Glaznitsa
Glaznica , orbita, is a four-sided cavity, the walls of which form an irregularly shaped pyramid.
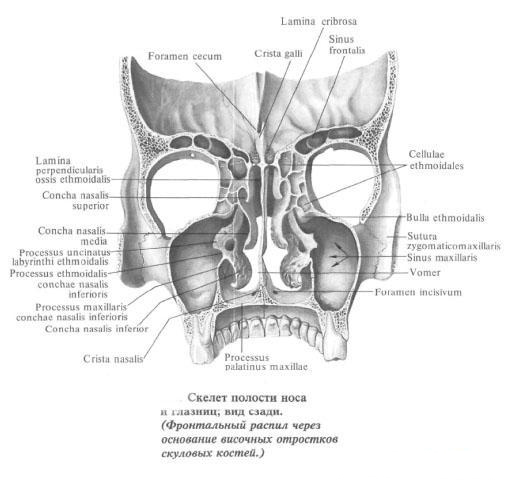
In the cavity of the eye socket there is an eyeball with its muscles, vessels and nerves, as well as tear gland and fatty tissue. The cavity opens anteriorly with a wide entrance to the orbit, aditus orbitae, which is, as it were, the base of the pyramid, bounded by the orbital margin, margo orbitalis. At the entrance itself, the orbit cavity expands, and gradually narrows toward the posterior. The longitudinal axes of both eye sockets, drawn from the middle of the entrance to them to the middle of the visual canal, converge in the area of the Turkish saddle.
Glaznica borders medially with the nasal cavity , from above - with the corresponding part of the anterior cranial fossa, on the outside - with the temporal fossa, from below - with the maxillary sinus.
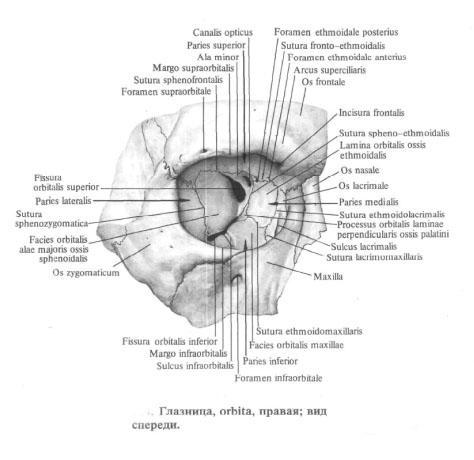
The entrance to the orbit cavity has a contour of a quadrilateral with rounded corners. Above the entrance is limited by the supraorbital margin, margo supraorbitalis. Which is formed by the eponymous edge of the frontal bone and its zygomatic process. On the inside, the entrance to the orbit is limited by the medial margin, margo medialis, formed by the nasal part of the frontal bone and the frontal process of the upper jaw. From below, the entrance to the orbit is formed by the infraorbital margin, margo infraorbitalis, the upper jaw and the adjacent section of the malar bone .
The lateral margin, margo lateralis, the entrance to the orbit forms the malar bone. All orbital walls are smooth.
The upper wall, paries superior, is formed by the ophthalmic part of the frontal bone, and the posterior part of it - by the small wings of the sphenoid bone . Between these two bones is a wedge-frontal suture, sutura sphenofrontalis. The root of each small wing has a visual canal, canalis opticus, through which the optic nerve and the eye artery pass. At the anterior edge of the upper wall, closer to the lateral corner of it, is the pit of the lacrimal gland, fossa glandulae lacrimalis, and anterior and inward from the margin - a block fossa, fovea trochlearis, and bloc awn, spina trochlearis.
The lateral wall of the orbit, paries lateralis orbitae, is formed in the posterior part by the orbital surface of the large wing of the sphenoid bone, in the anterior - by the orbital surface of the zygomatic bone. Between these bones is a wedge-cheek suture, sutura sphenozygomatica. The upper and lateral walls are separated from each other by the superior globular fissure, the fissure orbitalis superior, which lies between the large and small wings of the sphenoid bone. On the orbital surface of the malar bone there is a cheek-eyed orifice, foramen zygomaticoorbitale.
The lower wall of the orbit, paries inferior orbitae, is formed mainly by the ophthalmic surface of the maxilla, as well as part of the orbital surface of the malar bone and the orbital process of the palatine bone. Between the lower edge of the ophthalmic surface of the large wing and the posterior edge of the orbital surface of the maxilla is the lower glandular fissure, fissura orbitalis inferior, reaching the anterior end to the malar bone. Through this gap the orbital cavity communicates with the pterygo-palatine and inframammary fossa. At the lateral margin of the orbital surface of the upper jaw, an infraorbital fissure begins, sulcus infraorbitalis, which passes into the infraorbital canal, canalis infraorbitalis, lying in the thickness of the anterior sections of the orbital wall of the orbit.
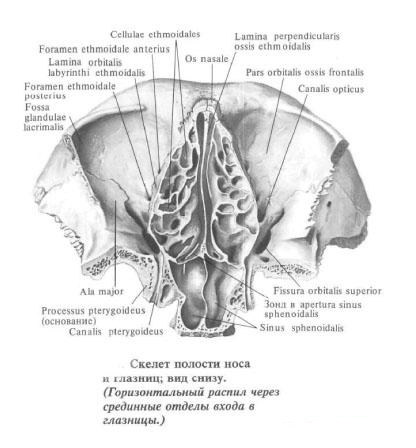
The medial wall of the orbit, paries medians orbitae, is formed (from the front back) by the lacrimal bone, the orbital plate of the latticed bone and the lateral surface of the body of the sphenoid bone. In the anterior wall there is a tear sulcus, sulcus lacrimalis, continuing into the fossa of the lacrimal sac, fossa sacci lacrimalis. The latter passes down to the nasolacrimal canal, canalis nasolacrimalis.
On the upper edge of the medial wall of the orbit are two holes: the anterior latticed aperture, foramen ethmoidale anterius, at the anterior end of the frontal-latticular suture, and the posterior latticed aperture, foramen ethmoidale posterius, near the posterior end of the same suture. All the walls of the orbit converge near the optic canal, which connects the eye socket to the skull cavity. The walls of the eye socket are covered with a thin periosteum.
You will be interested to read this:









Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.