal metaplasia.
Serum IgG concentration is sharply reduced - 6.6 g / l.
2. Patient P., 61 years old. Case report 3605/268 Diagnosis: Duodenal ulcer with ulcer localization on the anterior wall of the bulb associated with Helicobacter pylori. Chronic course. Active phase. Cicatricial deformation of the bulb of the duodenum. Bleeding from the 27.03.00. Resection of the stomach according to Hofmeister-Finsterer (28.03.00.).
Has been suffering from peptic ulcer since 1970. Remission from 1 to 5 years. With endoscopic examination, an ulcer of the anterior wall of the bulb of the duodenum of average depth, with a diameter of 7 mm, was detected.
Histology 30592 / 98-30594 / 98 - chronic atrophic highly active antrum - gastritis with lymphofollicular hyperplasia and high degree of Helicobacter pest.
Histology 9253-58 - high degree of duodenitis with complete gastric metaplasia, Helicobacter pylori ++. The concentration of immunoglobulin G in serum was 4.5 g / l.
3. Patient X., 22 years old. Case history 011155. Diagnosis: Duodenal ulcer with localization on the posterior wall of the duodenal bulb associated with Helicobacter pylori (++). Chronic current. Active phase. The flow of light degree.
Has a peptic ulcer for 4 years. Exacerbations once a year. A moderately deep ulcer with a diameter of 5 mm was found on the posterior wall of the bulb.
Histology 21600/98 - 21602/98 - chronic atrophic inactive antrum - gastritis with moderate Helicobacter pestosemiology.
5316 / 98-5320 / 98. Chronic duodenitis of moderate degree of activity. Helicobacter pylori -.
The level of immunoglobulins of G class is 8.0 g / l.
4. Patient G., 35 years old. Case history 12245. Diagnosis: Duodenal ulcer with localization on the anterior wall of the bulb, associated with Helicobacter pylori (+). Chronic course. Active phase. The course of moderate severity.
He suffers from peptic ulcer for 12 years. Exacerbations 1-2 times a year. A superficial ulcer with a diameter of 4 mm was detected, the bulb of the bulb was deformed, and we passed through it.
Histology 28233/98 - 28235/98. Chronic antrum - gastritis with the phenomena of initial atrophy, moderate degree of activity with the phenomena of lymphofollikular hyperplasia, weak (+) Helicobacter pestosemiology.
15488 / 98-15490 / 98 - chronic ulcer of the duodenum, periulcerous duodenitis, Helicobacter pylori -.
The concentration of immunoglobulins of class G in serum is 8.1 g / l.
Thus, clinical examples demonstrate the role of contamination of the duodenal mucosa by the infection of non-Illicobacter pylori, gastric metaplasia on the duodenal mucosa in the formation of complications of duodenal ulcer.
This is the result of a persistent persistence of Helicobacter pylori infection in the gastric epithelium, and then as the foci of gastric metaplasia and duodenum form. This phenomenon can be explained by switching off the mechanisms of bicarbonate secretion by epithelial cells of the duodenum due to the mechanical replacement of its gastric epithelium. Persistence of Helicobacter pylori and recurrent ulcerative process lead to fibrosis of the wall of the duodenum. The vessels of the microcirculatory bed are entangled in the fibrous tissue, as a result of which this line of protection of the epithelium of the duodenum also suffers.
IgG - the response of plasma cells is Helicobacter pylori - specific. As the formation of gastric metaplasia on duodenum mucosa and the colonization of its Helicobacter pylori, a gradual depletion of the IgG-mediated response occurs, which is ascertained in patients with complicated duodenal ulcer. That is, colonization of the duodenal mucosa of Helicobacter pylori, complete gastric metaplasia and a decrease in IgG concentration in the serum of patients with peptic ulcer of the duodenum are the links of one pathological process.
The proposed method is highly informative and reflects the depth of reactions occurring in the body in response to Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with duodenal ulcer, meets the current level of examination and management of a gastroenterological patient. Can be used in a medical institution, diagnostic unit, research laboratory, equipped with equipment for routine morphological and immunological studies.
Therefore, the claimed invention meets the criterion of "industrial applicability".
CLAIM
A method for predicting complications of duodenal ulcer associated with Helicobacter pylori by histological and immunological examination, characterized by the histological examination of duodenum mucosa biopsy specimens in the periulcerous zone and determining the level of immunoglobulins of class G in the blood serum and in the presence of Helicobacter pylori full of gastric metaplasia In the periulcerous zone and a decrease in immunoglobulins in the blood serum below 6.62 ± 0.8 g / l predict the likelihood of complication.
print version
Date of publication 29.03.2007gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.