| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2022547
![]()
Method of treating acute destructive calculous
occlusive CHOLECYSTITIS
Name of the inventor: Mejidov RT .; Dalgatov GD .; Inchilov MG
The name of the patentee: Mejidov Rasul Tenchaevich; Dalgatov Gimatov Dalgatovich
Address for correspondence:
Starting date of the patent: 1990.07.04
Use: medicine, surgery for the treatment of acute destructive calculous occlusal homtsistita. The inventive applied mikroholetsistostomu dissolved concrements solvent and in the presence of stones and pigment mixed type cavity gallbladder through a tube with an external diameter of not more than 2.8 mm administered 70% ethanol, treated with ultrasonic bubble content rate 27 kHz, vibration amplitude 30-100 mm for 1 min, aspirated alcohol fill the gallbladder hydrophobic solvent, repeatedly voiced by the contents of the bladder, remove the products of lysis stones and replace the handset mikroholetsistostomicheskim drainage.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to medicine, namely to methods of endoscopic treatment of diseases of the abdominal organs, and can be used for the treatment of destructive forms of acute calculous cholecystitis occlusion in individuals with an increased risk of surgical intervention.
It is known that acute cholecystitis currently stands at 18-20% of the total number of patients admitted to the hospital with urgent surgical diagnosis. According to various reports, the specific proportion of patients elderly among them is 39,4-87%, and the numerical ratio in this group over the last 10 years has moved toward the predominance of elderly patients by 30%. In 92-92,2% of cases in this cohort of patients with acute cholecystitis combined with cholelithiasis. The main role in the development of acute cholecystitis is the sudden violation of the outflow of bile. As a result of obstruction of the cystic duct bile congestive infected, inflamed bladder wall, increasing bladder wall edema exacerbates pathological process. According to the known data from 43,4-50% of patients of elderly and senile age with acute calculous cholecystitis, the disease was caused by occlusion of the cystic duct. Among the 138 patients with a similar contingent, which was imposed laparoscopic mikroholetsistostoma, occlusal cholecystitis was detected in 94 (68, 1%).
It should be added that when acute cholecystitis is not developing because of the obstruction of the cystic duct concrement, but because of other reasons, it is developing a second obturation due to the inflammatory swelling of the mucous membrane, as evidenced by studies conducted rentgenologcheskimi.
Since the outcomes of radical surgical treatment of acute calculous cholecystitis in patients with middle and old age, and having a high risk of surgery due to the presence of intercurrent diseases at the moment are not satisfactory, and postoperative mortality reaches 10-26%, are being made new attempts nonradical create new and highly effective methods for treating such patients. In particular, increasingly used in the treatment of acute destructive calculous cholecystitis in patients who have a high risk of surgery, laparoscopic finds transparientalnaya chrezpechenochnaya mikroholetsistostomiya. According to current data, this method is the most secure in the technical and medical terms. Overlay mikroholetsistostomy by this method prevents the leakage of bile from the puncture hole is less traumatic for the hepatic tissue and the wall of the gall bladder, and generally on the safety and therapeutic effect can be considered as method of choice before applying cholecystostomy by suturing the bottom of the gall bladder to the anterior abdominal wall or by puncturing it through bottom, bypassing the hepatic tissue in both laparoscopic and in other embodiments these operations.
When using laparoscopic transhepatic mikroholetsistostomii in patients with acute destructive calculous cholecystitis mortality according to the data obtained does not exceed 2.5%, which corresponds to current data. This operation allows you to reach in a short time of regression of acute inflammation in the biliary tract and operate patients in a "cold" period. However, a substantial proportion of patients (12%) to improve the state refrain from radical surgery or operation is not performed due to the presence of intercurrent diseases. Patients are written with stones in the gall bladder, which determines the subsequent recurrence of the acute inflammatory process, which takes place against the background of already more severe general condition of patients.
Consequently, the obvious necessity and relevance of search solutions for non-operational removal of gallstones at a destructive cholecystitis in patients with high risk surgery.
Methods are known for the treatment of acute destructive cholecystitis, is to impose mikroholetsistostomy and removal of gall bladder stones by dissolving them or breaking the direct influence of energy such as a laser beam, ultrasonic or electrohydraulic lithotripter. These methods are selected as equivalents.
A method of treating acute calculous cholecystitis destructive, consisting in draining the gallbladder and the impact on the calculi through the drainage hole low-frequency ultrasound power, sufficient for their destruction of the contact, followed by removal of the products of destruction of stones through the drain hole.
The method includes the steps of:
- transparietalnaya transhepatic puncture of the gallbladder, sucking its liquid contents, the imposition mikroholetsistostomicheskogo drainage and sanitation of the gall bladder in various ways to the remitting acute inflammation. This step takes at least 1-2 weeks; posledovavtelnoe razbuzhirovanie puncture channel rigid dilator to a size corresponding to the diameter of an optical device, but not less than 10 mm;
- administration in bladder cavity optical devices, such concrements nephroscope and detection;
- introduction to the operating channel of an optical device ultrasonic lithotripter and the destruction of stones;
- laundering cavity bladder stones from the decay products; removing stone fragments by mechanical means in the case of the remaining stones or their excessively large fragments, but also with the possibility of direct exposure to lithotripter - a repetition of the destruction process;
- replacing optical devices plastic drainage;
- confirmed in postoperative fact of destruction and removal of stones. Repeated destruction of concretions method described above in the case of abandoned stones or large fragments;
- drain removal after improving the patient's condition and stop the flow of abnormal discharge from the drainage. This period takes on the average, about 1-2 weeks.
Removal of stones in this group of patients by destroying them with a laser beam or an electrohydraulic lithotripter of the described method is not significantly different.
The essential features of this group of peers:
- kokrementov removal procedure performed to patients suffering from calculous cholecystitis in stage of disease remission. Translation of acute inflammation in remission achieved preliminary drainage of the gallbladder by imposing mikroholetsistostomy;
- It is part of the treatment effect on kokrementy located in the gall bladder, ultrasound or other type of energy, by the device, introduced into the cavity of the gallbladder;
- lithotripter injected into the gallbladder through holetsistostomicheskoe hole diameter must match the diameter of an optical device, introduced together with the lithotripter and should not be less than 10 mm;
- destruction and removal amenable kokrementy in the immediate vicinity of the working end of the lithotripter and clearly discernible in the optical device;
- stones destruction process must be accompanied by a permanent visual inspection using an optical device, introduced into the lumen of the gallbladder along with lithotripter. Erodible calculus and the working end lithotripter at the time of the destruction of calculus should be clearly distinguishable;
- Power lithotripter energy impact should be sufficient to break the calculus. Destruction efficiency stones when exposed to known methods, reaches 70-98%;
- destruction undergo all kinds of stones. The most effective destruction of pigment gallstones;
- treatment procedure is to alternate the destruction of stones. In the case of postoperative stones, not destroyed during the first session, the procedure is repeated destruction;
- concretions in the form of fragments or suspensions are removed by laundering the gallbladder through mikroholetsistostomu or captured by traps, administered through the operating channel of an optical device.
