| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2273625
![]()
METHOD FOR PROCESSING solid waste
Name of the inventor: Reshetnyak Aleksandr Filippovich (RU); Leonid Sokolov (RU); Tikhonov Igor Ivanovich (RU)
The name of the patentee: Reshetnyak Aleksandr Filippovich (RU); Leonid Sokolov (RU); Tikhonov Igor Ivanovich (RU)
Address for correspondence: 398005, Lipetsk, st. Krupskaya, 10a, ZAO "Soyuzteplostroy-Lipetsk"
Starting date of the patent: 2004.02.03
The invention relates to methods for the processing of municipal solid waste and can be used in municipal services and agriculture for the processing of poultry manure and manure. The method comprises immersion of municipal solid waste in a pool of milk of lime in which the alkaline medium is maintained at pH 8.5 ÷ 8.65 and temperature 20 ÷ 70 ° C. After 5 ÷ 8:00 waste is removed from the pool, give obtech liquid and sort the components. Part of the solution with the precipitate is constantly output for processing by known methods, and the organic portion of municipal solid waste compost. The invention reduces the capital and operating costs of waste management in achieving environmentally sound technologies.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to methods for the processing of municipal solid waste (MSW) and can be used in municipal and agriculture.
Environmental protection - a multifactorial problem of cities. Each of the factors (transport, industrial plants, landfills, etc..) Is a significant source of environmental danger to the population. Thus, experts estimate emissions from transport by 70% of air pollution. Moreover, it should be noted that transport pollutes the air only environment.
However, it is impossible to estimate what the total damage on the total account for household waste landfills that pollute the air environment (from spontaneous combustion and intensive emission of harmful volatile substances, including dioxins and furans), underground reservoirs (against penetration of atmospheric precipitation pathogens Product decomposition and putrefaction of food waste) and the soil, contaminating and deadening her for many years. It is very significant, especially since the zone of its impact on the environment is continuously expanding due to the disposition and providing additional areas for more increasing amount of household waste, from waste transfer to other places birds and stray animals.
Consequently, the elimination of household waste landfill and a significant detrimental effect on the environment - the first and main task.
Some are known to date methods of disposal of waste professionals either do not solve the basic problem, or it requires huge resources and means. So, some of them in its manufacturing process capable of releasing secondary harmful and toxic substances, and are therefore not inactivated (composting, pyrolysis).
Others - highly energy-intensive (burning "slag melt" plasma combustion), which is why they are expensive, not only in capital cost, but also in operating costs, and therefore the businesses based on them, may not be without significant grants from the city budget.
In this regard, special mention should be fundamental "PIROKSEL" technology shortcomings (VNIIETO, Moscow), aggressively imposed by the authors for the incineration of municipal waste. This technology includes a two-stage thermal processing of household waste: pyrolysis and combustion in the slag bath.
The first phase - pyrolysis of household waste does not apply, because as it is carried out by oxygen deficiency (ie excess air ratio ![]() <1), then the chlorine and fluorine-containing components -. Rubber, plastic, polymers in which garbage total weight of about 6.5% is allocated very dangerous and toxic substances (dioxins, furans, phosgene, etc.), which act directly through a layer of fresh waste to the environment.
<1), then the chlorine and fluorine-containing components -. Rubber, plastic, polymers in which garbage total weight of about 6.5% is allocated very dangerous and toxic substances (dioxins, furans, phosgene, etc.), which act directly through a layer of fresh waste to the environment.
The second stage - in the waste incineration slag bath, although occurs at high temperature (2000-2100 ° C), however, after entering the pyrolysis waste before diving into the liquid slag on the liquid surface is thermally decomposed, releasing large amounts of harmful and poisonous substances that nowhere neutralized. In addition, energy expending this stage, since there is no point to melt all the remaining litter weight (93.5%) at high temperature, which does not contain chlorine and fluorine.
In general, the technology "PIROKSEL", borrowed from the metallurgical industry, the household waste is absolutely not acceptable.
In most countries (Germany, France, Denmark, Sweden, Japan, USA, England, etc.). The most rational, simple and common method recognized by incineration in furnace devices special boilers, which essentially involves the use of household waste as fuel. However, used in these countries processes waste incineration does not include non-waste, and therefore do not solve the main problem - the elimination of landfills.
Therefore, seeing now the desire of foreign companies to impose Russian cities their technology, design and build incinerators and other (eg briquetted waste and disposal of briquettes on the same dump or landfill) of the enterprise, it is a very negative phenomenon of the present time. The goal - to spread its influence in the Russian market, even with the help of their money. However, the experience we have. Unfortunately, it is very negative. Thus, in 1975-1985, the we (in Russia and Ukraine) have been designed and built 10 incinerators for borrowed abroad rather primitive and subsidy from the city budget technology. And they are in their cities have not solved the problem of the elimination of landfills. These were purchased overseas factories (in Czechoslovakia, Denmark and France). Currently, most of the waste incineration companies are only 50% capacity, and some of them even stopped due to lack of endowment funds and spare parts.
