Pancreas. structure
The pancreas, pancreas, is a complex alveolar gland of mixed secretion, has two parts: the exocrine (excretory, or exocrine) part of the pancreas, pars exocrina pancreatis and the endocrine part of the pancreas, pars endocrina pancreatis; The latter in the form of islets is located in different parts of the parenchyma of the pancreas.
The parenchyma of the gland consists of pancreatic vesicles, acini, which have excretory ducts (exocrine part), and pancreatic islets, insulae pancreaticae (islets of Langerhans), which are glandular formations of internal secretion of the pancreas (endocrine part). 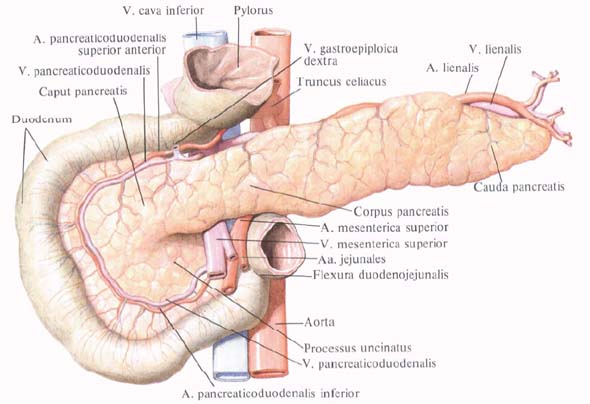
Pancreas - structure
Pancreatic islets, like the entire pancreas, being derived from the endoderm, develop from the glandular epithelium of the duodenum. They are oval or rounded formations up to 0.3 mm; Some of them reach 1 mm in diameter. The islets are located throughout the thickness of the pancreas, most of them in the tail. They have no outlet ducts.
In the surrounding tissue, the spicules are distinguished by their yellowish color.
The number of islets at an early age is not the same: in fruits and in the first years of life there are more of them; With age, the number of them gradually decreases.
The islets consist of epithelial cells surrounded by a connective
A tissue containing a dense network of blood capillaries of sinusoidal sinus.
Some authors believe that the total mass of islands is approximately 1/35 - 1/100 of the mass of the entire pancreas.
Cells of pancreatic islets produce insulin hormones and
Glucagon, which enter the bloodstream and regulate carbohydrate metabolism.
Innervation: plexus celiacus, hepaticus, lienalis send nerve trunks, partially surrounding the pancreatic vessels, partially going outside the vessels; In addition, a number of stems that innervate the stomach and duodenum, also send branches to the pancreas.
Blood supply : the head of the pancreas from the side of its anterior surface - aa. Pancreaticoduodenales superiores, anterior and posterior, branches a. Gastroduodenalis (from a hepatica communis); The head of the gland is predominantly on the side of its posterior surface - aa. Pancreaticoduodenales inferiores, branches a. Mesenterica superior (or a. Jejunalis); These arteries anastomose with each other on the surface of the organ and in its thickness; Body and tail of the gland - a. Lienalis, rr. Pancreatici. Venous blood flows from the head of the pancreas by vv. Pancreaticoduodenales in v. Mesenterica superior, from the body and tail of the gland by vv. Pancreaticae in v. Lienalis; Venous blood from the pancreas flows into the portal vein system. Lymphatic vessels are sent to the celiac, pancreatic and splenic lymph nodes.









Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.