EMERALD


 Characteristics of the mineral.
Characteristics of the mineral.
Bright green variety of beryl. A dense green, completely transparent variety of beryl, which is rare and highly valued (it can cost more than a diamond). This stone is precious not only for its price, but also for its properties. One of the most expensive beryl is the emerald dense green, that is, beryl, dyed with chromium. It differs from ordinary green beryl in that green beryl is pale, its color is created by impurities of iron or vanadium rather than chromium. The hardness of beryl varies from 7.5 to 8, and the emerald is somewhat softer than the other varieties. Small inclusions do not in any way reduce the cost of the stone. On the contrary, the emerald of a bright deep green color, even with inclusions, is more valued than the purest emerald (beryl) of a pale green color. Synthetic emeralds of hydrothermal origin usually contain small liquid or gaseous inclusions. Natural emeralds often have inclusions of plates and microplates of mica and pyrite crystals (even a natural emerald clogged with mica is much more expensive than its ideal synthetic analog).

Prismatic crystals of green beryl (emerald) in mica rock. China.
Emerald is the most beautiful and favorite jewel of all times. Emeralds were known even in ancient Egypt and Babylon. For many centuries, deposits of emeralds were being developed in Colombia. Europeans learned about the wonderful stones of South America in the 16th century. In connection with the conquest of the Spanish conquistadors. Currently, about 180 emerald deposits are known in Colombia. Emeralds of Colombia give from 55% to 90% of world production. Significant in scale, the Brazilian deposits, which currently produce about a quarter of the world's emeralds. Emerald deposits in India have been known since ancient times, but they lost their former importance by the beginning of the 20th century. Emerald mining is also being carried out in Pakistan and other regions of the globe.
Dimensions of emerald crystals are different: crystals of jewelry quality are often small. The intensity of the color of emeralds is different. In the jewelry business emeralds are used from a weak green to a dense juicy emerald color. At the same degree of transparency, defectiveness (the presence of cracks and inclusions) and the size of the cost of a stone, the higher its intensity, the difference in the cost of stones of different shades of color is significant. The intensity of the color is related to the content of the chromium impurity. Emeralds of different deposits differ in different shades of green. So, Colombian emeralds are characterized by a bluish hue, for the Ural and North American - light yellowish or bluish. Perhaps some influence on the shades of green emerald may have an admixture of vanadium.
Often in the emeralds there is a zonal coloration. There are crystals with a slightly colored peripheral and intensely colored green central part and vice versa. Another type of zoning is a change in the intensity of the color along the long axis of the crystal, and several intermittent bands of different intensities are seen. Sometimes the crystals are not uniformly colored. The color of the emerald is stable and does not change under the influence of light and heat. However, when the crystal is heated to 700-800 ° C, the crystals become somewhat pale. All large crystals are usually turbid and opaque. They contain inclusions of small flakes of mica or spines of black tourmaline. At best, a sharp eye specialist can detect in them centimeter areas, suitable for cutting. Mica is an admixture that distinguishes emerald from other stones.
Vivacity and game gives the emerald its property of slightly changing the shade of color when turning the stone. You will look across the crystal - it is yellowish green, warm, fresh, you turn and look along the axis - there was a characteristic emerald blue. This property is natural to change the shade of color, depending on the optical orientation (pleochroism), all beryl have, but in pale-colored crystals it is almost imperceptible, and in emeralds it often manifests itself clearly.
For the processing of transparent emeralds, the following types of cut are used: stepped, rectangular emerald (quads), less often diamond. Stones translucent are processed in the form of cabochons. It should be noted that only a very small part of emeralds is processed in the countries where they are mined. In jewelry, expensive emeralds are often combined with colorless diamonds to accentuate an expensive dense green stone.
As imitations, green minerals are used, less expensive and more common - corundum, dioptase, chrome diopside, tourmaline, grossular, chrysolite, giddenite, jadeite, zircon, fluorite, chrysoprase. In Burma and the CIS there is a beautiful emerald-green color of chrome diopside, which we often get for an emerald. Dear uvarovite (large crystals), demantoid and Ural alexandrite can also be confused with an emerald, but at a price they are comparable. Emerald green uvarovite because of the very small size of crystals is extremely rare in faceted form.
There are cases of pseudo-refinement of fractured emeralds and beryls by impregnating them with oil and dyes. Such stones can be detected by immersing them in water containing a fat thinner (for example, household detergent or liquid for washing fattyware in cold water). It is also advisable to slightly warm the stone, removing oil from the cracks, but at home it is extremely undesirable (it is safer to rinse the suspicious stone in household solution).
Magic properties of stones.
Emerald is a stone of heaven and heavenly guidance, it gives advice precise and unequivocal, urging people to become better, purer and with a greater desire to accept the activities of everlasting institutions that are characteristic of all traditional cultures and peoples. You can call the emerald without any reservations a talisman of full luck, happiness and prosperity. Traditionally, it is believed that it protects the owner from all conceivable and unthinkable sorrows and misfortunes, to strive to correct even the mistakes committed by man in the distant past. Emerald protects its owner from dull life, addictions, evil spells, gives victory over negative influences, chastity. It is better if the stone is inherited, but it can also be given. The emerald makes the Guardian Angel unrelenting, since this stone is an accessory to the angelic world and, as it is often said about it, brought to earth, but not born of it. In the composition of the stone there is an element of beryllium: this aspect makes the emerald a heavenly stone and connects it with the whole universe. It can be a talisman of those people who dedicated their lives to the secrets of the universe, who purposefully walk this road and find heavenly revelations in spiritual perfection, higher sciences and the arts.
Emerald is a mascot of mothers and seafarers. He gives joy and joy, spiritual harmony and hope, victory in battle, tact and generosity, talent and grace, eloquence without a shadow of falsehood and self-esteem, insight, foresight ability. Emerald keeps love, it becomes brighter when love flares up in the heart, and it breaks when a vow of loyalty and love is violated. It strengthens memory and restrains harmful passions. He was hung up at the head of the bed to drive away bad dreams, to dispel anguish. However, an emerald helps only a clean, spiritually perfect person. He brings misfortune to the lying and evil. To the emerald fully manifested itself, the location of the moon in the horoscope of its owner should be favorable. In India, it is believed that he has a connection with the world of spirits, allows you to read the past and the future in the mysterious depths of his green facets. Emerald helps to promote health and longevity, because Has the ability to neutralize the negative "qi".