Known and the method of treatment of calculous cholecystitis, which consists in applying mikroholetsistostomy followed by introduction into the cavity of the gall bladder of a substance capable of dissolving gallstones. A special case of this method is a method for the treatment of acute destructive calculous cholecystitis occlusion in patients with a high risk of surgical intervention, by introducing into the cavity of the gallbladder through a solvent mikroholetsistostomichesky drainage. The method chosen as a prototype, comprising the steps of:
- puncturing the gallbladder, otsasyvavnie its liquid content and wash his oral antiseptics;
- imposition mikroholetsistostomicheskogo drainage;
- sanitation gallbladder within 8-11 days by introducing into its cavity antiseptic solutions, and a general therapeutic treatment aimed at eliminating the acute effects and correction of comorbidities;
- frakitsonnoe introduction of solvent into the cavity gallbladder stones until dissolution (18-22 days from exposure to a solvent for several hours according to the prototype method);
- Verification by dissolving the stones X-ray;
- sanitation of the oral gallbladder inflammation subsided before the final process of the biliary tract;
- removal of drainage and treatment of patients to the normalization of their condition. The duration of treatment in the hospital on the prototype method is 30-48 days.
The essential features of the prototype:
- procedure for removing stones is done to patients suffering from acute calculous destructive cholecystitis, after a preliminary reduction of acute inflammation in the bile ducts by imposing mikroholetsistostomy and rehabilitation oral gallbladder within 8-11 days;
- concrements are removed by dissolving them a substance capable of dissolving gallstones by direct contact with them;
- the duration of the complete dissolution of stones is 18-22 days (it is known that any of the currently applied in the most effective solvents able to dissolve calculi within 5-40 days);
- dissolution efficiency when applying the solvent by prototype method ranges from 50 to 80%. Efficacy of all the currently used solvents ranges from 20 to 70%;
- solvent is introduced through mikroholetsistostomu for 18-22 days;
- Solvent exposed simultaneously all concretions located in the cavity of the gallbladder;
- dissolving prototype method is effective only in relation to pure cholesterol stones or calculi, in which cholesterol is the dominant material. The same applies to any of the solvents currently in use;
- concretions in the form of a solution or suspension is removed through mikroholetsistostomu by laundering the gallbladder;
- dissolving concrements exposed and not fracture.
According peers ways to proceed with the destruction of stones, you must first arrest the acute inflammation of the biliary tract. This significantly prolongs hospitalization of patients and is economically disadvantageous. In addition, relief of acute inflammatory process can lead to the restoration of patency of the cystic duct, the previously occluded inflammatory edema or concrement, wedged into it due to mucosal edema. At the same time during the destruction of stones, and in the postoperative period, there is a significant probability of migration of fragments of stones in the biliary tract occlusion or damage to them, with the development of later complications such as cholangitis, obstructive jaundice, pancreatitis and others.
For administration with an optical device lithotripter is necessary that the diameter of the hole through which they are held, is not less than 10 mm. This, according to the methods peers, achieved consistent razbuzhirovaniem rigid dilator puncture channel. This procedure is not indifferent to the patient, causing unnecessary tissue trauma of the liver and gallbladder to the intra- and extraperitoneal bleeding, bile leakage into the free abdominal cavity, ascending cholangitis, and in any case, extend the operation.
Removal of stones in the methods of peers is possible only in the following cases:
- if calculi undergoing destruction, are in close proximity and in a forward direction of the working end lithotripter;
- if and calculus, and working end lithotripter are under constant visual control. This greatly reduces the possibility of the method as concretions located in the "dead" zone of influence with respect to energy, as well as nevizualiziruyuschiesya concrements can not be removed.
In addition, it can not be removed easily dislodged and running for calculi and calculi and multiple large, densely filling the gallbladder. Destroy and remove fails and concretions, occlusive cystic duct. It should be noted that multiple concrements large diameter does not allow to bring them mikroholetsistostomicheskoe through hole and can not be removed and by mechanical devices. Consequently, Edinstennoe way to remove them is through transhepatic mikrholetsistostostomu dissolution.
The destruction of the stones in the methods of peers requires a lot of energy coming from the working end of the lithotripter. Energy effect of ultrasound, as well as a laser beam or an electrohydraulic shock, enough to break the calculus, it is quite enough for the gallbladder wall damage. This can happen if the calculus loose, small or sliding easily if too many stones, and in the case of incorrect or careless direction of ultrasound on the wall of the gallbladder. Thus, the destruction of calculus by ultrasound according to the method-analogue was successful in 8 cases out of 11. The immediate cholecystectomy, to the occurrence of complications was performed in 3 cases. In addition, 5 of the 11 cases of postoperative residual calculi were discovered that forced to make repeated sessions of destruction. Thus, the destruction of concretions in the methods of peers is unsafe for the patient procedure.
Application of the prototype method assumes that you have (to remove stones) relief of acute inflammatory process by imposing mikroholetsistostomy. This period takes 8-11 days, which significantly prolongs the duration of inpatient treatment and is economically disadvantageous. It should be noted, and that the walls of the gallbladder, thickened due to inflammatory edema (gangrenous lesions in the absence of them), are more resistant to the damaging effects of the solvent. When relieving inflammation walls become thinner and their resistance decreases.
The term dissolution of stones on the prototype method excessively long (18-22 days). This significantly extends the period of hospital stay and is economically disadvantageous.
As for relief of the inflammatory process period and during the introduction of the solvent, there is a substantial likelihood of release of the cystic duct, the previously occluded wedged concrement or inflammatory edema. This can lead to migration of decomposition products in the form of stones or small fragments zamazkoobraznoy mass into the overlying sections of the biliary tract and the subsequent development blockade of the common bile duct or nipple Vater, jaundice or pancreatitis.
