Sulfides: Wurtz (wurtzite)
 Diagnostic Card.
Diagnostic Card.
Zn S
Crystal system hexagonal
Hardness of 3.5-4
The proportion of 3.9-4.1
Cleavage is good
The break in the wrong
Color from brown to black
Color brown powder
Gloss resin
rare; mass occurs as a layered, columnar fibrous structure. Good crystals are rare. Color yellow-brown to brownish-black, gloss resin to diamond. The name in honor of French chemist Sh.A.Vyurttsa
Typically contains impurities Fe, koichestve but smaller than sphalerite (8%). In contrast Cd impurities are more constant (1-1.5 to 3.7%) to Tsumeb (Namibia) set mineral containing up to 50; Cd. Characterized by small impurities Ge. It sets as small impurity Mn, Pb, Ag, Tl, Sn, Co, As. Isolation: Small up to 2cm pyramidal crystals, usually with bazopinakoidom, underdeveloped or non-existent at one end. Often radiating education.
Diagnostic features.
Orange fluorescence upon irradiation with ultraviolet light.
Origin.
Wurtz found in hydrothermal deposits, often in association with sphalerite, very rarely - in the sediments.
Place of Birth.
Interesting patterns are known in Stolberg in the Rhineland-Sate (Germany), Butte, Montana, and Joplin, Missouri (USA), Oruro and other places in Bolivia, as well as from Romania and England. In Italy, can be found a wonderful crystals of from 1 to 6 mm; while they polychrome - yellow, red and black; geodes found in Carrara marble, together with sphalerite, enargite-how kolusitom, tetrahedrite, geokronitom, gray.

Wurtzite. Czech Republic, EU. (2011).
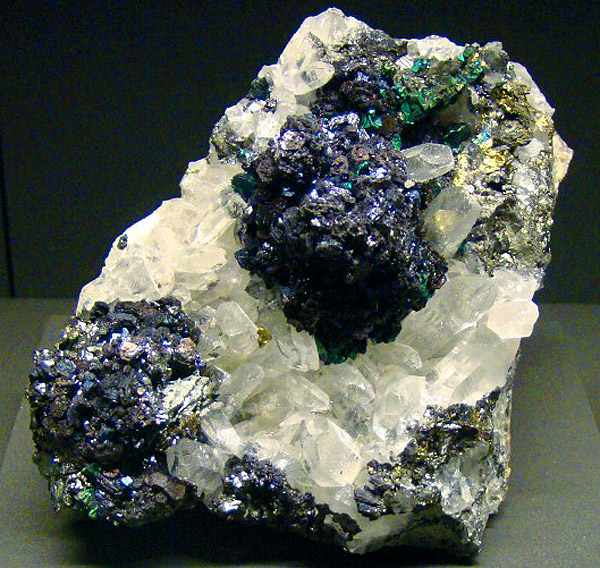

Wurtzite, quartz (white), harkopirit, arsenopyrite. China. (2011).
Thallium (prisutstvet) - toxic to the human body ultramicroelements. Toxicity due to his violation of the ion balance the body's major cations - sodium and potassium. Optimal daily intake of thallium - about 2 micrograms. Thallium is well absorbed in the gut. As well as potassium (equivalent), thallium body accumulates intracellularly. Thallium has a pronounced toxicity due to violation of the ion balance of the body two nervous cations - sodium and potassium ( "palitrogon" brain hallucinations). Oxidizes tissue.
Elevated levels of thallium. Thallium has a pronounced toxicity. The lethal dose for humans - 600 mg. In criminology describes cases of thallium salts use to murder or suicide. Kimberlite chemical element. The risk of poisoning by thallium is present in workers employed in industries such as pyrite roasting, smelting ore (sulphide ores rich in potassium minerals - potassium level II of kimberlite, white), the combustion of coal, production of semiconductors, cement, glass, with the addition of thallium.
Ingested thallium can through contaminated food or dust. The sources of thallium poisoning may be domestic agents: chemicals intended for rodent control - rodenticides (thallium sulfate). In acute poisoning with thallium affects the peripheral nervous system (nerves, hallucinations, according to the "palettes electrician", 10 black spots), central nervous system, heart, smooth muscle, liver, kidney, skin and hair (alopecia - alopecia). Thallium is a diffuse lesion of the neurons of the central nervous system and diffuse hair loss.
Manifestations of excess thallium: severe pain on the type of neuralgia (pain when moving a certain place, the nerves); hyperesthesia of the extremities (from the 4th day after oral admission of thallium), the onset of paralysis, insomnia (ankylosing spondylitis); hysteria; visual disturbances; confusion (psychosis), tachycardia (resistant to treatment by conventional means); destruction of sweat and sebaceous glands of the skin; Hair loss due to violation of the synthesis of keratin (10-13 days after exposure or later). Baldness.
Thallium is needed: Connection and thallium salts are used for hair removal with ringworm - lead to temporary ( "seasonal") baldness. Widespread use of thallium salts in medicine (self) prevents the fact that there is no difference (psychiatry) between therapeutic and toxic doses of salt. Treatment - such as red cinnabar and arsenic (known toxic components Chemotherapy by electrocution in the brain). Silicates and phosphates, alkaline earth metal, thallium-activated, are used in non-psychiatric (general) fizeoterapii (electric shock treatment, microwave, electrotherapy, darsonval).
Food sources of thallium: beets, spinach, grapes, raisins, pomegranates, pears, figs, figs dried, feijoa, soft wheat, Durum wheat, white rice Long grain white rice Round rice unpolished rice wild rye, barley, chicory roots, tobacco.
ADR 5.1
Substances which are oxidized
Risk of vigorous reaction, ignition and explosion in contact with combustible or flammable substances
Do not allow the formation of a mixture of cargo with flammable or combustible substances (eg sawdust)
Yellow diamond, the number of ADR, a black flame over a circle
ADR 6.1
Toxic (Poison)
Risk of intoxication by inhalation, skin contact or ingestion. Constitutes a danger to the aquatic environment or the sewage system
Use a mask for the emergency leaving the vehicle
White diamond, the number of ADR, black skull and crossbones
| Name of especially dangerous during transportation of cargo | room
UN |
Class
ADR |
| Thallium (I) nitrate | 2727 | 6.1 |
| Thallium (I) chlorate | 2573 | 5.1 |
| Thallium compounds, notarized copy | 1707 | 6.1 |
- Gatchell - "New Almadén snag" - arsenide and antimony sulfide (modern sulphosalts)
- Antimony - toxic metal (semi-metal) are widely used in industry, medicine and engineering
- Zirconium - a rare and non- metal and dangerous jewel in the oxide and salts
- Gold - yellow dangerous and toxic metal -date and accurate digital cable technology
- Sulphur - a golden-yellow toxic substance and a sign of volcanic activity
- Cadmium - a toxic uncirculated unknown wide range of people silvery metal
- Lead - a poisonous gray simulator silver metal and toxic metal snag
- Arsenic - poison classic medieval and modern poisoners and medicine in medicine
Toxic and hazardous radioactive rocks and minerals
** - Poisonous stones and minerals (obligatory check in chemical laboratory + clear indication of toxicity)
** - Radioactive rocks and minerals (obligatory check on a regular dosimeter + ban on the open sale of radioactivity in the event of more than 24 mR / hour + additional measures to protect the population)
Catalog minerals and gems in groups of the world
** - Poisonous stones and minerals
** - Radioactive rocks and minerals



Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.