HTTP protocol
For the source, find out for yourself what is the general protocol. Protocol - is a set of rules and key characters, intended for communication between a device. It is necessary for that to computers or their elements can clearly understand the buddy buddy.
Minutes - speaking communication computers on the network.
In fact, just a set of commands allowed to name the protocol, but in practice the concept of protocol applies only to so-called network protocols - language communication computers on the network. Each protocol has a specific purpose and supported by specialized software.
URL, IP and DNS addresses, domains
So URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is the full path of the document. URL is the address at which permitted definitely find the document (file) on the Internet. That line that you type in the box "e" vyshego browser also eat the URL of the document.
URL may possess enough kind of tricky, as sotoyat from various parts. First, consider a simple URL:
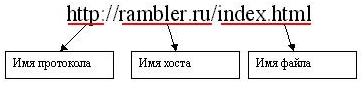
This URL has three constituent elements: the host name where the document, the name of the protocol are used to transmit the document, as the actual name of the act (the file name plus the extension). The base (and the only obligatory share for http protocol) address - a host name. It identifies the machine on which the act (in individual computers hostname network). Each computer on the network is the host also has a unique (to the network) name. In the sample rambler.ru the computer name on which we want to find a document.
Host names can be defined redundant ways: by using the DNS and using IP addresses. An IP address consists of four numbers separated by periods. Each amount may be in the range from 0 up to 255. For example 192.168.2.1.
In practice, however inconvenient to use the IP address as the number of hard to remember. So was vvedna Domain Name System (Domain Name System - DNS), in which each IP address is placed in a relationship or a name consisting of letters or numbers. For example in the above sample DNS name was rambler.ru, as it corresponds to the IP address 217.73.192.109.
It should be noted that different IP addresses prkticheski always correspond to different DNS names, but different DNS names can answer the same IP address. For example, such as a different DNS names, and www.rambler.ru rambler.ru have one well that blah blah IP address. The URL addresses are allowed to use as DNS names, and IP addresses. Thus, the two addresses as URL http://rambler.ru/index.html http://217.73.192.109/index.html equivalent. Some IP address assignment methods are described here http://www.xakep.ru/post/11980/default.htm .
We also note that, in principle, the host does not have to own the domain name. That is, to some hosts are allowed access only by IP address.
You probably already noticed the care that any DNS name consists of several words separated by dots. Each name domain alone means to which the host. The entire DNS system is built in a hierarchical manner. All domains level 1 (com, org, ru, etc.) included in the root domain of level 0 (which is generally not written to because the DNS is the default). another level domains (such as rambler, mail or kiev) come into domains of the main level and etc. The domains in the DNS are written from right to left, in the daily increase in the level.
Note two important features: 1. The domain is purely an administrative unit also is not a host. 2. IP Numbers does not depend on the domain in which the host.
Thus the domain system has been introduced just for the classification of sites by geographical or target attribute, and does not own any relation to the physical device to the Internet.
In privdennom the sample URL that we explicitly asked the name of the act we are interested in the index.html, but there is a document on each site to be opened by default. He holds the position as the name index.html or default.html also located in the root folder of the site. If we enter the URL address of the site does not specify how we want with the file name, the server will automatically open to us an act adopted by default. Thus address http://crackchat.h1.ru equivalent at http://crackchat.h1.ru/index.html. Just as there is a blah blah file opens by default, there is also the Inbox folder by default. In most servers, the default folder for HTTP documents has the name WWW.
After the DNS in the URL must be the name of the act to which we refer. This assumes that the file is in the root folder. If blah blah it does not, then we can specify the full path to the certificate, listing the subfolders through the forward slash:
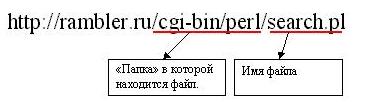
In this example, we refer to a file in the cgi-bin / perl / directory. This path is relative to the root folder. For example, if the path to the root of f: / www, then in our example, we turn to the file f: /www/cgi-bin/perl/search.pl. At the same time proudly note the following: as most of the Web Server is built on the UNIX-like systems, then when specifying the path to the file you need to take into account the difference between lowercase and uppercase letters. So if we refer to the file by URL http://rambler.ru/CGI-BIN/perl/Search.pl, the server would have such a file not found. The difference is also impressive small letters comes only route to a file, DNS is is case-insensitive (that eat rambler.ru address as RAMBLER.RU equivalent).