Exposure of the solvent in the overlying and biliary tract in the duodenum can result in the development of local (erosion, ulceration, gastritis, duodenitis) and common (pain, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, respiratory disorders, sepsis) complications. Casting through a common solvent vial Vater nipple Virsungov duct may cause pancreatitis. There are also cases of general toxic effects due to the solvent resorption mucous membranes of the biliary tract and intestine, with the subsequent development of hepato-renal failure. Long-term, multi-day, with prolonged exposure of the solvent administration exacerbates the likelihood of developing these complications.
Treatment for the prototype method involves considerable solvent consumption (1210-3075 ml) that yavlyaetsyav uneconomical.
The prototype method does not provide continuous visual control of the progress of dissolution. This eliminates the possibility of early diagnosis of complications arising during medical manipulations, in particular insolvency or perforation of the gallbladder wall, bile leakage of solvent or by drainage into the peritoneal cavity, and so on.
In the course of treatment by the method of prototype there is a need for multiple (4) X-ray examinations, leading to undue radiological burden on patients, medical staff, but also to organizational and ekonomichesikm costs. Hospital stay, according to the prototype method, lasts 30-40 days, which is economically disadvantageous.
In the application of the prototype method to dissolution, typically undergo purely cholesterol concrements specific ratio which is 37-50% of mixed composition concrements changeably dissolved or incompletely concrements pigment hardly soluble. Since currently there is no clear methodology developed pre- and intraoperative differentiation of gallbladder stones, according to the method holelitolizis prototype will be made at random.
The aim of the invention is to reduce the duration of the treatment of patients with acute destructive calculous cholecystitis, having a high risk surgery, but also improving the efficiency of dissolving concrements mixed type and enabling dissolving concrements pigment type, reducing the time necessary for dissolving concrements, duration solvent effect on the biliary tract and body as a whole, reducing the amount of solvent used to treat intra-operative visual control of the progress of dissolution, and reducing the number of medical X-ray study and manipulation, warning intra- and postoperative complications and reducing mortality in this group of patients.
This goal is achieved by simultaneous dissolution of intraoperative laparoscopic gallbladder stones in the acute stage of disease. Potentiation process of dissolution in the presence of gallbladder stones mixed or pigment type, carried out by their preliminary scoring and dehydration among 70%-tion of ethyl alcohol, but also by the simultaneous use of a solvent capable of conducting ultrasonic vibrations and diffuse under their influence to gallstones and an ultrasound frequency of an average of 27 kHz is directed into the cavity of the gallbladder through the hub of ultrasonic vibrations, the working end of which has an amplitude of the longitudinal vibrations of not less than 30 and not more than 100 microns, acting simultaneously on all concretions located in the cavity of the gallbladder, with conducting medium for ultrasound serves as the solvent.
Reducing the duration of treatment is ensured by accelerating the dissolution of stones and remove them, and in the acute stage of the disease and thereby eliminate the waiting stage regression of the inflammatory process in the biliary tract.
Combined use of solvent and ultrasound in this way and in this mode for simultaneous intraoperative holelitolizisa at acute destructive calculous cholecystitis in acute stage zaboloevaniya not found. not found potentiation dissolving pigment stones and mixed type by first scoring them in ethanol.
the proposed method of treatment is carried out in patients with acute destructive calculous occlusal cholecystitis who have a high risk of surgical intervention and having gallbladder rentgennegativnye concretions classified as concretions mixed or pigment type, and in cases where the concretions type to identify failed or calculi can not be dissolved routine methods.
Posredstvovm laparockopicheskogo study verified the diagnosis of acute destructive cholecystitis and defined indications and contraindications for transparietalnoy chrezpechenochnoy puncture of the gallbladder and the imposition mikroholetsistostomy, with the possibility of simultaneous production of laparoscopic holelitolizisa.
Contraindications to holelitolizisu a gangrenous lesion gallbladder wall, lack of blending transparietalnoy chrezpechenochnoy mikroholetsistostomy.
The gall bladder is punctured in the seam area of his liver chrezpechenochno, needle with pre-assembly in its plastic tube. The needle is injected closer to the bottom, the direction of injection focusing mainly on dlinniku gallbladder. For pnuktirovaniya using a needle having an outer diameter of not more than 2.5 mm, the inner - not less than 1 mm, length - not less than 200 mm.
After extraction of the liquid contents of his bladder cavity cautiously washed with a solution of antiseptic and novocaine (to anesthesia), while avoiding the creation of excessive negative pressure, to avoid potential unblocking of the cystic duct.
With the help of X-ray contrast studies verified the diagnosis of obstructive calculous cholecystitis and determine the indications and contraindications for simultaneous holelitolizisa.
Plastic tube rotational movement carried out by the needle into the cavity of the gallbladder. The outer diameter of the tube should be not more than 2.8 mm, inner - not less than 2.5 mm, the material - plastic, preferably Teflon. The working end of the tube must not rest against the wall of the bladder, and the lateral hole should be approximately in the center of the bubble in its transverse diameter.
The needle is removed, the contents of the gall bladder was aspirated and the gallbladder through a tube filled with 70% ethanol. The lumen of the bladder is introduced through the tube concentrate ultrasonic waves (hereinafter - the waveguide) so that the working end is at the level of the lateral pipe opening.
Produce stones scoring for 1 min, and slowly rotate the tube around the waveguide. Scoring produce low-frequency ultrasound, the average frequency of 27 kHz, guided into the cavity of the gallbladder using a waveguide, which has a working end of the amplitude of the longitudinal oscillations of not less than 30 and not more than 100 microns. The length of the working part of the waveguide about 110 mm, diameter - no more than 2.2 mm. Alcohol aspirated and gallbladder filled hydrophobic solvent such as t-butyl methyl ether, and re-voiced content bladder.
Dissolution is accompanied by a continuous visual inspection of the external condition of the surface of the gallbladder and liver, and general condition of the patient. In the event of any complications (a reaction to the solvent, perforation of the gallbladder wall, pain, respiratory disorders and so on.) Procedure immediately stopped and the transition to the final phase of the operation, as described below.
Every 3-4 minutes with a syringe replace spent solvent. This removes stones lysis products, including grains, passable through drainage. After 10 minutes, the procedure is completed holelitolizisa removed through a waveguide tube and a cavity in the bladder lumen injected plastic such as polyethylene, drainage diameter not exceeding 2.5 mm and the perforation with a bend at the tip end, wherein the pre-bend is straightened by an elastic conductor. Once all the working end is curved drainage cavity in the bladder, the conductor, and then the outer tube was removed. The cavity bubble washed sanitizing solution. Fix the drainage to the skin. Laparoscopy is completed, leaving holes in laparotsenteznogo elastic segment, for example a silicone, a tube for subsequent, if appropriate, be, dynamic control laparoscopy.
