Oxides and hydroxides: Corundum
 Diagnostic Card.
Diagnostic Card.
Al 2 O 3
Crystal system trigonal
The hardness of 9
Specific weight 3,95-4,1
Cleavage psevdospaynost on-lookalike vaniyu
fracture conchoidal
Colour colorless, raznookra- Weighted
Color white powder
diamond Gloss
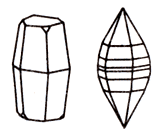
According corundum hardness is second only to diamond, although 140 times softer than his. However corundum 7 times harder topaz - mineral next reference Mohs scale. Thus clearly hardness ruby varies depending on the direction in the crystal, which must be considered in the process of cutting. High hardness of corundum makes it suitable not jewelry varieties as an abrasive. Aluminium oxide is the main component of the sandpaper.
Emery, who is second in hardness and inferior in this respect only to diamond, is widely known. Its crystals are mostly bipyramidal and prismatic bipyramidal. Short prism ending pinacoids broad, disk-shaped crystals give the appearance. Mineral forms a complex polysynthetic twins. Such twinning is recognized by the naked eye with difficulty.
 Photo: Prismatic crystals red corundum (ruby, North Mysore, India). At the bottom. The crystals of corundum bipyramidal shape, typical of this mineral.
Photo: Prismatic crystals red corundum (ruby, North Mysore, India). At the bottom. The crystals of corundum bipyramidal shape, typical of this mineral.
If twinning is seen, it is possible to see a lot of densely spaced plates having a clear geometric orientation. Emery has allohromaticheskuyu color: if it is devoid of impurities, it is quite colorless, but if there are a lot of other elements, it becomes colored. Among the species we should mention garmofan (gray and opaque); oriental amethyst (Padparadsha - orange), ruby (red); blue sapphire, emery - granular corundum, mixed with iron oxides. The presence of tiny inclusions oriented in a special way, causes the phenomenon of asterism (star-shaped corundum).
Chemical composition-content (%): Al- 53,2; O - 48.8; observed slight impurities of chromium, iron, manganese, titanium. Trigonal- scalenohedral kind of symmetry. It occurs in the form of crystals bochonkovidnogo, dipiramidalnogo, prismatic, plate appearance. Root simple form:. (0001) (1,010) (1,120) (1,011) (2,241) (2,243), etc. Often, polysynthetic twins observed on the (1011) and (0001). The crystals are often deformed. Face of the prism, and dipyramids pinacoid covered with oblique hatching. Sometimes there separateness and horizontal shading due to twinning on pinacoid. Cleavage - absent.
Diagnostic features.
Many corundum easily separated on the plate along certain planes. But this phenomenon - not a real cleavage, and a special phenomenon called psevdospaynostyu. It is caused by polysynthetic twinning in the form of plates. Emery - only mineral with a hardness of 9. It can only scratch the diamond. Many corundum samples can fluoresce in ultraviolet light.
Origin.
Aluminium oxide - a mineral of metamorphic rocks. It is also found in rocks formed from deep magma rich in silica.
Place of Birth.
Large crystals of this mineral found in ancient rocks in the Urals, in Canada, the United States and Madagascar. Emery otichnogo gem-quality mined in Burma, Thailand, Cambodia, Sri Lanka, Australia, in Montana (USA). Emery produced in Turkey and the island of Naxos in Greece.
Application.
Due to its hardness of corundum is used as an abrasive; but now it is increasingly replaced by synthetic materials. It is used in watch making and precise instrument for bearings and bushings. From it also prepared aluminum. Currently in jewelry corundum is used infrequently - for this purpose it is already more than a century produced artificially.
Aluminium excess in the body (arises in the production of synthetic corundum, rubies and sapphires - from the manufacturing facility operators) reduces resistance to infection, causes anemia, can be nerve poison - paralyzes the central nervous system and heart, causing tremors of the head and convulsions (nervous disorders - actively It affects the nerves directly coming from the brain). Causes "hallucinations electrician" - black spots on the image (up to 10 pcs.) And defects (offset) in the image. Aluminium inhibits the uptake of many vitamins and bioelements (calcium, magnesium, iron, vitamin B6, ascorbic acid), and sulfur-containing amino acids (lose weight).
