Addresses on the Internet
Any computer connected to the network (no matter the Internet or local network) has a unique electronic address, the Internet address uses an IP address, it consists of 4 digits separated by dots for example: 213.156.69.141 But in order to be easier to remember, the addresses are recorded as a domain name , Consisting of several parts that determine the ownership of the resource. For example, at http://narod.yandex.ru you can see that the resource is in the first level domain .ru , on the server http://yandex.ru.

Superserver.com and superserver.com.
The end point (after com) is called the root domain, or the zero-level domain, it is a database distributed by predefined servers around the world that contains a list of all first-level domains, such as com., Net., Ru. etc
First-level domain:
These are all country codes (en, uk, fr ..) as well as com. Net. Org. ...
The address written in numerical form can be transferred to a domain name and back, using the utility Resolve, which is in the program
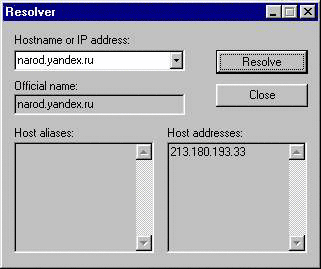
IP Address
The IP address (v.4) is 4 digits, each digit can be from 0 to 255. The entire address consists of the network identifier and the host ID. For example, 121 . 13.54.211. 121 is the network identifier, and 13.54.211 is the identifier of the host, i.e. at this address it is visible that the computer is on the subnet 121 (see Table 1-126 is the address of class A and read about it), and the company's own address is 13.54.211
There are 5 classes of IP-addresses, differing in the number of bits in the network number and host number. Those. In the envy of which figure (octet) begins the address, this class will be. The address class is determined by the value of its first octet. In the addresses of different classes, the identifiers of the network and the node are defined differently, for example, in the class A address, the network identifier is the first octet, and the others designate the nodes (individual computers), ie, there are few networks, but they are large, in the class B address The network identifier already includes two octets, i.e. Networks in this address space is greater than in A but the network is smaller in size because The node identifier consists of two octets, and so on.
| Class | IP Address | Network ID | Node ID |
| A | Abcd | A | Bcd |
| B | Abcd | Ab | Cd |
| C | Abcd | Abc | D |
Class A addresses are intended for use in large public networks.
They allow a large number of node numbers.
Class B addresses are used in medium-sized networks, for example, networks of universities and large companies.
Class C addresses are used in networks with a small number of computers.
Class D addresses are used when accessing machine groups, and class E addresses are reserved for the future.
Class |
The range of the values of the first octet (in the text is highlighted in yellow) |
Possible number of networks |
Possible number of nodes |
A |
1-126 |
126 |
16777214 |
B |
128-191 |
16382 |
65534 |
C |
192-223 |
2097150 |
254 |
D |
224-239 |
- |
268435456 |
E |
240-247 |
- |
134217728 |
In a local network, all computers work through a proxy server (the computer through which all the others are connected), so for "external Internet" all computers have one IP address, but in fact it is not.




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.