The positive effect of the application of the method in the analysis of physical and chemical processes occurring in the system: the gallbladder, bile-filled and calculi, bile-soaked + low frequency ultrasound cavitation mode + 70% ethyl alcohol + hydrophobic solvent is achieved primarily by the combined impact of on ultrasound concrements dehydrating agent (ethanol) and a solvent.
It occurs when this synergistic effect is due to the following factors:
- immersion ultrasonic waveguide in a liquid medium capable of conducting ultrasonic vibrations on a solid object, which is in this environment, the following physical factors affect: Ultrasonic wind, radiation pressure of ultrasound, ultrasound cavitation.
In addition, there is a phenomenon of the ultrasonic capillary effect, which consists in the active introduction of fluid under the influence of ultrasound in the capillaries present in the solid is placed in this environment. As numerous studies have shown that gallstones have pronounced porosity, it is relevant to substantiate the positive effect of the proposed method.
The process of dissolving the stones for the proposed method is accompanied by the phenomenon of chemisorption and hemokataliza. If the conductive medium is a substance reactive with respect to the solid body located therein, the chemical processes that take place between them, largely activated.
The joint action of this phenomenon with all the above there is a synergistic effect - chemisorption takes place not only on the outer surface of the stone, but also throughout its numerous capillary surface. Since cholesterol is a substance gallstone cementing (if mixed stone and the type of the pigment), it splits into fragments sequentially destructively when dissolved concrement. Ultrasonic wind, radiation pressure of ultrasound and ultrasonic cavitation promote active mixing of the solution, the better penetration of the solvent into the capillaries of gallstones and active "money" and the destruction of the surface layer. These factors contribute to the rapid physical fragmenting stones having voids in the center, and degradation and conversion products in suspension capable of output through the drain tube.
In a preliminary scoring concrements in 70% ethanol dehydration sposobstvvuyut factors listed concrements both the outer surface and along the capillaries. This enhances their solubility as tert-butyl methyl ether, as well as many other most effective solvents, insoluble in water and therefore poorly wets gallstones. This is especially true with regard to mixed and pigment gallstones, having increased porosity, but poorly soluble in all modern hydrophobic solvents.
As previously never been proposed a method of treating patients with acute calculous cholecystitis in the acute phase of the disease, part of which would potentiation dissolving concrements sonicated, using a solvent as a medium conducting ultrasound, a and potentiation dissolving concrements mixed and the pigment composition by their prior sound in environment, ethanol, then were selected for a comparative analysis of the essential features separate ways-analogues and the prototype method of the invention.
The essential features methods analogues which coincide with essential features of the invention but do not coincide with essential features of the method-prototype:
- an integral part of the treatment is the effect on the calculi located in the cavity of the gall bladder, ultrasound or other form of energy;
- method of treatment is effective against all kinds of stones;
- energonosyaschego the working end of the device inserted into the cavity of the gallbladder through mikroholetsistostomu.
Essential features of the method-prototype match the essential features of the invention:
- Treatment, including the removal of stones by dissolving them, made to patients suffering from acute destructive calculous cholecystitis and have a high risk of surgical intervention;
- treatment superimposed drainage mikroholetsistostomichesky having a diameter less than 10 mm;
- concrements are removed by dissolving them a substance capable of dissolving gallstones by direct contact with them;
- concretions are not subject to destruction;
- Solvent exposed simultaneously all concretions, located in the cavity of the gallbladder, including obturiruschie cystic duct;
- Products lysis stones in the form of a solution or suspension is removed by laundering through mikroholetsistostomu gallbladder.
The essential features of the invention, the essential features different from analog methods:
- treatment by the proposed method is performed in the acute phase of the disease, during the initial laparoscopy, immediately prosle decompressive puncture of the gallbladder;
- concrements removed through the plastic tube, the diameter of which does not exceed 2.8 mm and the diameter of the puncture hole in the liver and gall bladder;
- Effects of ultrasonic vibrations, sufficient to treat at the same time exposed to all the concretions located in the cavity of the gallbladder;
- concretions rastvoryayutcya, not destroyed;
- gall bladder into the cavity optical device is not inserted, since the process of ultrasonic impact on the contents of the gallbladder via the present invention does not require visual inspection intrapuzyrnom;
- power ultrasound energy effects emanating from the working end of the waveguide (while wearing protective tube) is insufficient to neposredstvvennogo breaking stones, as the waveguide is not in contact with the calculi. This is possible, and damage to liver and gallbladder ultrasound;
- all concretions located in the cavity of the gall puzyary are removed at the same time during the initial laparoscopy;
- concretions in the form of a solution or suspension is removed from the gallbladder through the laundering of its cavity through mikroholetsistoctomu. Mechanical tools for removing stones or their fragments are not applicable;
- significantly reduced the likelihood of complications such as bleeding on the ground breaking of the liver parenchyma and bile leakage, and since the gallbladder puncture needle is carried out, having a diameter of not more than 2.5 mm, and on it, as through a wire in the gallbladder lumen plastic tube inserted whose diameter does not exceed 2.8 mm, the clearance is not wound in the channel between the tube and the tissue of the liver and gallbladder.
The essential features of the invention, the essential features different from the prototype method:
- treatment by the proposed method is performed in the acute phase of the disease, during the initial laparoscopy, srauzu after decompressive puncture of the gallbladder;
- dissolving concrements full duration of about 10 minutes;
- the solvent is in the cavity of the gallbladder no more than 15 minutes;
- dissolution is effective in all types of konkremetov, especially those who, according to the prototype method, considered insoluble or poorly soluble (mixed and pigment gallstones);
- if in the gallbladder there are calculi or pigment mixed type, made of pre-scoring (to dehydration) in ethanol.
Thus, on the basis of a comparative analysis, we can conclude that the proposed method for the treatment of acute destructive calculous cholecystitis in patients with a high risk surgery, meets the criterion of "substantial differences", as first suggested in clinical practice aprobirvoannaya experiment a new method of operation - a one-time intraoperative laparoscopic dissolution and removal of the gall bladder stones in the acute stage of the disease through mikroholetsistostomu diameter less than 2.8 mm, for a period not exceeding 10 minutes. and never-before-used method of pre-scoring stones, with the aim of dehydration and increase their solubility in ethanol. The novelty has, in addition, the original method of using drainage to protect the liver and gall bladder from the effects of ultrasonic vibrations. Drainage is both energy directions of oscillation in the right direction.
