Chernobyl: Part 4. CAUSES OF THE ACCIDENT AT CHERNOBYL AEROSPACE.
Information on the Chernobyl accident and its consequences prepared for the IAEA Report No. 1 (INSAG-1)
C O R E R A N E E
Flash drive
0. Introduction
1. Description of the Chernobyl NPP with RBMK-1000 reactors.
2. Chronology of the development of the accident.
3. Analysis of the process of development of the accident on a mathematical model.
4. Causes of the accident.
5. Preventing the development of an accident and reducing its consequences.
6. Control over radioactive contamination of the environment and public health.
7. Recommendations for improving the safety of nuclear power.
4. CAUSES OF THE ACCIDENT AT CHERNOBYL NPP
As shown by the above analysis, the accident at the fourth block of the Chernobyl nuclear power plant belongs to the class of accidents associated with the introduction of excessive reactivity. The design of the reactor facility provided protection from this type of accident, taking into account the physical characteristics of the reactor, including a positive steam reactivity coefficient.
Among the technical means of protection are CPS for exceeding the power and reducing the period of acceleration, blocking and protection for faults or switching equipment and systems of the power unit, as well as ECCS.
In addition to technical means of protection, strict rules and procedures for maintaining the technological process at nuclear power plants, as determined by the operating schedule of the power unit, were also provided. Among the most important rules are the requirements on the inadmissibility of reducing the operational margin of reactivity below 30 rods.
During the preparation and testing of TGs in the run-out mode with the load of the unit's own needs, the personnel disconnected a number of technical means of protection and violated the most important provisions of the operating procedure in terms of process safety (Table 1).
Table 1.
The most dangerous violations of the operating regime, committed by personnel of the fourth block of the Chernobyl NPP.
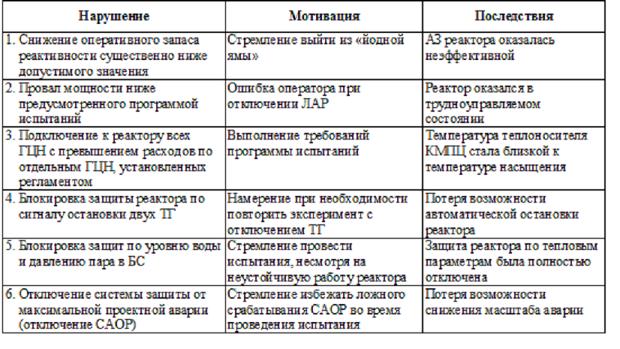
The main motivation for the staff's behavior was the desire to finish the tests faster. Violation of the established order in the preparation and conduct of tests, a violation of the test program itself, negligence in the management of the reactor facility indicate
Insufficient understanding by the personnel of the peculiarities of the technological processes in the nuclear reactor and the loss of a sense of danger.
The developers of the reactor installation did not provide for the creation of protective safety systems capable of preventing an accident if there was a set of deliberate outages of technical means of protection and violations of the operating procedure, since such a combination of events was considered impossible.
Thus, the primary cause of the accident was the extremely unlikely combination of violations of order and operating conditions, admitted by the personnel of the power unit.
Catastrophic size of the accident was acquired due to the fact that the reactor was brought by personnel into such an unregulated condition, in which the influence of the positive reactivity factor on the growth of power was significantly increased.


Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.