Silicates: andalusite, chiastolite
 Diagnostic Card.
Diagnostic Card.
The crystals of andalusite from Villa di Kyaw (Italy)
Al 2 O SiO 4
Crystal system orthorhombic
7.5 Hardness
Specific gravity 3.16-3.20
Cleavage see on prism
The break in the wrong
Colour colorless, differently colored
Color white powder
Gloss glass
Andalusite - aluminum silicate. Gloss glass or dull. Opaque. Colours: gray, pink, purple, dark green. The bar is white. Fracture is uneven. Fragile. Cleavage imperfect, on the faces of the surface often grow small leaves muscovite. The crystals are orthorhombic. granular aggregates. Distribution Area: Tyrol (Austria), Switzerland, Spain, the CIS. Chiastolite or Araneus - columnar variety of andalusite yellowish-gray or gray with a cross-shaped arrangement of the smallest of the carbonaceous particles.
These minerals are of interest mainly to collectors; Only in exceptional cases, they can also act as jewels. In the treatment of andalusite, which got its name from the place of discovery - Province of Andalusia in Spain, should take into account its strong pleochroism. The large crystals or aggregates of the more rarely andalusite are gem quality. Luster in mineral glass.
Andalusite is often represented by large crystals of prismatic shape, with a few faces, mostly short, square in section, generally opaque. They are usually found in quartzites, gneisses, schists microcrystalline. andalusite crystals often covered with mica or products of secondary alteration. Transparent difference suitable for jewelry use, often corrode or outside are small pebbles in the sand. Constant andalusite, very solid and quite heavy. It is easily divided by cleavage parallel prism, usually opaque and translucent.
 Alumina (Al2O3) 63,1%, silicon dioxide (SiO2) 36,9%, often present in a small amount of iron oxide (Fe2Oz). Form crystalline precipitates. Columnar with a square cross-section, compressed, elongated prism. Andalusite crystals during growth can capture carbonaceous, or clay material. Its concentration occurs in certain crystallographic directions, causing cross arises characteristic figure; This kind is called hiastolitom (Greek "hiastos." - crossed, "lithos" - stone). Class symmetry. Rombo-bipyramidal - mmm. Cleavage. Parallel to the axis, perfect. Aggregates. Solid, radiant ( "bundles"), columnar, fibrous, grainy.
Alumina (Al2O3) 63,1%, silicon dioxide (SiO2) 36,9%, often present in a small amount of iron oxide (Fe2Oz). Form crystalline precipitates. Columnar with a square cross-section, compressed, elongated prism. Andalusite crystals during growth can capture carbonaceous, or clay material. Its concentration occurs in certain crystallographic directions, causing cross arises characteristic figure; This kind is called hiastolitom (Greek "hiastos." - crossed, "lithos" - stone). Class symmetry. Rombo-bipyramidal - mmm. Cleavage. Parallel to the axis, perfect. Aggregates. Solid, radiant ( "bundles"), columnar, fibrous, grainy.
Chiastolite or cross stone, "Araneus" - is opaque gray, whitish or grayish-yellow variety of andalusite. Crystals dlinnoprizmaticheskie, in cross-section is clearly visible dark cross formed by selectively absorbing the growing face of the crystal of carbonaceous and clay particles from the surrounding rocks. Andalusite deposits are known in South Australia, Bolivia, Chile, France (Brittany), Spain (Galicia), the CIS (Siberia), USA (Calif.). The figure in the form of a black cross, in the cross section of a crystal has always attracted attention, and the mineral is used mainly by monks and pilgrims for the manufacture of amulets. Currently, it is a rare collector's stone. GRINDER flat or slightly convex. It can not be confused with anything.
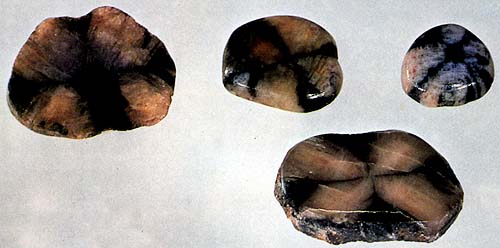
Diagnostic features.
If the mineral is exposed cathode radiation, it fluoresces greenish-yellow tones. In Andaluzine (Spain) were found beautiful stones that change color depending on the angle at which they fall sunlight. Andalusite is named after Andalusia region of Spain, where it was first discovered. It can be confused with chrysoberyl, smoky quartz, tourmaline.
Origin.
It occurs in rocks affected by contact metamorphism. Andalusite is formed in metamorphic rocks (schists, gneisses), accumulates in the river alluvium. The stones are suitable for cutting, supply Brazil and Sri Lanka, as well as Canada (prov. Quebec), Spain (Almeria in Andalusia) and the US (pcs. Maine, Massachusetts).
Place of Birth.
There are crystals of Andalusia (Spain) and the Austrian Tyrol (License text Ridge). In Italy, good reddish-brown crystals can be found in quartzites Villa di Kyaw (province of Sondrio) and in a variety of metamorphic rocks in the Adamello area, located in the Brescia province. Rare pink crystals found in pegmatites near Isoelly in the bottom of the Valsesia. Light green or reddish-brown andalusite in concretions (radiant-fiber structure) in the tens of centimeters in size is represented in pegmatites in the area of Douai-Fontane near San Giovanni Morgeto (Calabria).
Application.
Because andalusite forms large clusters (in Russia and California), it is developed as a raw material for you-sokoprelomlyayuschih and acid materials. Transparent difference used in jewelry and are highly regarded for the excellent pleochroism which varies from green to pink and red.

