CORUNDUM
 Characteristics of the mineral.
Characteristics of the mineral.
After diamond, corundum is the hardest gemstone (hardness 9). They are almost eternal stones. From a chemical point of view, corundum is the common aluminum oxide Al2O3. Chemically pure corundum is colorless. Different colors impart to it impurities of chromium, iron, vanadium and other chemical elements and compounds. There are corundums with a star effect (asterism).
Most of the extracted corundum is used for industrial and technical needs. Non-iron corundum has long been known as abrasive materials. It is no accident that the word "emery" is an old synonym for corundum. In the jewelry world, transparent corundums of intense coloration traditionally have their own names. Red corundums are known as rubies, blue and yellow - like sapphires. These are very expensive stones. High quality sapphires and rubies can be valued equally or more expensive than diamonds.
Corundum among minerals ranks second in hardness and abrasive ability after diamond. Sapphires and rubies - colored varieties of noble corundum - occupy the leading place in all classifications of jewelry stones along with diamond and emerald. By brilliance, light refraction and dispersion, they are much inferior to the diamond, but no precious stone can match the color of a blue sapphire or red ruby. The color of noble corundums can be different: colorless (leucosapphire), red of different intensity and shades (ruby), blue or blue of varying intensity and shades, pink (due to the impurity of titanium), green, purple, orange, yellow, brown (sapphires) . There are noble stones that possess asterism in the form of a six-beam star or the effect of a cat's eye, the appearance of which is due to oriented inclusions of rutile. Corundum is an optically uniaxial mineral.
The very term "corundum" is probably derived from the Sanskrit word kurivinda, which was used to name rubies. Often in the names of various options for corundum traders and jewelers used the word "eastern", which was supposed to emphasize the quality of the stones. Corundums of jewelry quality are traditionally mined in the territories of Burma, Thailand, India (Kashmir), Madagascar and Sri Lanka. There are stones from Kazakhstan, Canada, Norway, USA. In Russia, corundum deposits exist in Primorye, the Urals, the Krasnoyarsk Territory and the Chelyabinsk region.
Corundums are also formed in those parts of the rocks where granite magma is introduced into crystalline limestones; Such deposits are called skarns. Corundums can also arise during "steaming" with hot vapors and gases of dark rocks of basic composition, as, for example, in the areas of micas in the Polar Urals. Corundum often appears in the thick strata of crystalline rocks - gneisses - under the influence of large pressures and temperatures, when these strata are involved in the grandiose processes of mountain building. Small, invisible rock-forming corundums are incommensurably greater than jewels (quartz-healed) rubies and sapphires. Corundums grow auto-epitaxy - thin and wide crystals, growing on themselves.
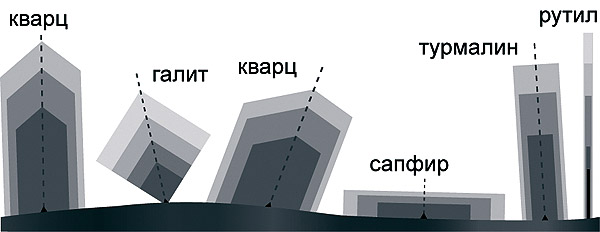
Scheme of crystal growth of various types of crystal lattice, incl. Tabular - corundum (flat)

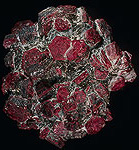
Corundums of different deposits. Ilmen Mountains (village Selyankino and others). Russia (Russia, CIS). Madagascar. Photo: © А.А. Evseev.
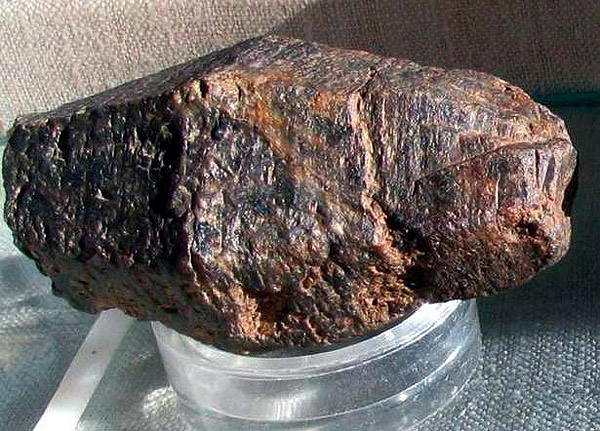

Corundum. Mochalin Log, Kyshtym district, Ural, Russia. (The Russian Federation, the CIS). Photo: © А.А. Evseev.

