Silicates: Thorite
 Diagnostic card.
Diagnostic card.
Th SiO 4
Tsingonia tetragonal
Hardness 4,5-5
Specific weight 4.34-4.8
Cleavage is poor, difficult to manifest
Fracture brittle, brittle
Color from brown-yellow to almost black
Color in powder brown, orange-yellow
Glitter is glassy, greasy
Strongly radioactive.
The crystals of thorite (thorium sulfate) are very similar to zircon (which is also often radioactive), have a prismatic appearance and amorphous structure. The color varies from almost black to brown and yellow (in orangite - an almost transparent crystalline variety of thorite - a dangerous imitator of precious stones). Black, reddish-brown, yellow-brown, orange (orange). Unchanged urano-thorite is transparent, olive green to green - very dangerous; Farritorite brown, dark brown, black, wax-red and red. Often colored unevenly.
The composition varies widely, the ThO2 content ranges from 45 to 75%. The most common admixture of U (from fractions of up to 10% and more UO2), impurities of Fe, Ca, P, Al, Ti are also common. The content of Fe, Ca and P can reach several percent, respectively, in ferritorite, calcitotrite, aurelite (phosphotorite). Differentiation of species in terms of chemical composition is not clear. Granular, crystals and their aggregates (from microscopically small to several cm in length), partly colloformed and even gel-like (reminiscent of the gel-these fractures of the crystal lattice of thorite are caused by high levels of radiation) of the release of this mineral.
Diagnostic signs.
Torite melts in the flame of a candle, dissolves in hydrochloric acid and is very radioactive. After processing the grain of thorite for 4-5 hours. Hot concentrated HC1, it loses Fe and Th (up to 80%); Remains a fragile white non-magnetic skeleton of silica. In a sealed tube, many thorites liberate water; On the coal does not melt, only the edges of the grains are melted; Black thorite becomes calcipary brownish-red and gives a yellowish-brown slag, the orange becomes frosted brown, and after cooling becomes orange again. Hydrochloric acid readily decomposes with the release of gelatinous silica; After calcination it decomposes with difficulty. It gives characteristic reactions with fluxes on U and Fe. It is not analyzed in conventional laboratories and in factories.
Origin.
A typical mineral of some pegmatites, which poses a great danger to the unenlightened, is a radioactive mineral, especially in association with the most dangerous uranium and uraninite, a typical pegmatite mineral, the basic raw material of the nuclear industry (including the military). Beautiful crystals of pegmatite veins, found without the use of dosimetric equipment, can pose a significant danger to the health and life of the incompetent mineralogist "truth-seeker". Pegmatites - the place of basic accumulation of various radioactive minerals that mimic gemstones , so visiting pegmatites without dosimeters and qualified conductor experts is strictly prohibited.
Place of Birth.
Not too common in nature, thorite occurs in the syenite pegmatites of Brevik and Arendal in Norway and in Madagascar, together with zircon, biotite and amphiboles. In association with sulphides, thorite is found in the vein (hydrothermal) deposit of Lemi Pass in the state of Idaho and in the mountains of Bittertur in the state of Montana (USA).
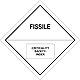
ADR 7


Radioactive materials ( radiation , Ukraine)
Risk of absorption of external and internal radiation exposure
Limit impact time, radiation burns, radiation exposure of photographic and cinematographic materials
Yellow upper half of rhombus, white - lower, equal, ADR number, black sign of radiation, inscription
ADR 7