In general, the developed method can significantly as compared to the comparative method and the prototype, to reduce intra- and post-operative trauma, reduce the number of complications, accelerate the process removing stones and reduce the time of hospitalization and mortality of patients.
A series of experiments on the dissolution of gallstones in vitro was carried out using solvents and low frequency ultrasound. Experiments were performed in vitro using gallstones taken immediately after surgery in patients with cholelithiasis in the acute phase of the disease. dissolution method was compared with the same techniques used in similar experiments in vitro.
Used for the experiments: an ultrasonic surgical device Urschi-7H-18, the hub of ultrasonic vibrations (hereinafter - waveguide) having specified parameters beaker 50 ml.
As solvents were used: ethyl Pribram (85% diethyl ether and 15% ethanol) and tert-butyl methyl ether, the most highly-established in preliminary experiments.
It has been tested and other solvents that are used in modern medicine - oktaglin, chloroform, miskleron. Because these drugs was the most effective chloroform, but the high pathogenicity does not allow its use. The remaining two drugs dissolved or not one of the various types of gallstones in a few weeks (in a series of experiments with no ultrasound). The use of ultrasound for the potentiation of the dissolution of gallstones in these substances was considered hopeless because of the high viscosity of the latter and, consequently, poor conduction of the ultrasound.
In operation concrements cholesterol were classified as (1) metalloholesterinovye (mixed type) (2) and a pigment (3). For this known technique used. A total of two series of in vitro experiments, each in two variants. Series of control experiments were those that were used cholesterol calculi (in the tables marked with number 1, and a series of experiments (versions 1a, 2a) in which the pre-scoring of concrements in ethanol medium was carried out.
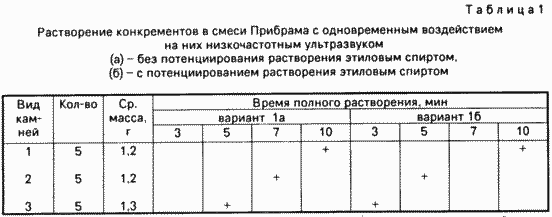
Appliances 1st series of experiments are as follows
Variant 1a, 5 experiments. Svezheizvlechennye gallstones immersed in 15 ml of Pribram. Then the beaker was immersed working end of the waveguide with a plastic tube previously so that the distance between the stone and the end of the tube is not less than 3 mm. We produce stones in scoring for 10 minutes. After the experiment the solution was evaporated and the residue was subjected to spectral analysis.
Variant 1b, 5 experiments. Svezheizvlechennye gallstones previously voiced for 1 min as described above using as the medium the conductive ulrazvuk - 70% ethanol. Then stones, as in the embodiment 1a exposed to ultrasound in the medium Pribram mixture.
Option 2a, 5 experiments. Svezheizvlechennye gallstones were immersed in 15 ml of tert-butyl methyl ether. The rest of experiment was conducted in the same manner as in the embodiment 1a.
Option 2b, 5 experiments. The experiment was performed in the same manner as in the embodiment 1b, but was used as the solvent tert.-butyl methyl ether.
Throughout the experiment observed the following
Variant 1a. During the first minute of the solvent quickly painted in brown. Within 10 min stones dissolved completely (30%) or disintegrate into smaller pieces (70%). Noted the following patterns:
- slowly dissolve cholesterol stones (average for 10 min) practically does not decompose into fragments;
- stones mixed type break into fragments during the first 3-5 minutes;
- pigment stones dissolved worse other, but almost immediately disintegrated to a suspension of sand (about 30% in the first minute and approximately 70% in the next 3 min);
- stones degradation product was zamazkoobraznuyu mass alone quickly precipitated. Pure cholesterol stones almost completely into solution.
Option 1b. The course of the experiment is almost no different from the version 1a, but noted the acceleration of dissolution of mixed and pigment stones (see. Table 1).
Varinat 2a. Progress in this series of experiments differed from the embodiment 1a acceleration dissolving concrements all kinds.
Option 2 b. In this series of experiments acceleration dissolving concrements noted mixed type, compared with the case 2a, an average of 2 minutes (see. Table 2).
The spectral data: 68% of the stones were mixed, 18% - cholesterol and 14% - pigment.
Efficacy accounted for dissolving concrements dissolution rate (% of original size) until a suspension with particles less than 1 mm.
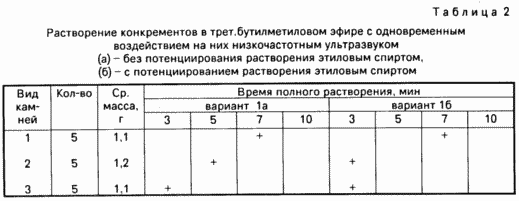
APPLIANCES next series of experiments are as follows
Variant 1a, 5 experiments. Svezheizvlechennye concrements dipped in 50 ml Pribram mixture and incubated for up to complete dissolution, solvent while the temperature was maintained at 37 ° C.
Variant 1b, 5 experiments. The experiment was performed in the same manner as in the embodiment 1a, but pre concrements voiced by the above procedure in 70% ethanol for 1 min.
Option 2a, 5 experiments. Svezheizvlechennye concrements dipped in 50 ml t-butyl ether and kept therein until complete dissolution, the solvent and the temperature maintained at 37 ° C.
Option 2b, 5 experiments. Just like the embodiment 2a, but preliminary voiced concrements in 70% ethanol for 1 min.
Throughout the experiment observed the following
Variant 1a. Within 10 minutes, it does not dissolve any stone. During the first three days of a 10% pure cholesterol stones, within the next three days 15% cholesterol stones remaining dissolved in 2-3 weeks. The solution is completely for the duration of 12% of stones mixed type, the others are more loose. Pigment stones are not dissolved.
Option 1b. Within 10 minutes, it does not dissolve any stone. During the first three days, a solution of 20% pure cholesterol stones type and 10% of the mixed type, for the next three days and still 17 to 30% of stones respectively. The rest of the cholesterol stones dissolve within 2-3 weeks, stones mixed type and become more loose and spontaneous fragmented. Pigment stones are not dissolved.
Option 2a. Within 10 minutes, it does not dissolve any stone. During the first three days in the t-butyl ester A solution of 15% pure cholesterol stones and mixed type and for the next three days an additional 25 and 20%, respectively. Completely dissolve the stones within 7-10 days, during this time partially fragmented pigment stones (13%) or dissolved, the resulting suspension (20%).
