Sulfates: gypsum
 Diagnostic Card.
Diagnostic Card.
Ca SO 4 * 2 (H 2 O)
Crystal system monoclinic
Hardness 2
The proportion of 2.3-2.4
Cleavage is perfect
The break in the wrong
Colour colorless, colored razno-
Color white powder
Shine from glass to pearl
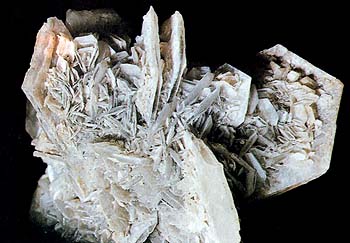
Gypsum - the name refers to both the mineral and to it consisting of the breed. Water-containing calcium sulfate. Gloss glass to pearl. The bar is white. Fracture uneven, flexible, but not elastic. Cleavage very perfect. Formed in association with rock salt and anhydrite. The crystals (monoclinic system) are frequent, often tabular, elongated or needle-like (fibrous). Usual cruciform twins sprouting or twin growths in the form of "dovetail". In areas with dry climates occur splices assembled socket - "Desert Rose." Deposits: Thuringian Forest, Harz (Germany), Carinthia (Austria), Switzerland, Italy, France, Chile.
Alabaster - dense white or mramoropodobnaya variety of gypsum. The most famous field in Tuscany, Italy.
 Pure gypsum - colorless mineral; but the presence of inclusions and the presence of trace elements may account for a variety of colors. For the plaster counterpart characteristic dovetail and spearhead.
Pure gypsum - colorless mineral; but the presence of inclusions and the presence of trace elements may account for a variety of colors. For the plaster counterpart characteristic dovetail and spearhead.
gypsum crystals are mostly white, but can also have a gray, yellowish and other coloration due to inclusions or impurity elements. Distributed units, such as selenite - crystals or wide plate; serikolit -voloknistye clusters of elongated crystals; Alabaster - granular mass solid build, sometimes zoned, like wax. Gypsum is soft, has a perfect cleavage, splitting into thin plates and scales.
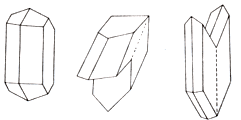
Chemical composition. Calcium Oxide (CaO) 32.6% sulfur trioxide (SO3) 46,5%, water (H2O) 20.9%. Form crystals. Tabular, prismatic, columnar, needle; frequent twins sprouting on one of the two laws:
1) dovetail counterparts, are most spread-twinning on the faces of the prism;
2) Montmartre (Paris) twins ribs prisms arranged in parallel twinning seam.
The crystal structure. Layered. Class symmetry. Prismatic - 2 / t. Cleavage. Perfect parallel to the lateral faces (010); break on the prism faces fine splintery, and basal faces - a distinctive conchoidal. Aggregates. Dense, granular (plaster), fibrous, scaly, earthy, nodules.
Diagnostic features.
Mineral soluble in hydrochloric acid and hot water; painted in pink and red flame of a blow tube; can luminescence in ultraviolet light. Decomposes with the loss of water of crystallization and melts into a white enamel. In a closed tube loses crystal water, turning into calcium sulfate ( "tightly calcined gypsum"). Behavior in acids. Slightly soluble.
Origin.
Gypsum is a typical mineral evaporite origin. It may, however, be formed upon hydration and anhydrite precipitate from fumarole gases (sublimation - the transition from the gaseous to the solid state). Further, gypsum is formed under the influence of water on the metal sulfides. It is often associated with brimstone, especially in the so-called gypsum-sulfur-bearing formations - earth formation, the outputs of which are bordered by the outer arc of the Apennines and ends in Sicily.
Place of Birth.
In Italy, a well-known gypsum Pavese, Bologna Apennines and Sicily. From here comes the giant crystals. Very beautiful specimens found in Mexico, Chile and the United States. Gypsum deposits are developed on a commercial scale in the Paris Basin (France), in Canada, in many areas of the United States and Russia. In Italy, they are found in Volterra (Pisa Province), where the alabaster mined.
Finally, the well-known so-called "desert rose" - fusion of gypsum in the form of socket; painting of pinkish-yellow. "Desert Rose" come from the desert regions of Morocco and Tunisia (Africa) and the states of Arizona and New Mexico (USA). In the photo: a characteristic "desert rose" of the plate crystals from Algeria. There are some interesting formations of gypsum in Russia.



Application.
Finely milled and partially dewatered, and then molded plaster is used in the construction business as a binder and as a component of Portland cement and mortars. Due to its low hardness of gypsum used in the creation of sculpture and decorative arts. Some varieties of plaster are used as a finishing material.
- Gatchell - "New Almadén snag" - arsenide and antimony sulfide (modern sulphosalts)
- Antimony - toxic metal (semi-metal) are widely used in industry, medicine and engineering
- Zirconium - a rare and non- metal and dangerous jewel in the oxide and salts
- Gold - yellow dangerous and toxic metal -date and accurate digital cable technology
- Sulphur - a golden-yellow toxic substance and a sign of volcanic activity
- Cadmium - a toxic uncirculated unknown wide range of people silvery metal
- Lead - a poisonous gray simulator silver metal and toxic metal snag
- Arsenic - poison classic medieval and modern poisoners and medicine in medicine
Toxic and hazardous radioactive rocks and minerals
** - Poisonous stones and minerals (obligatory check in chemical laboratory + clear indication of toxicity)
** - Radioactive rocks and minerals (obligatory check on a regular dosimeter + ban on the open sale of radioactivity in the event of more than 24 mR / hour + additional measures to protect the population)
Catalog minerals and gems in groups of the world
** - Poisonous stones and minerals
** - Radioactive rocks and minerals


Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.