Hip bone
Pelvic bone , os coxae, paired, in children consists of three separate bones: iliac, ischial and pubic. In an adult, these three bones coalesce into a single pelvic bone. 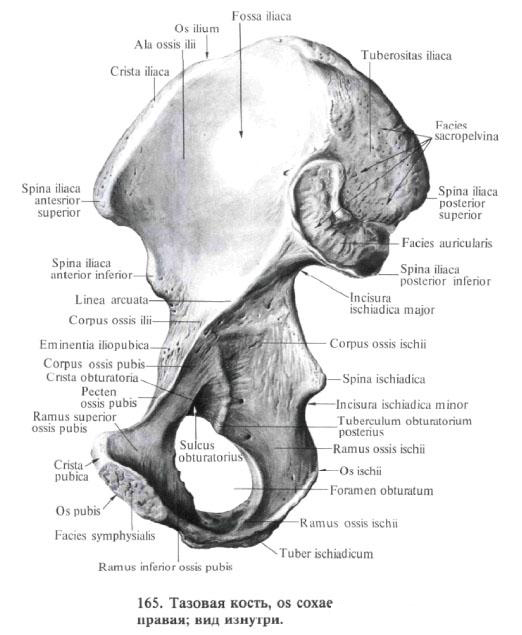
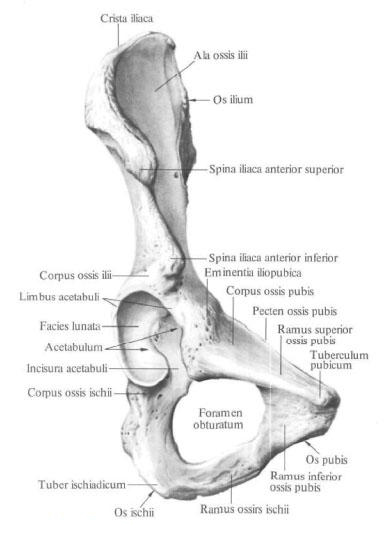
The bodies of these bones, joining together, form on the outer surface of the pelvic bone acetabulum. The iliac bone represents the upper part of the acetabulum, the ischium - the posterior and the pubic bone - the anterior section. In the process of development in each of these bones, there are independent points of ossification, so that until 16-17 years of age in the acetabulum, the iliac, ischial and pubic bone are joined by cartilage. Further, the cartilage ossifies and the borders between the bones are smoothed out.
The acetabulum acetabulum is confined to the thickened edge of the acetabulum, limbus acetabuli, which in the anterior section is interrupted by a notch of the acetabulum, incisura acetabuli.
Inside this edge, the inner surface of the acetabulum carries a smooth
Articular semilunar surface, facies lunata, which limits the acetabulum fossa located at the bottom of the acetabulum; fossa acetabuli.
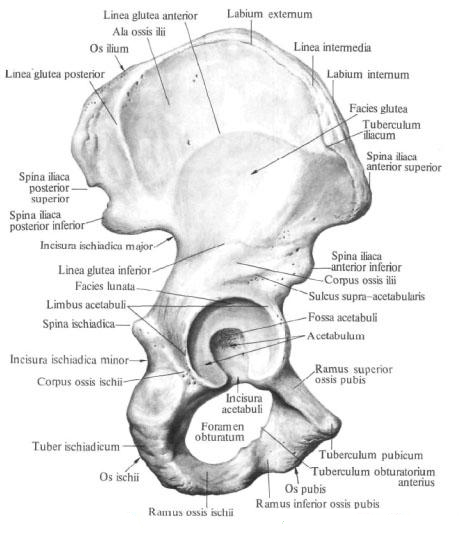
The ischium , os ischii, consists of two parts: the body of the ischium, corpus ossis ischii, and the bent at the angle of the branch of the ischium, ramus ossis ischii.
The body of the bone forms the posterior part of the acetabulum. On the back surface of the body there is a bone protrusion - the ischium head, spina ischiadica. Above and behind it is a large sciatic fillet, incisura ischiadica major, under it - a small sciatic fillet, incisura ischiadica minor.
At the anterior margin of the ischium, in the upper part, there is a posterior obturator, tuberculum obturatorium posterius. On the posterior surface of the curved section of the branch there is a thickening with a rough surface - the ischial tuber, tuber ischiadicum. The lower part of the branch in the anterior part fuses with the lower branch of the pubic bone, ramus inferior ossis pubis.
The pubic bone , os pubis, consists of three parts: the body and two branches - the upper branch of the pubic bone, ramus superior ossis pubis, and the lower branch of the pubic bone, ramus inferior ossis pubis.
The body of the pubic bone, corpus ossis pubis, forms the anterior section of the acetabulum and directly passes into the upper branch, which is directed forward, downward and medially.
The upper edge of the upper branch is pointed and is called the crest of the pubic bone, pecten ossis pubis. Ahead the ridge ends with the pubic tubercle, tuberculum pubicum. The lower edge of the upper branch is acute and is called the blocking crest, crista obturatoria. The anterior end of this crest forms the anterior inhibitory tubercle, tuberculum obturatorium anterius. Inside of it extends the pubic comb, crista pubica, to which the rectus abdominis is attached. The anterior part of the upper branch passes at an angle to the lower branch. On the medial surface of the upper branch there is a rough symphysial surface, facies symphysialis.
The branches of the pubic bone along with the sciatic bone limit the locking hole, foramen obturatum. On the upper edge of this hole, a wide locking groove, sulcus obturatorius, in which the vessels of the same name and the nerve are located, lies in front of the medial and medially.
You will be interested to read this:









Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.