Synthetic emeralds
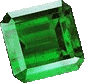 SYNTHETICAL EMERALD.
In recent decades, in addition to a large number of hydrothermal rubies and sapphires, most synthetic emeralds have also been produced by the hydrothermal method. Such emeralds are characterized by tubular inclusions, brownish inclusions of iron oxides. In ordinary jewelry stores, it is possible to distinguish natural emeralds from synthetic ones on the basis that most natural emeralds in our jewelry are imperfect, have cracks and visible internal defects, uneven coloring, and sometimes opaque. The synthetic origin of emeralds is not indicated on the labels. Too pale colored stone can be detected not by an emerald, but by ordinary beryl.
SYNTHETICAL EMERALD.
In recent decades, in addition to a large number of hydrothermal rubies and sapphires, most synthetic emeralds have also been produced by the hydrothermal method. Such emeralds are characterized by tubular inclusions, brownish inclusions of iron oxides. In ordinary jewelry stores, it is possible to distinguish natural emeralds from synthetic ones on the basis that most natural emeralds in our jewelry are imperfect, have cracks and visible internal defects, uneven coloring, and sometimes opaque. The synthetic origin of emeralds is not indicated on the labels. Too pale colored stone can be detected not by an emerald, but by ordinary beryl.
Perfect dark green and perfectly transparent emeralds of the same color should be passed on to independent experts for analysis, since it is too likely to get a very high quality synthetics, issued for natural stones (especially in imported gold products). Synthetic emeralds have a very characteristic intense bluish-green color, which partly gives their origin, although almost the same shade have some Colombian emeralds. Synthetic emeralds of hydrothermal origin usually contain small liquid or gaseous inclusions. Natural emeralds often have inclusions of plates and microplates of mica and pyrite crystals (even a natural emerald clogged with mica is much more expensive than its ideal synthetic analog). When choosing what to buy: green synthetic zircon or synthetic emerald, preference should be given to the emerald if possible, since it is much more beautiful and durable.
There is another kind of emerald , which is in the intermediate stage between synthetic and refined. They are non-jure beryls that do not represent jewelry in the initial raw material, but are covered with a layer of an advanced synthetic emerald with a thickness of 0.3 mm or more. The color of these stones is pale green. With the use of the popular hydrothermal method, an emerald layer 0.8 mm thick is growing in a day. The structure of the stones is imperfect, the cracks and the structure of the stone are underlined. The stones are opaque or translucent, characterized by cracks-like lines in the surface layer, which look when immersed in liquid as a thin, intensively green bezel. In jewelry stores appear silverware, dotted with such ennobled beryl. In stores, the most expensive giant domed silver ring, strewn with these enriched beryl, costs about $ 200, small rings with several stones cost up to $ 50.
Poisonous and radioactive dangerous stones and minerals
** - poisonous stones and minerals (mandatory check in the chemical laboratory + explicit indication of toxicity).
** - radioactive stones and minerals (mandatory check on the standard dosimeter + ban on open sales in the case of radioactivity over 24 milli / g / h + additional measures of population protection).
All rare stones are subject to mandatory inspection at the standard dosimeter for the permissible level of radiation and in the chemical laboratory for the absence of poisonous and evaporating components that are dangerous to humans and the environment.


Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.