Corundum. Sinarsky deposit, near Snezhinsk, Ural. Russia (Russia, CIS). Photo: © А.А. Evseev.
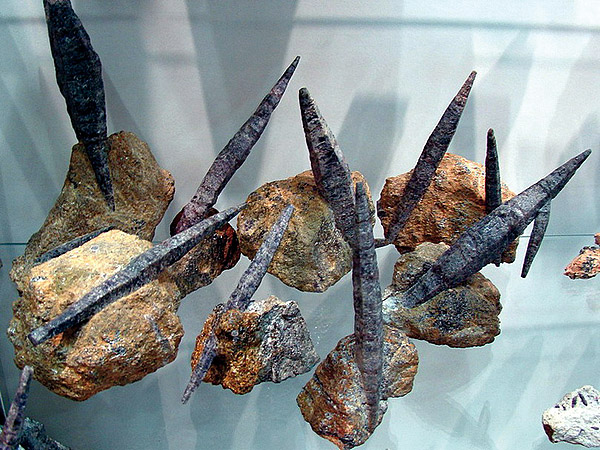

These spindle-shaped corundum crystals seem to be collected from a multitude of fragments - autoepitaxy
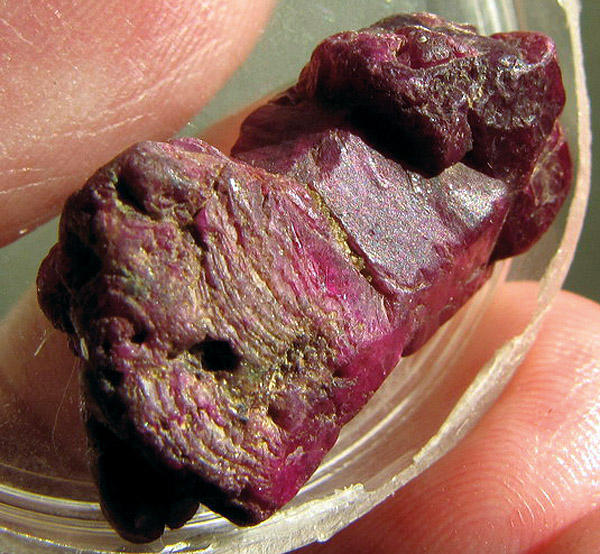

Corundum. Kamenka river, Kochkar, South. Ural, Russia. The crystal is more than 3 cm. Russia (Russia, CIS). Photo: © А.А. Evseev.
At present, the production of synthetic corundum is put on an industrial basis. Today we have learned how to obtain excellent chemically pure and uncomplicated corundums - synthetic rubies and sapphires. Unlike their natural counterparts, which in most cases are cloudy and covered with cracks, and can also have uneven coloring, synthetic stones are optically perfectly clean and transparent, evenly colored, much cheaper than their natural counterparts and practically eternal in jewelry (and, unfortunately , In jewelry today they are quite rare and difficult to access).
Magic properties of stones.
Red corundums (rubies) in many countries were considered symbols of passion and sensual love. They were revered as stones, helping to concentrate sexual energy. Blue and blue corundums (sapphires), on the contrary, can tame passions. The magical properties of noble colored corundums depend on their jewelry variety.
Corundum as such does not have a wide range of magical properties. It is a mineral used in industry. Grayish and colorless corundums are usually not used for magical purposes, but they and their synthetic counterparts are very popular in industry (scientists and production workers "pray" for it, so to speak figuratively).