Andalusia. Sectorial diamond-shaped cross-section of andalusite (hiastolita) on the polished slice
mica slate. Cave, Kola Peninsula, Russia. The crystals up to 8 cm Photo:. © AA Evseev.
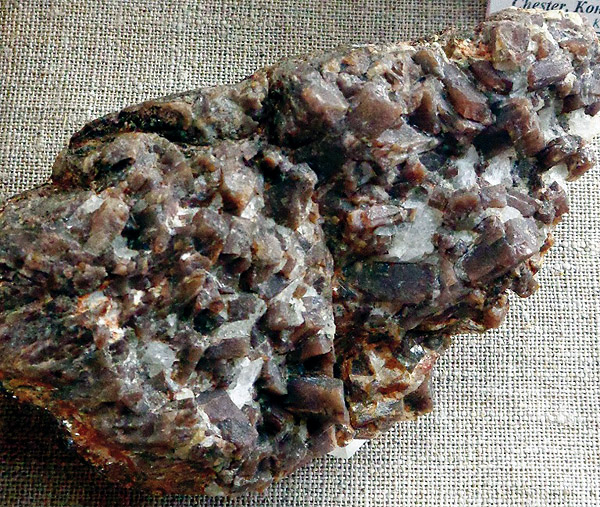

Andalusite with quartz and feldspar. Cheget, at Elbrus, North. Caucasus, Russia, the CIS.
The crystals 1.5-2 cm Photo:. © AA Evseev.
- Gatchell - "New Almadén snag" - arsenide and antimony sulfide (modern sulphosalts)
- Antimony - toxic metal (semi-metal) are widely used in industry, medicine and engineering
- Zirconium - a rare and non- metal and dangerous jewel in the oxide and salts
- Gold - yellow dangerous and toxic metal -date and accurate digital cable technology
- Sulphur - a golden-yellow toxic substance and a sign of volcanic activity
- Cadmium - a toxic uncirculated unknown wide range of people silvery metal
- Lead - a poisonous gray simulator silver metal and toxic metal snag
- Arsenic - poison classic medieval and modern poisoners and medicine in medicine
Toxic and hazardous radioactive rocks and minerals
** - Poisonous stones and minerals (obligatory check in chemical laboratory + clear indication of toxicity)
** - Radioactive rocks and minerals (obligatory check on a regular dosimeter + ban on the open sale of radioactivity in the event of more than 24 mR / hour + additional measures to protect the population)
Catalog minerals and gems in groups of the world
** - Poisonous stones and minerals
** - Radioactive rocks and minerals


Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.