FLINT
 Characteristics of the mineral.
Characteristics of the mineral.
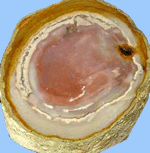
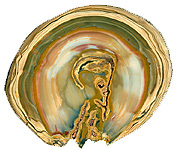
Flint - one of the many varieties of rocks, consisting almost one hundred percent of silica, painted with mineral salts in different shades of brown and black. The shape of the flint is very diverse: it is rounded, finger-shaped, lamellar and other forms of concretion, often having outgrowths, holes and voids filled with small quartz crystals. Flint and silicon are not the same. It is a viscous strong aggregate of cryptocrystalline and amorphous silica. A mixture of cryptocrystalline and amorphous silica: chalcedony, quartz and opal, very slightly translucent. Often flint has an organogenic origin, since flint is a part of the skeletons of some marine unicellular organisms. When such micro-skeletons are compacted on the ocean floor for millions of years, sedimentary rocks are formed in which the flint gradually turns into opal, and then passes into chalcedony. Distinguish chalcedony-quartz, quartz chalcedony and opal-chalcedony flints. Color from gray, yellow-gray to black. Many variegated specimens. Flax is perfectly polished, has a great hardness (6-7), why it is made of mortar, large plates for facing. Beautiful figured flint is used as a jewel stone. Sometimes in the stones there are tiny cavities filled with rock crystal.
Under a microscope in silicon, one can distinguish between spicules and needles of sea sponges, delicate lanterns-skeletons of unicellular organisms of radiolarians, valves of tiny shells. Waves of the oceans and seas, the streams of rivers flowing into them from a great antiquity (hundreds of millions of years), eroding the banks, demolish the smallest parts of the destroyed rocks in the water. Volcanic ash also falls into the sea from eruptions of underwater or volcanoes located on the coast. Silica gradually dissolves in sea water or hangs in it in the form of the finest non-sediment particles (they are called colloid particles). Part of the silica from the sea water is extracted by microorganisms for the construction of skeletons (radiolaria or unicellular diatoms). A lot of silica is in the water and now, but part of it, especially near active volcanoes, fell out in the form of a flint sediment. The simultaneous precipitation of silica and organic substances causes the formation of black flints. Sometimes silica fills the remains of plants: whole stone forests are known. Today, flint is used in the production of ceramics, abrasives and building materials.
The flint splits into fragments with sharp edges. Because of this viscosity, the flint blocks did not disperse when impacted on small fragments, but split into rather thin, usually slightly curved plates with a sharp cutting edge. How long have people known with flint? As much as they exist in the world. Treated flint tools - the main advantage of an ancient man in front of his animal brethren. In ancient times due to its properties, flint served faithfully our ancestors for the manufacture of arrowheads, tools and tools, and then was replaced by metal. Flint cuts sparks, hence the name of the mineral (from the Latin cremare - "burn"). In the Stone Age, flint served as the main material for the manufacture of cutting tools and gun tips. First choppers, hammers, axes, tips of spears - from flint. According to historians, the age of the oldest processed tools from flint is slightly less than the age of the remains of the most ancient man. Below are the fossil tools and flint points.
Magic properties of stones.
He is the talisman of people who want to increase their knowledge, to open a new, for people purposeful. Flint gives a strong energy feed, so it is very useful for people engaged in intensive activities, both intellectual and otherwise. As an amulet and charm amulet, the flint gives protection from enemies, ill-wishers, seeking to suspend a person's activity. It helps to overcome obstacles, persistence in difficult circumstances. The stone is very well worn on the body: it harmonizes the person and generously endows power.









Poisonous and radioactive dangerous stones and minerals
** - poisonous stones and minerals (mandatory check in the chemical laboratory + explicit indication of toxicity).
** - radioactive stones and minerals (mandatory check on the standard dosimeter + ban on open sales in the case of radioactivity over 24 milli / g / h + additional measures of population protection).
All rare stones are subject to mandatory inspection at the standard dosimeter for the permissible level of radiation and in the chemical laboratory for the absence of poisonous and evaporating components that are dangerous to humans and the environment.


Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.