(On the technical solution of the problem of municipal solid waste disposal and liquidation of dumps in the city of Lipetsk. OOO «TEPenergo." V.R.Purim, N.N.Timakova. M., 1999).
The disadvantages of incineration technology should include the high capital costs of construction.
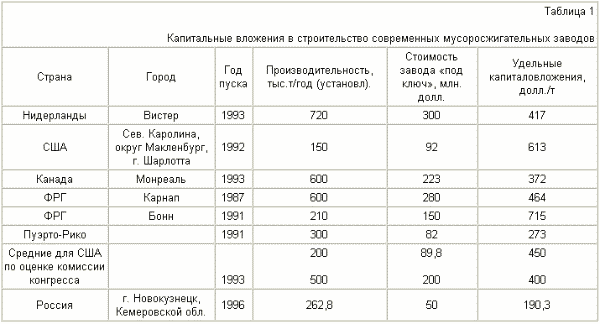
The closest to the proposed method the technical essence and achieved result in the destruction of dioxins and furans is a method for processing of municipal solid and fine industrial waste for which waste facility is carried out in the calcium-containing slag melt (RU 2208202 C2 patent, cl. 7 F 23 G 5 / 00, 5/32, 2001).
The disadvantages of this method are:
- The complexity of hardware design;
- High energy consumption;
- High specific investment costs (about 150 USD / ton annual capacity MSW).
The invention aims to reduce unit capital and operating costs for solid waste management in achieving environmentally sound technologies.
The goal is achieved by the fact that:
- TBT immersed in a pool of milk of lime in which the alkaline medium is maintained at pH 8,5-8,65 and temperature 20-70 ° C, 5-8 hours after MSW removed from the pool and allow fluid obtech sorted by component, part of the solution with the precipitate is constantly output for processing by known methods, and the organic component of MSW compost;
- As a chemical reagent is potassium, sodium and ammonium-containing compounds;
- MSW in the pool is purged of ozone.
The organic component (food waste) after treatment with chemicals and oxidation is an environmentally friendly fertilizer with a wide range of use.
In the development of MSW recycling technologies found in its composition they contain dangerous substances of Class - halogenated dioxins and dioxin-like substances (UP).
TO - it supertoxicants - especially harmful and dangerous synthetic chemistry products, by-products of a number of chemical plants and passing mikrovybrosy industry and human activities. TO - almost never mentioned to the 90s in the educational and scientific literature class of hazardous substances. Unlike simple dioxins halogens and dioxins (DOs) are chlorinated or brominated benzene rings connected by oxygen bridges. This so-called polychlorodibenzodioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans and accordingly polibromdibenzodioksiny and polibromdibenzofurany. To represent particular danger due to the fact that, despite its insolubility in pure water and pure air to perfectly dissolve in water comprising humic or fulvic acid from a humus soil owing to their high ability to form complexes with the components of humus. From the air, aerosols to form complex compounds and due to their high ability to adhere, they are well tolerated, not only on land but also in the air. In the soil to decompose for 20-30 years or more, in water to the decomposition lasts 2 years or more (L.A.Fedorov "Dioxins as environmental hazards: retrospective and prospects". M .: Nauka, 1993. , 267 pp.).
In the chemical industry a major source of income to the scope of data is the production of chlorine and bromine-containing drugs. There has been increased pollution due to the smooth transfer of many food chains, especially meat and dairy products of nature.
In recent years, a typical source of infection halogenated to the environment besides the production is low-temperature combustion of MSW. Special tests of a number of foreign experts have shown that to resistant to high temperatures. Moreover, at a temperature of 800 ° C is formed to bromine, but not their disruption.
The study of the conditions of formation and decomposition of dioxins and furans (F) incineration in a large number of works that result, it was found that dioxins and furans are badly decomposed up to a temperature of 750 ° C and is almost completely decomposed at a temperature of over 1000 ° C (Chemistry solid fuel, number 4, 1995, str.67-72). According to other sources for complete decomposition of dioxins and furans sufficient exposure at a temperature of 1000-1100 ° C for 3 seconds (J.Jap Soc Safety Eng, 1988, № 6, and r.336-343 ID:... Environ. et Techn., 1989, № 89, R.28, 30).
The formation of dioxins in the flue gas occurs most rapidly at their exposure at temperatures of about 300-400 ° C (Chemosphere, 1987, 16, № 8-9, r.1917-1922).
According to the JSC "Research Institute for the industrial and sanitary cleaning of gases" to the content and furans in the incineration zone can reach 6000 ng / m 3 (letter number 323/31 from 10.9.98).