Option 2b. Within 10 minutes, it does not dissolve any stone. During the first three days of dissolved cholesterol stones 40% and 70% of the mixed type and, besides, 15% pigment stones.
Spectral data (all versions): 78% of the stones were mixed, 12% - cholesterol and a 10% - pigment.
Efficacy accounted for dissolving concrements dissolution rate (% of original size) until a suspension with particles less than 1 mm.
CONCLUSIONS
A mixture of t-butyl ester of Pribram and able to dissolve gallstones. The most efficient solvent is t-butyl ether.
Exposure to low frequency ultrasound gallstones using a solvent as a medium, conducting ultrasonic vibration potentiates their dissolution.
This method potentiates the dissolution of all kinds of stones.
A preliminary scoring of stones mixed and pigment type in low-frequency ultrasound alcohol potentiates the dissolution of stones mixed type, and contributes to the dissolution of stones pigment type.
complete dissolution time is accelerated tenfold.
Degradation products of stones to remove the oil through the drain tube inner diameter of 2.5 mm.
The next series of experiments was conducted in chronic experiments on animals.
The aim of the experiments was - proof safety process, and the effectiveness of the method and dissolving and removing concrements inventive method.
Used for the experiments: a mixture of Pribram, t-butyl ether, concretions removed in patients with acute calculous cholecystitis, the unit Urschi-7H-18 waveguides with the specified parameters, generates a low-frequency ultrasound in a specified mode. Total operated on 21 mongrel dogs of both sexes.
Stones have been previously investigated and divided into above three groups (NN: 1,2,3). For three days before the experiment concretions soaked in sterile human bile. Series of control experiments were those that were used cholesterol calculi (in the tables marked with number 1, and a series of experiments (option (a)) in which the pre-scoring of concrements in ethanol medium was carried out.
Technology experiments was as follows. One day before the experiment, the dog was caused acute destructive cholecystitis by introducing into the gallbladder 0.1% solution of silver nitrate using transparietalnoy transhepatic puncture with a fine needle.
Produces verhnesredinnaya laparotomy, purse string suture was applied to the bottom of the gallbladder. In its cavity through a small incision placed 3 biliary stone of the same type, one of which is invested in the cystic duct. In the cavity of the gall bladder was introduced a thin-walled plastic tube, tightened purse string suture. The gall bladder is filled with solvent.
After that, the gall bladder through the tube lumen introduced the working end of the waveguide and concretions sounded for 10 minutes. This condition was evaluated macroscopically the outer surface of the gallbladder and liver.
Tool thereupon removed and through the same tube syringe aspirated liquid contents of the gallbladder. Filmed purse string suture. After visual inspection of the dissolution of stones and the lack of them in the bubble chamber operation is completed. In case of undissolved large stones or their fragments (over 1.5 mm) scoring continued as described above for an additional 3 minutes. At the same time and visually assess the state of the gallbladder wall.
After the dissolution of the gall bladder was washed through a plastic tube of lysis products stones and solvent. In the cavity of the gall bladder was introduced a thin flexible plastic drainage and strengthen the purse-string suture. The other end of the drainage withdrawn through the abdominal wall and here and reinforced seams. Superimposed layered seams on a wound.
All experiments were performed in two variants:
Variant and (10 experiments).
The stones were extracted from bile and immediately placed in the dog's gall bladder, which are dissolved. The solvent mixture used Pribram (5 experiments) and t-butyl ester (5 experiments).
Variant B (11 experiments). The stones were placed in a cavity of the dog gall bladder, whereupon the latter was filled with 70% ethanol and stones sonicated for 1 min manner described. Then stones are dissolved as in embodiment a. The solvent mixture used Pribram (5 experiments) and t-butyl ester (6 experiments).
Total proposed method performed 21 experiments.
The spectral data: 73% of the stones were mixed 16% - cholesterol and a 12% - pigment.
During the experiments, the following was observed. The solvent was quickly painted in brown color, while rising through the tube. disorders animal general condition was observed. At the end of the experiment using a mixture Pribram mucosa macroscopically gallbladder was brown in color, sometimes with hemorrhages. When using t-butyl ether hemorrhages were observed. Visually detectable damage to the mucous layer, extending below the submucosa, were observed in both sets of experiments in the application of both solvents. stones degradation products were removed through the drain tube.
The results are shown in Table 3.
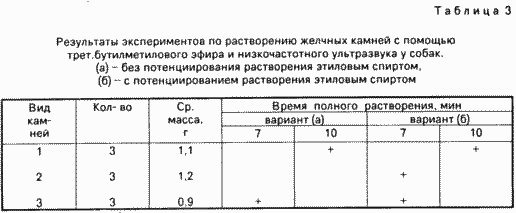
Survived 20 dogs. One dog died early in the experiment due to anesthesia overdose.
A study of the microcirculation of the gallbladder. Study drug serous and mucous layers of the gallbladder with acute destructive cholecystitis immediately before use of the method of treatment in experimental animals revealed that hemodynamic disturbances occurring in the gall bladder, leading to a significant transformation of the microvasculature. The contours of the large vessels (arterioles and venules) are deformed, sometimes atonic, overstretched accumulated in their blood, sometimes marked areas contraction (spasm) of the vascular walls.
Areas of local vasoconstriction of the lumen compared to other areas of the arteries is 25-40%. In the lumen of post-capillary venules and venules medium caliber marked glued conglomerates erythrocytes with uneven, somewhat "blurred" edges, separated by layers of plasma, which is typical for the "sludge-phenomenon".
Along with changes in vascular tone and permeability of their motility broken wall. Most of microvessels has high tortuosity and deformation of the wall contours. Comparison of the intensity and nature of the changes in the different layers of the gallbladder wall shows earlier and significant violations of the microcirculation in the mucosa and muscle layers.
Immediately after the experiment indicated strengthening diapedetic hemorrhage during the microvessels, the rest of the picture of the microcirculation of the gallbladder wall remained in its present form.
After 15 days of the experiment, the microcirculatory bed of the gallbladder wall was characterized by mild pronounced restructuring of microvessels. The contours of different vessels straightness strain. Sharp fluctuations in the course of the diameter of the resistive link microvasculature is detected, narrowing the lumen of blood vessels amounted to only 5-10% in comparison with the norm.
Stasis of blood in the post-capillary bed of the department was rare.
