Silicates: Kyanite (kyanite, "Kashmir sapphire")
 Diagnostic Card.
Diagnostic Card.
On the picture. Prismatic crystals of kyanite from the famous deposits Pizzo Forno (Ticino, Switzerland).
Al 2 O SiO 4
Crystal system triclinic
Hardness 4-7.5 (depending on direction)
Specific weight 3,53-3,67
Cleavage is perfect
The break in the wrong
Colour colorless, differently colored
Color white powder
Shine from glass to pearl
Forms prisms, flattened or elongated, generally without complete. Cleavage is perfect along the long edge. Crystals are often connected to subparallel beams, painted in a fairly intense blue color (at the center of the thick coloring). Less commonly, this mineral is white, gray or greenish color, distributes patches. Transparent or translucent, the luster of the glass to the pearl along the cleavage planes.
Kyanite, or kyanite, is very common in nature, it belongs to the rock-forming minerals. However, transparent beautifully painted designs, suitable for cutting, are rare. Kyanite crystallizes in the triclinic system, pinakoidalnom symmetry class. The shape of its crystals usually dlinnostolbchataya, plank-buttress. Rounded spindle-shaped crystals in the Urals called oatmeal. Often there are doubles with twin plane and radiating aggregates of crystals.
Chemical composition. Alumina (Al2O3) 63.1%, silicon dioxide (SiO2) 36,9%; present as impurities 1.2% Fe2O3, 1.8% Cr2O3 in minor amounts CaO, MgO, FeO, TiO2. Hardness. 6 and 4.5 and a transverse longitudinally elongated prismatic crystals; Fracture. Fibrous. Form crystalline precipitates. Columnar, plank, crystals, fibrous, radiant, foliated selection. Class symmetry. Pinakoidalny - 1. Cleavage. The average of the basis (perpendicular axis) (100) (010) (001). Aggregates. Radiating, granular.
The color blue kyanite, blue, green, purple, pink, notes and colorless. Blue color is associated with members of kyanite structure admixtures Cr, Fe2 + and Fe3 + ions or Ti, and green - Fe3 +. Painting in different crystallographic directions changes from violet-blue to colorless and cobalt-blue or yellowish-green to green. There are crystals with the effect of "cat's eye". Gloss glass, mother of pearl on the cleavage planes. Hardness is very different in different directions. This property led to the second name kyanite - kyanite, ie dvoyakosoprotivlyayuschiysya... Fragile.
Diagnostic features.
Kyanite hardness varies depending on the direction in which it is scratched. It is the most solid and perpendicular to the elongation of less solid and parallel to it. Kyanite tugoplavok not dissolve in acids.
Origin.
Jewelry kyanite refers to is not very common minerals. Its origin is due to metamorphism (under very high pressure) sedimentary rocks rich in aluminum. Usually found with staurolite, garnet and mica; very rarely has a pegmatite genesis. It is resistant to weathering, so it is easy to find among unconsolidated clastic sediments formed during the destruction kianitsoderzhaschih rocks (sedimentary genesis). Kyanite occurs in metamorphic rocks. Often it recovered from alluvial deposits. Beautiful cornflower-blue, sky-blue and purple Facetting kyanite mined in the Urals.
Place of Birth.
At the world famous blue translucent crystals in association with paragonite (light mica) and staurolite derived from Pizzo Forno in the canton of Ticino (Switzerland). Beautiful specimens discovered in Tyrol (Austria) and the department of Morbihan (France). Huge crystals (up to 30 cm in length) turquoise color, but opaque, revealed in the state of Minas Gerais (Brazil). Green kyanite opened in Machakos (Kenya).
Commercially kyanite field developed in the United States (Massachusetts, Connecticut, and North Carolina), and India, and Australia. The most famous jewelry kyanite India (Jammu and Kashmir, Punjab), in the XVII century where they were brought. In Russia, called the Indian kyanite Baus. Blue faceted kyanite similar to sapphire, but their hardness is much lower, as the refractive index, and density. Light blue and blue-green kyanite like aquamarine, but are characterized by a high refractive index and density. Jewelry kyanite also developed in Burma, Brazil, Kenya, Switzerland and the United States (in the states of Montana, Virginia, Vermont, Connecticut, Massachusetts, and others.).
Application.
Kyanite - valuable mineral raw materials for the production of electrical insulating materials, which are stable at high temperatures and under the influence of all acids, including phosphorous. Faceted kyanite is used in jewelry. Granite transparent stones of good quality in a stepped or diamond shape. Less transparent beautifully colored crystals or stones with the effect of "cat's eye" shaped cabochon.





The distribution of color is often banded. Granite kyanite difficult due to the anisotropy of hardness and perfect cleavage. The deposits are known in Burma, Brazil, Kenya, the United States (pcs. Of North Carolina), Austria (Tyrol), Switzerland (ch. Gothard). Kyanite can be confused with aquamarine and sapphire.
Distin, or kyanite - aluminum silicate. The hardness of the crystal along the 4.5 across 7. Luster pearly to glass, translucent. Colours: blue, green, rarely light gray; It is colorless. The bar is white. Fracture splintery. Cleavage is perfect. The crystals (triclinic) are common. Distribution Area: Spessart (Germany), Tyrol (Austria), Switzerland, India, USA, Brazil, CIS.
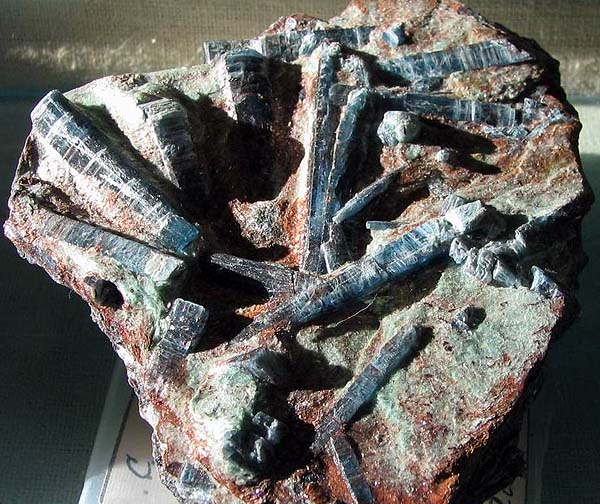

He kyanite in mica schist. Borisov hill, to the south of the town of Plast, South Urals, Russia. Photo: © AA Evseev.

Kyanite. Yazgulem hr., Pamir, Tajikistan. Photo: © AA Evseev.
- Gatchell - "New Almadén snag" - arsenide and antimony sulfide (modern sulphosalts)
- Antimony - toxic metal (semi-metal) are widely used in industry, medicine and engineering
- Zirconium - a rare and non- metal and dangerous jewel in the oxide and salts
- Gold - yellow dangerous and toxic metal -date and accurate digital cable technology
- Sulphur - a golden-yellow toxic substance and a sign of volcanic activity
- Cadmium - a toxic uncirculated unknown wide range of people silvery metal
- Lead - a poisonous gray simulator silver metal and toxic metal snag
- Arsenic - poison classic medieval and modern poisoners and medicine in medicine
Toxic and hazardous radioactive rocks and minerals
** - Poisonous stones and minerals (obligatory check in chemical laboratory + clear indication of toxicity)
** - Radioactive rocks and minerals (obligatory check on a regular dosimeter + ban on the open sale of radioactivity in the event of more than 24 mR / hour + additional measures to protect the population)
Catalog minerals and gems in groups of the world
** - Poisonous stones and minerals
** - Radioactive rocks and minerals


Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.