Spring
One of the features of the newborn's skull is fontanelles, fonticuli cranii. They are ossified areas located in the areas of formation of future seams.
It is known that the cranial vault undergoes structural changes during the intrauterine life.
Initially, it is presented in the form of a membranous formation covering the brain from the top.
Then, bypassing the stage of cartilage, it is gradually replaced by a bone tissue. This transition is characterized by the appearance of bone points that appear in the form of islets in a particular bone. Then these islands merge together, forming large bone plates, which are the bone base of various bones of the cranial vault .
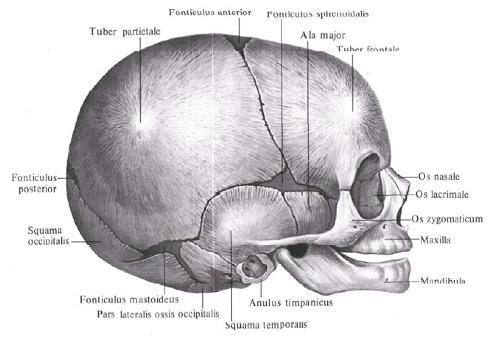
By the time of birth between the bones remain areas of the membranous skull in the form of narrow bands and wider spaces - fontanels , which, due to their elasticity, can either sink or protrude depending on the state of intracranial pressure, creating a semblance of pulsation, in connection with which they received their name . On the skull of the newborn, there are 6 fontanelles, two of them paired and two unpaired. Unpaired are the anterior and posterior fontanelles, to the paired ones are the wedge-shaped and mastoid fontanelles.
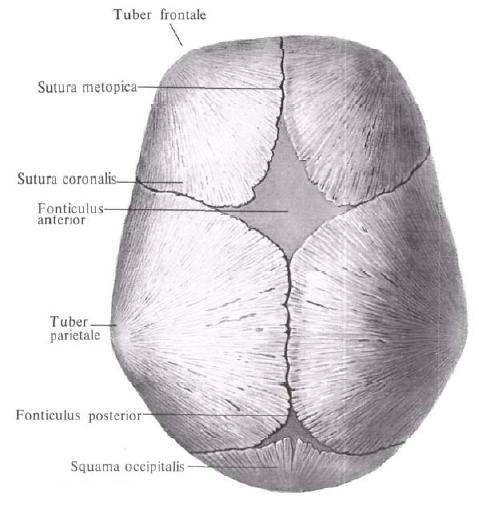
The anterior fontanel, fonticulus anterior, is more often in the form of a rhombus, located at the point of convergence of sutures - sagittal, coronary and metopic. The spring remains until 2 years and by the end of the second year ossifies.
The back fontanel, fonticulus posterior, triangular in shape, is located at the junction of the sagittal suture with the lambdoid. Ossified at the beginning of the first year of life.
The cuneate fontanel, fonticulus sphenoidalis, paired, lies in the anterior part of the lateral surfaces of the skull, between the frontal and parietal bones in front and from above and the large wing of the sphenoid bone and the scaly part of the temporal bone from below. It closes soon after birth, and sometimes even at the end of the intrauterine period.
The mosaic fontanel, fonticulus mastoideus, also paired, is located behind the previous one, at the junction of the occipital scales, parietal bone and mastoid process of the temporal bone. Ossified during the same period that the sphenoid.
The remnants of the membranous skull allow a significant displacement of the bones of the skull during childbirth, which facilitates the passage of the child's head through the narrow places of the birth canal.
You will be interested to read this:









Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.