As mentioned, DNS complies strictly opredelnie IP address, but it does not mean that the DNS name is equivalent to the host to which we refer. Often the host himself alone holds within itself a bottomless domains levels. For example h1.ru site is a host in a domain other level, but he contains the third-level domains, such as crackchat.h1.ru or crosswords.h1.ru. Therefore, the pair belong to a single host site and are naturally the same IP address! Physically, in this case, the third level domains look just like folders on the host disk h1.ru also accessed could be implemented such as: h1.ru/crackchat/ also h1.ru/crosswords/. access means (through the domain of 3rd level or through a disk path) is determined by the server settings.
Root domain is considered to be similar, and therefore the majority of URL addresses are allowed to indicate in a pair of formats: both the www domain (eg www.crackchat.h1.ru), as well as without it (crackchat.h1.ru) - in this case, the server will still automatically directs you to the www folder because it is adopted by default.
Protocols, ports, CGI protocol
As we have seen, URL address consists of three basic Elements: DNS name, file path, and the name of the protocol. If the first pair element can determine the location of the document, the protocol defines how access to the document. In other words, at what time the client attempts to obtain the document, he is forced to tell the server how it (the server) is forced to the act he (the client) to transfer. There are many different protocols of data transmission in the network, including the most common http (Hypertext Transfer Protocol - Hypertext Transfer Protocol), ftp (File Transfer Protocol - file transfer protocol), mailto (prefix mail protocol suite), file (file access protocols or folders). protocol type defines the program that will process the data in the protocol format. Because Internet Explorer can work with protocols http, file and ftp, but it can not work with the mailto protocol. Therefore, if you type in your browser, in the address bar mailto: microsoft.com, then run a specially crafted e-mail program that can work with the protocol (for example Outlook Express or The Bat!). The protocol name indicates the most important in the URL must also be followed by a colon. Register value does not matter.
Among the protocols found quite bizarre such as res protocol or about (for interest can type in the address bar of the browser this address about: <a href="mailto:[email protected]"> send greetings Bill </a> also see what will be the  . Another entertaining ldap protocol (try for example ldap: //microsoft.com).
. Another entertaining ldap protocol (try for example ldap: //microsoft.com).
As a protocol for the URL may not act all protocols. So reports about or javascript does not have any relation to the filling of the route the document, also because "the address" with these protocols are by no URL.
Protocol prefix indicates to the customer on what "language" will flow communication with the server. And the customer knows in advance what the program should keep this communication, which can not be said about the server. In order to be the server began to "talk" with us on the required protocol language, he (the server) has to run an appropriate program that will understand this protocol. To solve this problem, use ports. So if the DNS name or IP address of the machine is determined to which we refer, the port determines the program to which we turn on a given host. Ports designated integer ranging from 0 up to 65,535.
Each protocol is assigned the default port on which the server program will wait for client requests. For example, if the server supports the http protocol, the corresponding server software (eg Apache) will expect client requests on port 80 (the default port of the received protocol http). If this blah blah host supports besides ftp protocol, then the other server program listens on port 21 (the port is reserved for the ftp protocol).
Port to which we refer is determined automatically, depending on what protocol we have chosen in the URL. But the port also allowed to specify explicitly. The port number is specified through the colon after the DNS name or IP address:
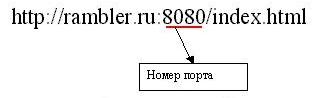
In this sample, we turn to a certain program, "hanging" on port 8080, also claims she has to give us the index.html file via http protocol. If srevere such a program does not appear (then eat requests to port 8080 no program in any way will not be tracked), the browser will give us a message about the wrong URL.
Because the default http server port 80 is adopted, the address http://rambler.ru:80 equivalent at http://rambler.ru. Although in principle, the hosts are not required to maintain it in the http port 80 th. The server can be configured for example to port 3128, also at the time to communicate with the host at http unceasing need to explicitly specify the port number: http://rambler.ru:3128
When accessing the server sometimes it happens it is necessary to specify in addition to act addresses to the same user idntifikator which accesses the server (or to which we turn on the server), but similar to a password. URL allows you to convey this information. To do this, before the DNS name is placed before the @ sign which indicates the user name:
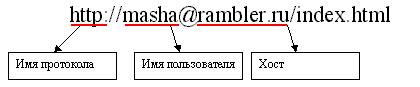
As a rule, for http protocol does not require user authentication, but for protocols such as ftp or mailto she required. In addition to the user name, specify the permitted and access password. Password is no longer on behalf of the colon. For example: ftp: // masha: [email protected]. This URL address requests via ftp root directory of the host yahoo.com for the user masha password kasha. But this address mailto: //[email protected] used to access the user's mailbox in the host masha mail.ru.
Name polzovaetlya similar may exist are structured on the domain principle, also be composed of different elements, separated by a dot. For example mailto: //[email protected].