Histological examination of the gallbladder pieces of tissue taken from the experimental animals with acute destructive cholecystitis directly after application of the claimed method, observed: redness, mucosal edema, desquamation of epithelium, leukocyte infiltration.
Histological examination of the gallbladder pieces of tissue taken from the experimental animals with acute destructive cholecystitis 15 days after the application of the claimed method, observed: thick, leathery wall gallbladder containing cell round and leukocyte infiltration. In the interior of the bladder - the scar tissue. From the muscle - the phenomenon of atrophy. Mucous lost velvety.
On gross examination of the gallbladder in 15 days after the experiment indicated the following: a bubble in some cases, has been soldered to the internal organs, stones in it is not found, the cystic duct in 25% of cases had been obliterated. Visual pathology is not observed by the liver and the rest of the biliary tract.
Histological examination of liver tissue slices taken from the gallbladder bed in experimental animals with acute destructive cholecystitis directly at the bed of bubble observed the following: diskompleksatsiya hepatic lobules in violation of trabecular orientation hepatocyte swelling and proliferation of Kupffer cells. In the course of portal tracts - razvoloknenie swelling and fibrous structures, sometimes patchy, sometimes diffusely spreading, lymphohistiocytic infiltrates the mass of leukocyte cells. Blood vessels of portal tracts congested, stagnant, but most stagnant and expanded the central vein and the surrounding sinusoid. As part of the lobules in the central areas of marked portions hemorrhage PER diapedesin.
Histological examination of liver tissue slices, taken directly from the gallbladder bed in experimental animals 15 days after the application of the method, the same changes were observed as to its use. Macroscopically, the liver tissue was not altered.
Therefore, the method can effectively dissolve all types of stones in the gall bladder of a dog, without aggravating the destructive lesions of the gallbladder wall and general condition of the animal.
The next series of experiments was carried out with the gallbladder, removed from the operated patients of elderly and senile age.
The purpose of the experiments was to - to check efficiency of the method, but also the establishment of the degree of human gall bladder wall damage, suffering from said disease, while the combined exposure to t-butyl ether and low-frequency ultrasound.
Technology experiments was as follows. Immediately after removal of the gallbladder from bile washed with saline, maintaining it of stones. One calculus climbed on the subsequent chemical investigation for the purpose of classification. After that bubble stitched at the neck thread-taped and hung on a tripod. Before dissolution procedure gall bladder was filled with 70% ethanol and concrements on voiced procedure described for 1 minute, after which the alcohol was aspirated and proceeded to dissolution procedure, which bubble filled with solvent; the working end of the waveguide with a pre-assembly in a plastic tube was introduced into the cavity of the gall bladder so that the end of the tube is at a distance of 1-5 mm from the wall of the gallbladder and the lateral hole is at the working end of the waveguide.
Concrements sonicated for 10 min, and the tube was rotated slowly around the waveguide periodically touching, without pressure, the end of the tube to different places of the gallbladder wall.
After the dissolution of the contents of the bladder procedures aspirated and subjected to spectral analysis, to determine the chemical composition and type of stones.
Gallbladder subjected to histological examination prior to the experiment (the sample is taken from the neck of the gallbladder) and then, in the latter case separately in areas where focused and do not touch the end of the tube.
Total produced 11 experiments. During the experiments, the following was observed. The solvent was quickly painted in brown. Small stones under the influence of cavitation moved inside the cavity of the gall bladder. After 10 minutes, all dissolved concrements, some of them dissolved during the first 7 minutes (see. Table 4). Visually, the outer surface of the gall bladder remained throughout the experiment without change. concrements degradation products were zamazkoobraznuyu mass with interspersed small particles, mainly of mucus diameter less than 2 mm.
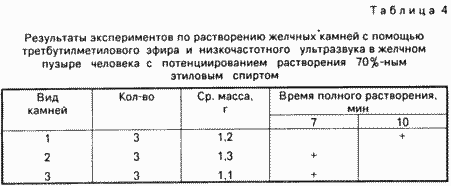
According to spectral analysis, 70% of the stones were mixed, 20% - pure cholesterol and a 10% pigment stones were.
The experimental results are reflected in Table 4 and in histological studies.
These histological studies. Histological examination of the gallbladder tissue slices taken immediately prior to use of the claimed method, observed the following: redness, mucosal edema, desquamation of epithelium, leukocyte infiltration.
Histological examination of the gallbladder tissue pieces taken immediately after application of the method, in addition to the above pattern, there were areas of mucous membrane degradation, sometimes penetrate the submucosal layer without departing from its scope, bleeding sites per diapedesin.
Therefore, the method can effectively dissolve all kinds of stones in the gallbladder itself, which has a destructive defeat of the walls. The proposed method of treatment is not significantly exacerbated existing destructive phenomena in the wall of the gall bladder, the effect of ultrasound on contact tube, which concluded works waveguide does not result in damage to the muscular and serous layers of the gallbladder.
One shot laparoscopic holetsistolitolizis using as solvent a mixture Pribram (85% diethyl ether 15% ethyl alcohol), preliminary dissolving concrements potentiation mixed type of low frequency sound by sonication in a specified mode in the environment of 70% ethanol was performed one patient, were treated at the clinic surgery N 1 Dagmedinstituta.
Disease history. Patient J., 70 years, history of disease N 482, was admitted to a clinic Surgical Diseases N 1 Dagmedinstituta 01.23.1991, complaining of a sharp pain in the right half of the abdomen, nausea, vomiting, pain in the heart, headaches. Sick for two days. These attacks were not previously noted, but bothered aching pain in the right upper quadrant in the last 8 years.
When a general serious condition. In the light diminished breath, against which dry rales are heard. Heart sounds muffled. Pulse is 120 beats / min, individual beats. BP 220/100 mm Hg Tongue dry, coated with white bloom. Bloating, increased in volume due to the large amount of subcutaneous fat, sharp pain in the right upper quadrant. There's also determined rigidity of muscles of the abdominal wall. Symptom Ortner sharply positive. The body temperature of 39 ° C blood test: hemoglobin 150 g / l, leukocytes 17.5 ![]() 10 9 / L. Diastase urine Wohlgemuth 32 units, blood bilirubin 19.2 m / l. The diagnosis of acute cholecystitis, a local diffuse peritonitis, ischemic heart disease, atherosclerotic koronarokardioskleroz, hypertension.
10 9 / L. Diastase urine Wohlgemuth 32 units, blood bilirubin 19.2 m / l. The diagnosis of acute cholecystitis, a local diffuse peritonitis, ischemic heart disease, atherosclerotic koronarokardioskleroz, hypertension.