Synthetic and fake corundum
 SYNTHETIC CORUNDUM FINISHES (!!) . It turns out that now not only natural natural stones are forged. Since the collapse of the USSR prices for synthetic corundum raw materials have become quite high, prices for synthetic corundums, sapphires and rubies are also not cheap.
SYNTHETIC CORUNDUM FINISHES (!!) . It turns out that now not only natural natural stones are forged. Since the collapse of the USSR prices for synthetic corundum raw materials have become quite high, prices for synthetic corundums, sapphires and rubies are also not cheap.
In the photo on the right is a typical specimen of fake synthetic corundum single crystals (synthetic rubies and sapphires). Quite bright colors and a characteristic collar (a shape resembling a shaved pebble) or cubes. It seems that it is similar to corundum, and it can be sold expensive, but it is not grown by the Wernelyov method.
On an industrial scale, artificial corundum materials are obtained by melting bauxite in electric furnaces with a reducing agent (iron sawdust). They are also used as abrasives; By methods of powder metallurgy, they make cutters for machining metals at high temperatures. They are not suitable for cutting as an insert.
 SYNTHETIC RUBY AND SAPPHIRES (CORUNDES).
Today, the market of precious stones presents a lot of synthetic rubies and sapphires, grown by various methods of synthesis, for each of which their distinctive features are known. Almost all red stones in jewelry are synthetic corundums. Most natural rubies have internal defects. Thus, the majority of synthetic rubies and sapphires found on the market are obtained by the Verneuil method, the distinctive features of these stones are curvilinear zoning (which is not observed in natural stones), sometimes inclusions of gas bubbles are encountered. But visually synthetic corundums look perfect. Moreover, it is synthetic corundums that are quite cheap and almost eternal red and dark pink inserts in jewelry. It is a very beautiful synthetic gem. Unfortunately, today red corundums have become very rare in jewelry stores, and synthetic sapphires can not be found at all.
SYNTHETIC RUBY AND SAPPHIRES (CORUNDES).
Today, the market of precious stones presents a lot of synthetic rubies and sapphires, grown by various methods of synthesis, for each of which their distinctive features are known. Almost all red stones in jewelry are synthetic corundums. Most natural rubies have internal defects. Thus, the majority of synthetic rubies and sapphires found on the market are obtained by the Verneuil method, the distinctive features of these stones are curvilinear zoning (which is not observed in natural stones), sometimes inclusions of gas bubbles are encountered. But visually synthetic corundums look perfect. Moreover, it is synthetic corundums that are quite cheap and almost eternal red and dark pink inserts in jewelry. It is a very beautiful synthetic gem. Unfortunately, today red corundums have become very rare in jewelry stores, and synthetic sapphires can not be found at all.
If someone else has preserved synthetic rubies of Soviet cut (stones produced by the USSR) in jewelry - do not rush to get rid of them. You have a sample of a beautiful machine cut stone and a rare example of a valuable synthetic stone. Now you can not buy them just in a jewelry store. Today, prices for cut synthetic corundums, rubies and sapphires for jewelry are many times higher than prices for traditional colorless and colored cubic zirconia (synthetic cubic zircon), although they are much cheaper than the prices for natural precious stones of the corundum group.
 BULLEY . Monocrystals of synthetic corundum are a modification of aluminum oxide, in which a small part of aluminum ions can be isomorphically replaced by ions of the iron group or copper ions. Cultivation of synthetic monocrystals of a wide range of colors (rubies, sapphires, topazes, amethysts, etc.) is carried out by the method of Verneuil.
BULLEY . Monocrystals of synthetic corundum are a modification of aluminum oxide, in which a small part of aluminum ions can be isomorphically replaced by ions of the iron group or copper ions. Cultivation of synthetic monocrystals of a wide range of colors (rubies, sapphires, topazes, amethysts, etc.) is carried out by the method of Verneuil.