Radioactive materials
Risk of absorption of external and internal radiation exposure
Limit impact time, radiation burns, radiation exposure of photographic and cinematographic materials
White, yellow upper half of diamond, white - lower, number of ADR, black sign of radiation, text
Active single-component (depleted) radiation materials. A white diamond, one vertical red line at the bottom - there is no nuclear warhead (including a simple hydrogen bomb on a nuclear fuse, depleted uranium, a burning Kosovo warhead, an EU one-component without a nuclear explosion). Competence - metrology of Ukraine.
The yellow diamond, two vertical red lines below - an active single nuclear charge (uranium, a Hiroshima-type nuclear bomb, including multicomponent one-type nuclear warheads, a single-component explosion and a simple chain nuclear reaction - "two in one"). Competence - the police of Ukraine and the military law and order.
The yellow diamond, three vertical red lines at the bottom - an active double raznocomponent nuclear charge (plus deuterium-tritium, a thermonuclear bomb of the "Pacific Ocean" type, including nuclear parts of a duplex warhead, a chain nuclear explosion and a chain reaction of fusion - "three in one") . Competence - the military of Ukraine and the military law and order.
ADR 7E
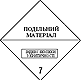
Radioactive materials are divisible (in the process of explosion )
The danger of a nuclear chain reaction (nuclear reaction, explosion). Active single-component (depleted) radiation materials.
White upper half of diamond, white - lower, equal, ADR number, black sign of radiation, text
| The name of a cargo that is particularly dangerous for transportation | room
UN |
Class
ADR |
| RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL WITH LOW SPECIFIC ACTIVITY NPA-I (LSA-I) is not divisible or divisible, radiation is free | 2912 | 7th |
| RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL WITH LOW SPECIFIC ACTIVITY NPA-II (LSA-II) is not divisible or divisible, radiation is free | 3321 | 7th |
| RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL WITH LOW SPECIFIC ACTIVITY NPA-II (LSA-II), DILY | 3324 | 7th |
| RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL WITH LOW SPECIFIC ACTIVITY NPA-III (LSA-III) is not divisible or divisible, radiation is free | 3322 | 7th |
| RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL WITH LOW SPECIFIC ACTIVITY NPA-III (LSA-III), DILY | 3325 | 7th |
| RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL WITH LOW SPECIFIC ACTIVITY NPA-II (LSA-II), DILY | 3324 | 7th |
| RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL WHICH IS TRANSPORTED IN SPECIAL CONDITIONS, DILY | 3331 | 7th |
| RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL, PACKAGING - PRODUCTS MANUFACTURED FROM NATURAL OR LINED URANIUM, OR NATURAL THORIUM | 2909 | 7th |
| RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL, RELEASED PACKAGING - LIMITED QUANTITY OF MATERIAL | 2910 | 7th |
| RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL, RELEASED PACKAGING - EMPTY PACKAGING SET | 2908 | 7th |
| RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL, RELEASED PACKAGING - DEVICES OR PRODUCTS | 2911 | 7th |
| RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL, OBJECTS WITH SURFACE POLLUTION OF RADIOACTIVE ORLS-I OR OPP-II (SCO-I or SCO-II), DELIMIUM | 3326 | 7th |
| RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL, OBJECTS WITH SURFACE RADIOACTIVE CONTAMINATION OF ORPRES-I or OCRP-II (SCO-I or SCO-II), not divisible or divisible-free | 2913 | 7th |
| RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL, PACKAGING TYPE A, not a special kind not divisible or divisible - free | 2915 | 7th |
| RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL, PACKAGING TYPE C, not divisible or divisible - free | 3323 | 7th |
| RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL, PACKAGING TYPE A, SPECIAL TYPE, not divisible or divisible - free | 3332 | 7th |
| RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL, PACKAGING TYPE A, SPECIAL TYPE, DELIMI | 3333 | 7th |
| RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL, PACKAGING TYPE A, DELIMIY, not special type | 3327 | 7th |
| RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL, PACKAGING TYPE B (U) not divisible or divisible - free | 2916 | 7th |
| RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL, PACKAGING TYPE V (U), DELIMI | 3328 | 7th |
| RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL, PACKAGING TYPE B (M) not divisible or divisible - free | 2917 | 7th |
| RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL, PACKAGING TYPE B (M), DELIMI | 3329 | 7th |
| RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL, PACKAGING TYPE C, DELIMI | 3330 | 7th |
| RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL, URANIUM HEXAFLUORIDE, not divisible or divisible - free | 2978 | 7th |
| RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL, URANIUM HEXAFLUORIDE, DELIMI | 2977 | 7th |
| RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL WHICH IS TRANSPORTED IN SPECIAL CONDITIONS not divisible or divisible - free | 2919 | 7th |
- Ghetchellit - "New Almaden blend" - arsenide and antimony sulfide (modern sulfosol)
- Antimony is a toxic metal (semimetal) , widely used in metallurgy, medicine and engineering
- Zirconium - a rare and undiscovered metal and the most dangerous precious stone in oxide and salt
- Gold - yellow dangerous and poisonous metal of modern accurate digital and cable technologies
- Sulfur is a golden-yellow toxic substance and a sign of active volcanic activity
- Cadmium is an undisputed toxic silvery metal unknown to a wide range of people
- Lead - a toxic gray imitator of metallic silver and toxic metal blende
- Arsenic is a classic poison of medieval and modern poisoners and medicine in medicine
Poisonous and radioactive dangerous stones and minerals
** - poisonous stones and minerals (mandatory check in the chemical laboratory + explicit indication of toxicity)
** - radioactive stones and minerals (mandatory check on the standard dosimeter + ban on open sales in case of radioactivity exceeding 24 milli / g / h + additional measures of population protection)
Catalog of minerals and semi-precious stones of the world by groups
** - poisonous stones and minerals
** - radioactive stones and minerals


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.