Sulphides: Greenokite
 Diagnostic card.
Diagnostic card.
Cd S
Shingoniya hexagonal
Hardness 3-3,5
Specific weight 4,9-5
Cleavage distinct
Cracked shell
Color yellow, red, orange
Color in powder yellow
Glitter resin
Usually it is earthy crusts of yellow color, quite rare - clear hemimorph crystals. Their appearance is pyramidal, the color is yellow or orange-pink.
Diagnostic signs.
When exposed to hydrochloric acid, it releases hydrogen sulphide vapor with a characteristic smell of rotten egg. If it contains zinc, it fluoresces orange-yellow.
Origin.
It is usually deposited in association with zinc minerals, especially with zinc blende. It is also obtained artificially by heating cadmium oxide in sulfur vapors.
Deposits and applications.
It occurs in Bishopton in Scotland in the form of crystals longer than 1 cm, in Llaglagua in Bolivia, in Pirkitas in Argentina, in Sibai in the Urals, together with prenite and zeolites in Paterson (New Jersey, USA). In the mine of tin-silver ores of Asunca (San Vicente, Bolivia), crystals of red color, up to 2 mm in size, were encountered. Obtained for the extraction of cadmium.

Grinokit. Curly vulk., About. Iturup, the Kurils, Russia. Photo: © А.А. Evseev.
Metal cadmium has no toxic properties. Cadmium compounds, regardless of their aggregate state (dust, cadmium oxide smoke, vapors, fog) are toxic. By its toxicity, cadmium is similar to mercury or arsenic. Less soluble compounds act on the respiratory tract and gastrointestinal tract, and soluble - after absorption into the blood - affect the central nervous system (severe poisoning), cause degenerative changes in the internal organs (in the liver and kidneys) and disrupt the phosphorus-calcium metabolism.
For humans, a lethal dose is inhalation for 1 minute. Air with a content of 2500 mg / m3 of cadmium oxide (or 30 seconds at a concentration of 5000 mg / m3). The maximum allowable amount of CdO in the air is 0.1 mg / m3; For cadmium alloy dust is 0.3-0.4 mg / m3. Due to the toxic nature of cadmium and its compounds, their contact with food products is unacceptable.
Reduction of smell (until complete loss), golden staining of the gums in the region of the tooth necks ("cadmium rims"), dizziness, headache, disturbed appetite and sleep. In cities whose atmosphere contains more cadmium (gasoline), the mortality rate among those suffering from heart disease is higher. For acute poisoning, a long period (10-36 hours, sometimes 30 minutes, 2 hours). The smell of mucous membranes, an unpleasant astringent sweet sensation on the lips, a copper taste in the mouth, gullet spasms, pallor, weakness, dizziness and headache (in the forehead), nausea and pain in the epigastric region. Dermatitis and ulceration of the skin are possible; Pain in the chest and abdominal cavity, followed by vomiting. Then develop tracheitis, bronchitis with bouts of painful convulsive cough and severe shortness of breath, the temperature rises.
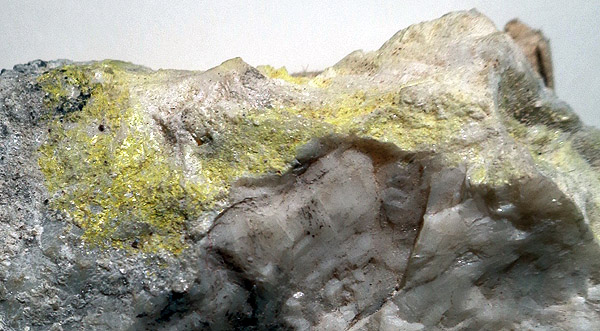
Grinokit (yellow primes) on calcite. Yun-Nan, China. 7х5 cm. Photo: © А.А. Evseev.
The main problems associated with cadmium in mankind are caused by technogenic pollution of the environment, and its toxicity to organisms at low concentrations. Signs of cadmium deficiency: with an experimental cadmium deficiency, a slowdown in growth is observed in animals. Cadmium refers to immunotoxic elements. Many cadmium compounds are poisonous. With excess intake of cadmium, cadmium develops, in which the urinary and reproductive systems are affected. There are proteinuria, glucosuria, aminoaciduria, beta2-microglobulinuria, the appearance in the urine of a protein that binds retinol and lysozyme, prostatopathy with the risk of developing tumors and necrosis of the testes.
The defeat of the bronchopulmonary system is accompanied by fibrotic changes and an increased risk of developing emphysema. Anemia develops, associated with a decrease in iron absorption in the intestine and with erythrocyte lysis. Increases blood pressure. There are osteoplastic and osteoporotic changes in bone tissue, which is associated with a violation of calcium absorption in the intestine and endocrine disorders (cadmium "washes out" calcium from the bones - osteoporosis). The symbol of cadmium is two flexible snakes (pharmaceuticals).
Smoking cigarettes increases the intake of cadmium in the body by 0.1 μg (significantly increases the risk of intoxication with cadmium). The role of cadmium in the induction of lung cancer and kidney cancer in smokers, the development of prostate pathology is proved. From the toxic effect of cadmium, the fetus during pregnancy protects the placenta (cervical cancer of the mother), and the newborn baby - breast milk (breast cancer). The main manifestations of excess cadmium: prostatopathy; Cardiopathy, hypertension; Emphysema, osteoporosis, deformity of the skeleton (duck walk); Nephropathy; anemia; Development of deficiency of zinc, selenium, copper, iron, calcium.
Cadmium is necessary: for violations of growth processes. Food sources of cadmium: seafood (mussels and oysters, kelp, seaweed), cereals, leafy vegetables (salad), mushrooms (ceps, oyster mushrooms, mushrooms, honey agarics - a lot of cadmium accumulates in their hats - the formation of a sporiferous layer of fungi , Disputes).
ADR 6.1
Toxic substances (poison)
Risk of poisoning by inhalation, in contact with skin or if swallowed. Dangerous to the aquatic environment or the sewage system (similar to ADR dangerous goods for transporting mercury, less dangerous)
Use a mask for emergency leaving the vehicle
White diamond, ADR number, black skull and crossbones
ADR Fish
Substances that are hazardous to the environment (ecology, including melting, soluble, powdery and flowing materials)
Dangerous to the aquatic environment or the sewage system (similar to ADR dangerous goods for transporting mercury, less dangerous)
| The name of a cargo that is particularly dangerous for transportation | room
UN |
Class
ADR |
| CADMIUM CONNECTION | 2570 | 6.1. |
| Cadmium Cyanide | 1588 | 6.1. |
Poisonous and radioactive dangerous stones and minerals
** - poisonous stones and minerals (mandatory check in the chemical laboratory + explicit indication of toxicity)
** - radioactive stones and minerals (mandatory check on the standard dosimeter + ban on open sales in case of radioactivity exceeding 24 milli / g / h + additional measures of population protection)
Catalog of minerals and semi-precious stones of the world by groups
** - poisonous stones and minerals
** - radioactive stones and minerals


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.