As mentioned, URL is the full path of the document. Under the act means any file, which can exist as text (eg html or pdf or doc files) and picture (jpg or a gif), and the program. This means that the http protocol if requested in the URL text, or a picture, then they need to be conveyed to the user in order to display them in their browser, but if the requested program or script, then it needs to be run on the server, and send the user to the result of its work. Itself the result can be either text or image. Type rezultirueschego act defined within the program itself, and the user does not know in advance what type of document it receives, causing the program. Call the server program through the normal URL address of the program or script. Typically, in a network using scripts with the extension .pl .php .cgi (the first two represent programs written in Perl and PHP, however, the last extension can be applied for all executables, including also for Perl and PHP also EXE). For example URL http://www.rambler.ru/cgi-bin/top.cgi address is required to run on the host rambler.ru certain application top.cgi also transfer to the customer the result of work of this application (eg html document or image).
But from the server applications have been a little confused if they have to pass parameters was impossible. URL allows it. To pass parameters to server-based applications (also called gateways) using a data format known as CGI (Common Gateway Interface). This format allows the program to set the input data in a single row.
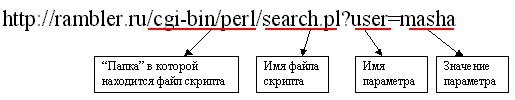
In this sample shows that a URL is called a gateway server also transmits the search.pl as input a parameter called user also zanacheniem masha. CGI string disappears from the script name sign problem? . If the script is necessary to pass multiple parameters, they are listed sequentially by an ampersand & character, for example: http://rambler.ru/cgi-bin/perl/search.pl?user=masha&password=kasha.
Note the following: as most of the WEB technologies based on text data formats, the bright and early or later there is a problem distinguish between code and data. For example, if as a CGI parameter, we want to pass a parameter expression with a value of C = A + B: http://site.com/script.cgi?expression=C=A+B such a request will be misunderstood as another CGI = sign will be perceived as a separator between the parameter name and its value. Therefore, the CGI protocol (as well as in any indoor URL) uses a special character encoding called Data Format URL.
This encoding displays letters of the alphabet as they are, and the rest of the characters in the form% nn where nn - hexadecimal character code. For example the double quote character "will look like 22%, but as a symbol =% 3D exception is the space character, which in addition to the standard coding
HTTP protocol
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) - the main protocol used on the Web. Although the protocol called the hypertext transfer protocol (i.e., HTML), the session on HTTP protocol can be used (and is used) for transmitting data of virtually any network. It also transfer text and images as files. HTTP popularity, in my opinion, is linked to several factors: it is versatile enough to use URL addressing, the ability to transfer any data (such as the customer's server as well as vice versa), but similar work in the no-line mode (ie predachi data directly between customer and server, without intermediaries). HTTP protocol called dual allowed in the sense that the client-server system, data can move in the directions of the pair, also from the customer to the server inside out and from the server to the client. Yet personally HTTP syntax is aimed at data transfer from the customer to the server.
So look at just a sample of the HTTP request. If the browser address window we type the address http://yandex.ru, the browser will identify the IP address of the server will also send yandex.ru his port 80 a HTTP request:
GET http://yandex.ru/ HTTP / 1.0
Accept: image / gif, image / x-xbitmap, image / jpeg, image / pjpeg, application / vnd.ms-excel, application / msword, application / vnd.ms-powerpoint, * / *
Accept-Language: ru
Cookie: yandexuid = 2464977781018373381
User-Agent: Mozilla / 4.0 ( compatible; MSIE 5.5; Windows 98)
Host: yandex.ru
Referer: narod.ru
Proxy-Connection: Keep-Alive
The request is sent in clear text form. The very first query is the share in the first line: This is the type of request (GET), URL address of the requested document (http://yandex.ru) as a kind of HTTP protocol (HTTP / 1.0). Further lists the parameters of the request. Each line corresponds to one parameter. At the source of the line moves the parameter name followed by a colon and parameter value. The meaning of parameter memory is intuitive, but we describe the main ones: Accept - the type of data that can take the browser (encoded MIME). Accept-Language - the preferred language of the browser wants to receive the data. User-Agent - a type of program that sent the request. Host - DNS (or IP) host name to which the request is addressed. Cookie - cookies (data that was stored on the server, the client's local drive, you visit the host last time). Referer - host with kotorgo pages we refer the request. So for example if we are on http://narod.ru page and click there http://yandex.ru link, then the request will be sent to the host yandex.ru, but the referer request field will have the name of the host narod.ru.
A set of query parameters is not fixed. In addition to the above, may also be present other options.
The most interesting parameter memory such as the referer and cookie. These settings are mainly used for user authentication server.
