Lower jaw
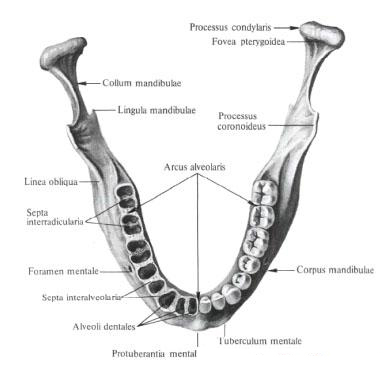
The lower jaw , mandibula, unpaired, forms the lower part of the facial skull . In the bone, a body is distinguished and two processes called branches (go from the posterior end of the body upwards).

The body, corpus, is formed from two mid-line halves (chin symphysis, symphysis mentalis) that join together in one bone in the first year of life. Each half is bent by a bulge to the outside. Its height is greater than the thickness. On the body distinguish the lower edge - the base of the lower jaw, the basis mandibulae, and the upper - the alveolar part, pars alveolaris.
On the outer surface of the body, in its middle sections, there is a small chin protuberance, protuberantia mentalis, outside of which immediately stands the chin, tuberculum mentale. Above and outside of this tubercle is the chin aperture, foramen mentale (the place of exit of the vessels and nerve). This hole corresponds to the position of the root of the second small molar. Behind the chin aperture an oblique line, linea obliqua, goes to the front edge of the mandible branch.
The development of the alveolar part depends on the teeth contained in it.
This part is refined and contains alveolar elevations, juga alveolaria. At the top it is bounded by an arcuate free margin-the alveolar arc, arcus alveolaris. In the alveolar arch 16 (8 on each side) of dental alveoli, alveoli dentales, separated from each other by interalveolar septa, septa interalveolaria.
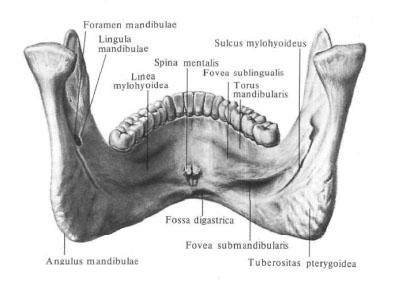
On the inner surface of the body of the lower jaw, near the median line, there is a single or forked chin, spina mentalis (the place of the beginning of the chin-sublingual and chin-lingual muscles). At the lower edge of it there is a depression - a digastric fossa, fossa digastrica, a trail of attachment of the digastric muscle . On the lateral sections of the inner surface, on each side and the direction to the branch of the lower jaw, the jaw-hyoid line passes obliquely, linea mylohyoidea (here the jaw-hyoid muscle and the maxillofacial part of the superior constrictor of the pharynx begin).
Above the jaw-hyoid line, closer to the hyoid awn, is the hyoid fovea, fovea sublingualis, - the trace of the adjoining hyoid gland, and below and behind this line is often a weakly expressed submandibular fovea, fovea submandibularis, the trace of the adjoining submandibular jaw.
The mandibular branch, ramus mandibulae, is a wide bone plate that rises from the posterior end of the body of the lower jaw upward and obliquely backward, forming with the lower edge of the body the angle of the lower jaw , angulus mandibulae.
On the outer surface of the branch, in the angle region, there is a rough surface - chewing tuberosity, tuberositas masseterica, a trace of attachment of the same muscle. On the inner side, respectively chewing tuberosity, there is a smaller roughness - pterygoal tuberosity, tuberositas pterygoidea, a track of attachment of the medial pterygoid muscle.
In the middle of the inner surface of the branch there is an opening of the lower jaw , foramen mandibulae, limited from the inside and from the front by a small bony protuberance - the tongue of the lower jaw, lingula mandibulae. This hole leads to the canal of the lower jaw, canalis mandibulae, in which the vessels and nerves pass. The canal lies in the thickness of the spongy substance of the bone. On the front surface of the body of the lower jaw, it has an exit - the chin hole, foramen mentale.
From the opening of the lower jaw, down and forward, along the upper border of the pterygoid tuberosity, passes the maxillofacial groove, sulcus mylohyoideus (the occurrence of the vessels of the same name and nerves). Sometimes this furrow or part of it is covered with a bone plate, turning into a canal. Somewhat higher and anterior to the opening of the lower jaw is the mandibular cusp, torus mandibularis.
At the upper end of the branch of the lower jaw there are two processes that are divided by the incision of the mandible, incisura mandibulae. The anterior, coronoid, processus coronoidus, on the inner surface often has a roughness caused by the attachment of the temporal muscle. Posterior, condylar, process, processus condylaris, ends with the head of the lower jaw, caput mandibulae. The latter has an ellipsoidal articular surface that participates together with the temporal bone of the skull in the formation of the temporomandibular joint , articulatio temporomandibularis.
The head passes into the neck of the lower jaw, collum mandibulae, on the inner semicircle of which the pterygoid fossa is visible, fovea pterygoidea is the place of attachment of the lateral pterygoid muscle.
You will be interested to read this:









Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.