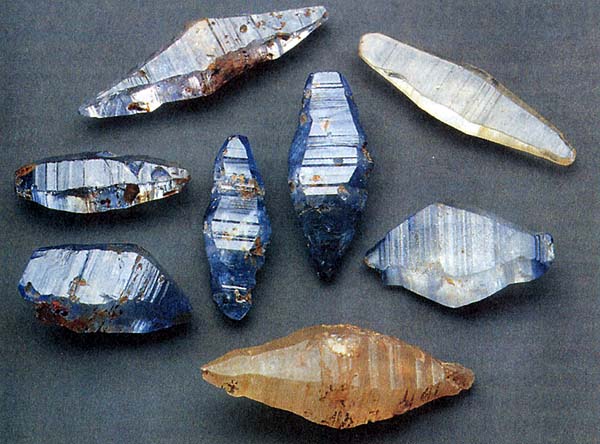

The use in jewelry.
Noble varieties of corundum - ruby and sapphire - are well-known jewelers. Ruby - red variety with a dash of chrome. It is extracted from the dolomitic marbles and alluvial. It comes mainly from the north of Burma, Thailand, Sri Lanka and Tanzania. Transparent rubies are always small: stone discovery in 10 carat an exceptional rarity. Extraordinary items are widely known - a "Rosser-Reeves-Ruby" in the 140-carat (Smithsonian Institution, Washington, DC) and "Long Star-Ruby" (Museum of Natural History, New York), which is a star-shaped ruby of 100 carats. Transparent rubies are exposed exclusively to cut facets; for translucent cabochon preferable. For very large specimens suitable intaglio (incised engraving). In the strict sense of the term "sapphire" applies only to the blue variety of corundum; but quite often so designate all corundum whose color is different from red.
Sapphire is produced mainly from placer alluvial deposits. The main production locations - Australia, Sri Lanka, Burma and Thailand. Sapphires are of exceptional size - it is the "Star of India" in the 563-carat (Museum of Natural History, New York) and the "Asian Star" of 330 carats (Smithsonian Institution, Washington, DC). The most common cut for a transparent sapphire -ovalnaya or round with facets; but also occurs in the form of a heart cut, hook and shelf-baguette.



Corundum: Ruby
The name Ruby has received for the red color (Latin Ruber -. Red). Only in 1800 it was found that ruby and sapphire are varieties of corundum. Prior to this, called ruby and red spinel, and garnet (all three minerals are also called carbuncles). The main chromophore is chromium in the ruby, brownish tones gives the iron. The color of rubies varies as different fields and within the same field, so to judge by the shade of the ruby of the place of origin is impossible.
Such names as "Burmese" or "Siamese" Ruby only misleading and are rather qualitative assessment stones. Most prized rubies "color of pigeon's blood" - a pure red with a slight purple tinge. Painting is often distributed unevenly spots or stripes. The raw stones are dim or shine zhirnovat but faceted ruby sparkles almost like a diamond.
Although cleavage in ruby there, but in certain areas is well defined separately. Fragility fractures and natural ruby determines careful handling them when cutting and pasting a stone in a setting (as opposed to the artificially grown rubies, which are strong enough). Often found in the inclusion of rubies. However, they are not considered defects in the stone, but on the contrary - evidence of their natural origin. The nature of the inclusions (minerals, channels or other cavities) may serve as an indication to the field of ruby. Inclusions of rutile needles give the stone a gentle silky shimmer or - with proper grinding cabochon - the effect of the cat's eyes, or detects highly valued asterism - a six-figure star, moving across the surface of a cabochon in its turn.
Corundum: Sapphire
 Pleochroism: from distinctive blue sapphire - from dark to greenish-yellow, and yellow; have a weak yellow - from greenish-yellow to yellow; have weak green - from yellow-green to green; It has a distinct purple - from purple to pink. Sapphires in ancient times called a variety of blue stones - from sapphire to lapis lazuli. At the beginning of the XIX century. It found that sapphire and ruby are varieties of corundum jewelry.