The presence of ammonia in the flue gases, compounds of potassium, calcium and sodium dramatically reduces the rate of formation of dioxins (J.Air and Waste Monag. Assoc. 1991, 41, number 5, p.761-722).
Reducing the formation of dioxins intensity is due to binding of chlorine compounds CaCl 2, KCl, NaCl, NH 4 Cl.
When entering into the flue gas stream having a temperature of about 100 ° C, pulverized dust collecting apparatus CaO captured:
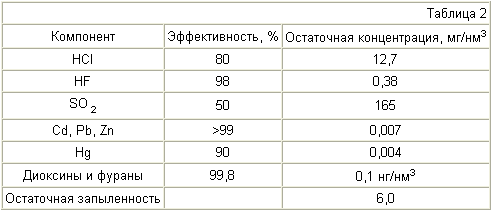
(JSC "Research Institute for the industrial and sanitary cleaning of gases from the letter number 321/31 of 09.10.1999)
Therefore, CaO destroys dioxins and furans, engaging with them in a chemical reaction, and the fullness of the chemical reaction - the question of temperature and time.
Empirically found that after 9-12 months after administration, uniform distribution in the MSW 3-5% CaO (KOH, NaOH, NH 4 OH or Ca (OH) 2), dioxins and furans are not found in MSW. Original content to and F is 80-100 ng / kg.
Specific capital costs of implementing the claimed method will be about 12-15 USD / t MSW.
Thus, the proposed method allows highly effective in capital expenditures in the 12-15 USD / ton annual capacity for MSW (versus 150-715 USD / t) process waste into recyclable materials and environmentally friendly fertilizer, with low temperature processing of solid waste prevents the formation of additional amounts of up to and F.
MSW in its composition except dioxins and furans contain other hazards, including:
- Pathogens (helminth contamination);
- Heavy metal compounds (Pb, Zn, Cd, Mn, Hg, Al, As, Si, Li, Ta, etc.);
- Heavy metal ions capable of forming highly volatile gaseous organometallic compound.
Mixing 30 kg of lime with 1 t of liquid manure is an effective means of disinfecting manure contamination with salmonella. Alkaline conditions increases disinfection efficiency of formaldehyde (Grin, V.N.Novikov. Industrial and household waste. Storage, disposal, recycling. M., 2002, Publisher GRAND trading house, p.83).
F concentration above 1.5 mg / L lead to increased risk of dental fluorosis, and even a large concentration causes skeletal fluorosis type osteosclerosis and joint stiffness (this disease, doctors put on a par with cancer).
Effectively defluorination of water calcium and magnesium oxides (Grin, V.N.Novikov. Industrial and household waste. Storage, disposal, recycling. M., 2002, the trading house GRAND Publisher, p.119, 120).
Alkalinization wastewater of pH 6.4 to pH 8.5 reduces the lead content of 486 mg / l to 0.14 mg / l, Manganese from 2700 to 900 mg / l (Grin, VN Novikov. Industrial and household waste. Storage, disposal, recycling. M., 2002, the trading house GRAND Publisher, p.121).
At high concentrations of metal ions are toxic, causing deformation and functional even fatal. Established synergies accumulation of heavy metals in the body due to their complex effects. In synergy effect of the action is magnified (eg, lead ion toxicity is compounded with a lack of calcium) (Grin, V.N.Novikov. Industrial and household waste. Storage, disposal, recycling. M., 2002, Publisher trading house GRAND , str.254).
MSW Processing lime milk (pH 8-12) allows the use of an organic component as a fertilizer.
Caught with the fertilizer into the soil heavy metals (even copper and zinc) practically do not get into the plant, and for chromium and cadmium were recorded only traces. This gives reason to believe that the lime contained in the fertilizer, prevent metal migration into plants (Grin, V.N.Novikov. Industrial and household waste. Storage, disposal processing. M., 2002, Publisher GRAND trading house, str.264).
The process of collecting, transporting and recycling of solid waste flow biological processes that do not provide sufficient clean drains. Therefore, often for purification of waste water using physical and chemical methods such as ozonation, which provides deep bleaching effluents and sufficiently complete removal of biochemical oxidation of organic matter (Grin, V.N.Novikov. Industrial and household waste. Storage, disposal, recycling . M., 2002, the trading house GRAND Publisher, p.172).
CLAIM
1. A method of disposing of municipal solid waste, characterized in that the solid waste is immersed in a pool of milk of lime in which the alkaline medium is maintained at pH 8,5-8,65 and temperature 20-70 ° C, after 8.5 h removed from the pool and allow fluid obtech sorted by components of the solution with the precipitate is constantly outputted by known methods for processing, and the organic portion of municipal solid waste compost.
2. A method according to claim 2, characterized in that the chemical reagent is used as the potassium, sodium and ammonium-containing compounds.
3. A method according to claim 1, characterized in that the solid waste basin purged with ozone.
print version
Publication date 12.12.2006gg





Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.