Ruby and sapphire are minerals that, although different in appearance, have an identical crystalline structure and properties, with the exception of the presence of insignificant concentrations of impurity elements that give them characteristic colors. Ruby and sapphire consist mainly of aluminum oxide Al2O3, the crystalline form of which mineralogists call corundum. Crystals grown according to the Verneuil method are known as Bulls, apparently due to the fact that initially they had a rounded shape. This term, introduced by Goden and used by Verneuil, has become common with crystal growth specialists, despite the fact that now the crystals have a cylindrical shape. Today, cylindrical boules of 20 mm in diameter and a cylinder height of 50-70 mm and a half-boule (half a cylinder cut along, with a base of 10 x 20 mm) are grown.
Single-crystal transparent boules and rods of artificial corundum (synthetic rubies and sapphires) are obtained by melting and recrystallization of alumina (aluminum oxide) in an oxygen-hydrogen flame. Bulls can be additionally colored: impurities of Cr ions (chromium, up to 2%) in red, V (vanadium) in gray-green in daylight and violet under artificial illumination, Mn (manganese) in yellowish pink, Ni ( Nickel) - in yellow, Ti (titanium) - in pink-violet colors. When cutting synthetic corundums under different names (sapphire, ruby, topaz, alexandrite, amethyst) they are used in jewelry. The density of synthetic corundum is 4 g / cc, the hardness is about 9 for stained corundum and 9.25 for optically pure sapphires (diamond hardness is 10 on the Mohs scale).
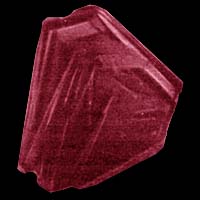 Rubies and sapphires, grown by flux and hydrothermal methods of synthesis , are the most complex objects for diagnostics (they are quite similar to natural ones). Flux rubies and sapphires are characterized by the inclusion of flux and materials of the growth chamber (crucible) - platinum, gold and copper, and the distinguishing feature of hydrothermal corundum is irregular microstructures of growth. Synthesizing rubies by the method of flux or hydrothermal method, you can get jewelry stones of very high quality, similar to natural ones. Using this technology, ruby crystals of about 40x40x12 mm are obtained. The seed crystal was suspended on the wire in the middle part of the solution, and small fragments and crumb of ruby were placed in the lower part, which served as feed material for the new growing crystal. In fact, ruby is obtained by recrystallization, not synthesis. The tendency of ruby crystals to grow from high-temperature solutions in the form of flat plates (in width), rather than acquire isometric forms, creates serious difficulties when using them as a precious material. The ratio of crystal growth rates in the plane of the plate and in the thickness can exceed 100: 1.
Rubies and sapphires, grown by flux and hydrothermal methods of synthesis , are the most complex objects for diagnostics (they are quite similar to natural ones). Flux rubies and sapphires are characterized by the inclusion of flux and materials of the growth chamber (crucible) - platinum, gold and copper, and the distinguishing feature of hydrothermal corundum is irregular microstructures of growth. Synthesizing rubies by the method of flux or hydrothermal method, you can get jewelry stones of very high quality, similar to natural ones. Using this technology, ruby crystals of about 40x40x12 mm are obtained. The seed crystal was suspended on the wire in the middle part of the solution, and small fragments and crumb of ruby were placed in the lower part, which served as feed material for the new growing crystal. In fact, ruby is obtained by recrystallization, not synthesis. The tendency of ruby crystals to grow from high-temperature solutions in the form of flat plates (in width), rather than acquire isometric forms, creates serious difficulties when using them as a precious material. The ratio of crystal growth rates in the plane of the plate and in the thickness can exceed 100: 1.
Poisonous and radioactive dangerous stones and minerals
** - poisonous stones and minerals (mandatory check in the chemical laboratory + explicit indication of toxicity).
** - radioactive stones and minerals (mandatory check on the standard dosimeter + ban on open sales in the case of radioactivity over 24 milli / g / h + additional measures of population protection).
All rare stones are subject to mandatory inspection at the standard dosimeter for the permissible level of radiation and in the chemical laboratory for the absence of poisonous and evaporating components that are dangerous to humans and the environment.


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.