Pleochroism: from distinctive blue sapphire - from dark to greenish-yellow, and yellow; have a weak yellow - from greenish-yellow to yellow; have weak green - from yellow-green to green; It has a distinct purple - from purple to pink. Sapphires in ancient times called a variety of blue stones - from sapphire to lapis lazuli. At the beginning of the XIX century. It found that sapphire and ruby are varieties of corundum jewelry.
First, a sapphire was called a blue kind of transparent corundum of other colors besides red, appropriated special, purely trade names: for example, green corundum called eastern peridot or oriental emerald, yellow - Oriental topaz, etc. Such names are often misleading... Today, under the name "sapphire" means jewelry corundum of any color other than red - ruby. The color of sapphire is now taken to indicate specifically. For example: green or yellow sapphire. If it says simply "sapphire" - it is only about a blue stone. Colourless sapphire is also called synthetic sapphire, orange and yellow - padparadzha (in Sinhala - "lotus flower").
Sharp boundaries between the pink and purple sapphires and ruby tones do not exist. The bright red, pink and purple corundum is usually referred to as sapphires: because among sapphires are listed pretty high, and rubies they would be considered low-grade. Sapphire blue chromophore are iron and titanium, in the violet - vanadium. A small admixture of ferric gives yellow sapphire, and ferrous - green. Pink shades are caused by chromium-doped. Most prized cornflower blue sapphires of pure water.
The hardness of sapphire is as high as that of a ruby, and as much depends on the direction in the crystal. The anisotropy of hardness is important to consider when cutting. There is no single color luminescence, characteristic of all the sapphires, does not exist - its color depends on the color of its own stone from the mine. Inclusions of rutile needles cause the silky luster of stone, in large quantities - the effect of "cat's eye" and a six-stars: star sapphire. According to some researchers, highly valued and rare sapphire asterism unlike ruby is not due to rutile needles and hollow channels oriented in three directions.
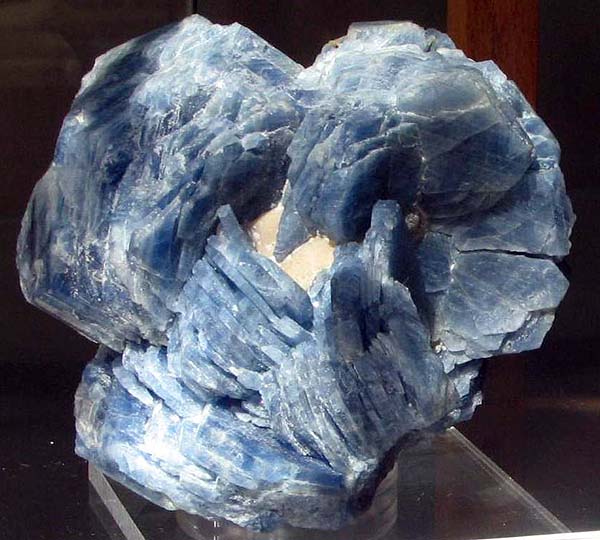

Corundum. The splice split crystals ( "Rose"). Size 11 cm. Ilmen Mountains. South Urals. Photo: © AA Evseev.
- Gatchell - "New Almadén snag" - arsenide and antimony sulfide (modern sulphosalts)
- Antimony - toxic metal (semi-metal) are widely used in industry, medicine and engineering
- Zirconium - a rare and non- metal and dangerous jewel in the oxide and salts
- Gold - yellow dangerous and toxic metal -date and accurate digital cable technology
- Sulphur - a golden-yellow toxic substance and a sign of volcanic activity
- Cadmium - a toxic uncirculated unknown wide range of people silvery metal
- Lead - a poisonous gray simulator silver metal and toxic metal snag
- Arsenic - poison classic medieval and modern poisoners and medicine in medicine
Toxic and hazardous radioactive rocks and minerals
** - Poisonous stones and minerals (obligatory check in chemical laboratory + clear indication of toxicity)
** - Radioactive rocks and minerals (obligatory check on a regular dosimeter + ban on the open sale of radioactivity in the event of more than 24 mR / hour + additional measures to protect the population)
Catalog minerals and gems in groups of the world
** - Poisonous stones and minerals
** - Radioactive rocks and minerals



Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.