An important detail where exactly the stomach hurts - in one of such places there is a serious danger!
Pain in the abdomen and pelvis or gastralgia (from the Greek gastric, stomach + dr.-Greek feel the pain, suffer) - an unpleasant feeling associated with actual or possible tissue damage or described in terms of this damage (definition of the International Association For the study of pain).
Gastralgia (from other Greek pain) - cramping pain in the stomach, usually due to stomach disease. Most common in inflammatory diseases of the stomach, dyspepsia, ulcerative lesions. It also occurs in certain constitutional diseases: gouty diathesis, anemia, hysteria; Often associated with lead colic, sometimes with diseases of the uterus and ovaries.
The abdomen is very large in itself. Therefore, pain in this area can develop for completely different reasons. And to find out the cause and the actual treatment, you need to determine exactly which part of the pain comes from.
Pain in the abdomen is one of the most common complaints. About 90% of people complain about it. Sometimes the intensity is frightening, at other times - the duration. Whatever it was, you can not ignore any ailments in the abdominal area.
If you notice that the pain in a certain area of the abdomen lasts more than 2 weeks , you should definitely consult a doctor, in order to avoid further complications.
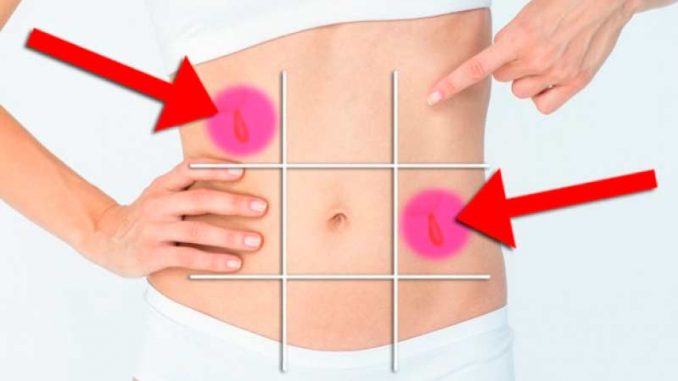
By the belly, we define the part of the body between the chest and groin. Having looked at this diagram and having understood from what area this or that indisposition comes, you can easily identify the problem, which will help to eliminate it in time.
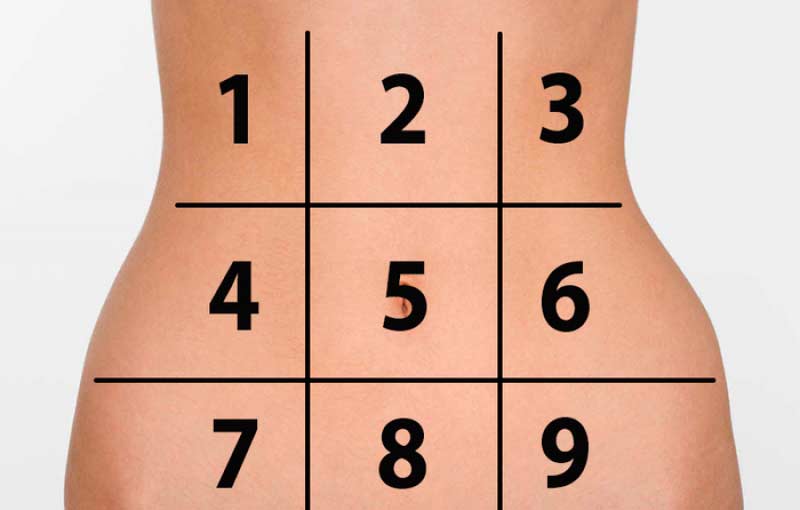

- Stones in the gallbladder, stomach ulcer, inflammation of the pancreas
- Gastric ulcer, heartburn, indigestion, inflammation of the pancreas, gallstones, epigastric hernia (keel above the navel)
- Gastric ulcer, duodenum, blockage of the bile duct, inflammation of the pancreas
- Kidney stones, inflammation of the urinary tract, constipation, lumbar hernia - displacement of the spine!
- Inflammation of the pancreas at an early stage of appendicitis, stomach ulcers, inflammatory bowel disease, small intestine inflammation, Crohn's disease, umbilical hernia
- Kidney stones, diverticular disease, constipation, inflammatory bowel disease
- Inflammation of the appendix, constipation, pain in the pelvis - this may indicate gynecological problems (endometriosis, etc.), and pain in the groin - inguinal hernia
- Urinary canals, appendicitis, inflammatory bowel disease, pelvic pain - again, gynecological problems (diverticular disease)
- Diverticular disease, pelvic pains - gynecological problems, pain in the groin area - inguinal hernia!
 Types of abdominal pain
Types of abdominal pain
Pain is the result of excitation of receptors of damaged tissue. There are two groups of receptors:
- Somatic pain mechanoreceptors (nociceptors), which have a high threshold of sensitivity, their stimulation causes a feeling of pain;
- Visceral polimodal receptors, which, with mild irritation, transmit information about the state of the organ and only give a sensation of pain when strong.
Accordingly, there are three types of abdominal pain: visceral, somatic and reflected. Somatic receptors are richly equipped with a parietal peritoneum (therefore such pains are sometimes called parietal), mesentery, they are in the bile ducts and ureters. This pain is very intense and the patient can well determine its location.
Visceral pain occurs directly in the affected organ. It is painful and usually accompanied by sweating, nausea, vomiting, sharp blanching of the skin. This pain, although with difficulty, can be localized in epigastric, peri-ocular or over the pubic symphysis.
Reflex pain in the abdomen appears with a very intense stimulation of the affected organ and is observed in diseases of the brain, meninges and many internal organs.
There are two main causes of abdominal pain - swelling of the abdominal organs (visceral pain) , and irritability of the peritoneum (somatic pain) . The swelling of any hollow organ (eg, bile duct, thick and small intestine, bladder, ureter, gynecological organs - uterus, fallopian tubes) leads to spasmodic and intermittent abdominal pain. Visceral pain is poorly localized and is usually noted in patients on the midline of the abdomen. The swelling of the anterior part of the digestive tract is usually localized in the epigastric region. Blood supply to the anterior part of the digestive tract is carried out through the celiac arterial trunk. It includes the stomach, duodenum, bile ducts. The bloating of the middle part of the digestive tract is usually localized in the near-buccal region. The blood supply of the middle part of the digestive tract (from the duodenum to the transverse colon) is carried out through the superior mesenteric artery. Inflammation of the lower part of the intestinal locus in the suprapubic region. The blood supply of the lower intestine (from the transverse colon to the rectum) is through the lower mesenteric artery. Unlike visceral pain, somatic pain is well localized. Irritation of the parietal peritoneum as a result of movement or stretching leads to acute pain.
Via tutkryto.su & wiki


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.