Produced emergency laparoscopy. An increase in intense and bluish-purple color of the gallbladder with the imposition of fibrin and multiple hemorrhages on the serous membrane. In subhepatic space and in the right lateral channel has a small amount of turbid effusion. On the upper and lower surfaces of the right lobe of the liver, loose spikes and fibrinous deposits. The duodenum, hepatoduodenal ligament and adjacent the gland swollen and bloodshot, vascular pattern in this area is strengthened. Produced transparietalnaya transhepatic gallbladder puncture with a needle put on her tube-conductor Teflon. It evacuated about 150 ml of purulent-hemorrhagic fluid, and then washing the produced gallbladder novocaine solution to a clear liquid. On the outer surface of the needle through the liver tissue in bladder cavity conducted Teflon tube. Produced straight cholecystography 10% solution Diodon - to define rentgenmonitore 2 rengtennegativnyh calculus sizes 3x2 and 2x2 cm, choledoch not contrasted by occlusion of the cystic duct in the neck of the gallbladder. Via teflon tube inserted into the cavity of the gallbladder, poured into 70% ethanol (150 ml), the contents of the gallbladder sounded for 1 min, aspirated and replaced with alcohol 150 ml Pribram mixture (85% diethyl ether 15% ethyl alcohol) and concrements in the gallbladder are repeatedly treated with ultrasound for 10 min. After the first 5 minutes, the solvent was replaced procedure - with a liquid aspirated (brown comprising cholesterol with a small amount of blood clots) noted the presence of an insoluble brown slurry particles with sizes forming a slurry is not more than 1 mm on average. The same was found in the aspirated fluid on completion of the procedure. Based on the presence in the suspension as insoluble fragments concrements concluded that the patient in the gallbladder were mixed concrements or pigment type.
Throughout the dissolution procedure was carried out by visual inspection of the surface of the laparoscope gall bladder and liver, but also clinical monitoring of the patient - no abnormalities were found. Upon completion of the procedure of dissolution of the gall bladder washed out with a solution and re-furatsillina contrast - on rentgenmonitore concretions are not revealed. Superimposed transparietalnaya transhepatic mikroholetsistoctoma through a drainage tube through the lumen, after which the tube-conductor removed.
Drain pipe is fixed to the skin of a silk suture. The laparoscope is removed from the abdomen and trocar sleeve inserted in a space obstructive drainage tube with an outer diameter of 7 mm. By the second day of pain and muscle tension anterior abdominal wall disappeared, body temperature returned to normal. White blood cells in the blood 9.2 ![]() × 10 9 / L ESR 39 mm / h. General clinical and biochemical assays in the normal range. Pain in the heart, and were stopped, blood pressure 150/80 mm Hg, the patient's condition gradually returned to normal. By drainage of the abdominal cavity during the first day was allocated about 20 ml of turbid fluid. According mikroholetsistostomicheskomu drainage in two days was allocated 60 ml of serous fluid with flakes, a small amount of blood clots and brown with sediment, sediment particle size is less than 1 mm, when biochemical analysis revealed the identity of the composition of pigment gallstones. Produced lavage solution furatsillina gallbladder. On the third day the catheter was the bile flow, beginning with flakes, and then the normal color. On the seventh day cholecystocholangiography accomplished by introducing tubing through mikroholetsistostomicheskuyu 10% solution Diodon 20 ml. On radiographs choledoch diameter of 11 mm, a contrast solution discharge into the duodenum satisfactory. On the 19th day mikroholetsistostomicheskaya tube gall bladder removed. The patient was discharged from the hospital in satisfactory condition at the 23rd day after the operation.
× 10 9 / L ESR 39 mm / h. General clinical and biochemical assays in the normal range. Pain in the heart, and were stopped, blood pressure 150/80 mm Hg, the patient's condition gradually returned to normal. By drainage of the abdominal cavity during the first day was allocated about 20 ml of turbid fluid. According mikroholetsistostomicheskomu drainage in two days was allocated 60 ml of serous fluid with flakes, a small amount of blood clots and brown with sediment, sediment particle size is less than 1 mm, when biochemical analysis revealed the identity of the composition of pigment gallstones. Produced lavage solution furatsillina gallbladder. On the third day the catheter was the bile flow, beginning with flakes, and then the normal color. On the seventh day cholecystocholangiography accomplished by introducing tubing through mikroholetsistostomicheskuyu 10% solution Diodon 20 ml. On radiographs choledoch diameter of 11 mm, a contrast solution discharge into the duodenum satisfactory. On the 19th day mikroholetsistostomicheskaya tube gall bladder removed. The patient was discharged from the hospital in satisfactory condition at the 23rd day after the operation.
Comparative analysis of laparoscopy results in this way has shown significant advantages of the method over the prototype and analogues, namely, the method provides a momentary intra holetsistolitolitolizis stones mixed and pigment type in the treatment of destructive forms of acute calculous occlusal cholecystitis in patients with middle and old age, have a high risk surgery.
Complications were not in any of the cases, both during the operation and after it. The method reduced the length of stay of patients in hospital.
Technical and economic advantages of the process.
Dissolution and removal of stones gallbladder in acute stage of calculous cholecystitis can significantly shorten the treatment of patients and their stay in the hospital. The method allows to combine the process of removing stones from the act of imposing mikroholetsistostomy and thereby drain the biliary system, which reduces the time of treatment.
The method allows you to remove all types of stones for the period, substantially lower than the corresponding period in the methods of analogue and prototype method. This can significantly reduce the risk of intra- and postoperative complications, both local and general. Ability to delete all kinds of stones allows you to minimize the risk of disease recurrence.
CLAIM
METHOD OF TREATING ACUTE DESTRUCTIVE Calculous occlusive CHOLECYSTITIS comprising overlay mikroholetsistomy dissolving concrements and solvent, wherein the stones mixed in the presence and type of pigment in the cavity of the gallbladder through a tube with an external diameter of not more than 2.8 mm is introduced 70% ethyl alcohol treated with the contents of the bladder ultrasound frequency of 27 kHz, the oscillation amplitude of 30 - 100 microns for 1 min, aspirated alcohol fill the gallbladder hydrophobic solvent, repeatedly voiced by the contents of the bladder, remove the product and replaced with lysis kongrementov mikroholetsistostomicheskim tube drainage.
print version
Publication date 28.01.2007gg





Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.