GET request can have the data transmitted by the customer server. they are transmitted directly through the URL for the CGI protocol. For example to enter the chat server, your browser may send a subsequent request:
GET http://chat.ru/? Login = Algol & pass = Algol HTTP / 1.0
Accept: image / gif, image / x-xbitmap, image / jpeg, image / pjpeg, application / vnd.ms-excel, application / msword, application / vnd.ms-powerpoint, * / *
Accept-Language: ru
Cookie: yandexuid = 2464977781018373381
User-Agent: Mozilla / 4.0 ( compatible; MSIE 5.5; Windows 98)
Host: yandex.ru
Referer: narod.ru
Proxy-Connection: Keep-Alive
Kaka we see the query string contains login and password of the user, sent messages through the URL string. Such a data transmission server type is convenient, but has limitations on capacity. Extremely impressive amounts of data can not transmit through the URL. For such purposes, there is another type of zprosov: POST request. Request POST very similar to the GET, with the only difference that only data POST request is transmitted separately from the actual request header. Since the sample in a POST form has the form above:
POST http://chat.ru/ HTTP / 1.0
Accept: image / gif, image / x-xbitmap, image / jpeg, image / pjpeg, application / vnd.ms-excel, application / msword, application / vnd.ms-powerpoint, * / *
Accept-Language: ru
Cookie: yandexuid = 2464977781018373381
User-Agent: Mozilla / 4.0 ( compatible; MSIE 5.5; Windows 98)
Host: yandex.ru
Referer: narod.ru
Proxy-Connection: Keep-Alive
login = Algol & pass = Algol
As we observe the data on the login and password are transmitted separately in the body of the request. Request body should fall away from the header empty string. If the server encounters a blank line in a POST request, then all further moves he considers the request body (transmitted data). Note the following: danyh format in the body of POST request is arbitrary. Despite the fact that most commonly used CGI format, it is not required. Besides POST request does not require a query body may also transmit data through similar URL.
In addition to CGI format, sometimes for transmitting an impressive amount of information (such as files) used the so-called multipart format:
POST http://photo.bigmir.net/form.php HTTP / 1.0
Accept: image / gif, image / x-xbitmap, image / jpeg, image / pjpeg, application / vnd.ms-excel, application / msword, application / vnd.ms-powerpoint, * / *
Referer: http://photo.bigmir.net/form.php
Accept-Language: ru
Content-Type: multipart / form- data; boundary = --------------------------- 7d20345dc
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
User-Agent: Mozilla / 4.0 ( compatible; MSIE 5.01; Windows 98)
Host: photo.bigmir.net
Proxy-Connection: Keep-Alive
Pragma: no-cache
Cookie: Ukrainian = 2;
BSX_TestCookie = Yes;
rich_ad = 1;
b = 1
----------------------------- 7d20345dc
Content-Disposition: form-data;
name = "id"
254353
----------------------------- 7d20345dc
Content-Disposition: form-data;
name = "d"
22
----------------------------- 7d20345dc
Content-Disposition: form-data;
name = "login"
Algol
----------------------------- 7d20345dc
Content-Disposition: form-data;
name = "passw"
Algol
----------------------------- 7d20345dc
Content-Disposition: form-data;
name = "email"
[email protected]
----------------------------- 7d20345dc
Content-Disposition: form-data;
name = "submit"
Add
----------------------------- 7d20345dc--
Let us concern on the title bar of Content-Type: multipart / form- data; boundary = --------------------------- 7d20345dc. This parameter expresses the server that the client sends the data in the format multipart c limiter --------------------------- 7d20345dc. The limiter is generated randomly by the customer is also required to ensure that serevere be able to separate the different elements sent in the request body. As you can see, the body contains a number of elements that are transmitted in ASCII format (but not in Unicode as needed for CGI) also shared that a string that was specified in the parameter memory Content-Type. Each lobe contains information about the type of data transmitted and the name of this part. Comfort multipart format is that the transmitted data have unlimited value also does not require pre-encoding.
In addition to GET requests and POST, there are also others, such as TRACE, PUT. But they are rarely used, and we will not dwell on them.
Another day I will turn the care of the fact that all information transmitted to the client server is contained in the title and body of the request. Another way the server can not get information from the client over HTTP.
On the other hand and the server can transfer to the customer iformatsii only objection to the request. Any exchange danymi in the HTTP protocol is initiated only by the client, the server can not pass anything "just because" but only on request.
Thus, if we possess the ability to control whether the transmitted request, we fully kontrolliruem received by the server and client information. This is useful for modification of transmitted / requested data does not need to change the files of HTML pages, izmenenyat, cookies and so on, but only enough to make changes in the HTTP request and send it to the server. But that is another chronicle  ...
...



