Caffeine in our body. What consequences?

Caffeine (also matein, guaranin) is a purine-type pseudoalkaloid, colorless or white bitter crystals. It is a psychostimulant, found in coffee, tea and many soft drinks. Caffeine is found in plants such as coffee tree, tea, cocoa, mate, guarana, cola, and some others. It is synthesized by plants to protect against insects that eat leaves, stems and grains, and to encourage pollinators.
How many times have I heard the phrase "Without coffee I can not!". Well what can I say? - you have big problems, friends. Read below and VNIKA;)
In animals and humans, it stimulates the central nervous system, enhances cardiac activity, accelerates the pulse, causes the expansion of blood vessels (mainly the vessels of skeletal muscles, brain, heart, kidneys), increases urination, reduces platelet aggregation. This is due to the fact that caffeine blocks the enzyme phosphodiesterase, which destroys cAMP, which leads to its accumulation in cells. CAMP is a secondary mediator through which the effects of various physiologically active substances, primarily adrenaline, are realized. Thus, the accumulation of cAMP results in adrenaline-like effects.
In medicine, caffeine is used as a part of the remedies for headache, migraine, as a stimulant of respiration and cardiac activity for colds, to increase mental and physical performance, to eliminate drowsiness. Dosages for caffeine should be selected individually. Higher doses for adults inside: single 0.3 g, daily 1.0 g, intravenously: single 0.4 g, daily 1 g.
Caffeine is on the list of vital and essential medicines.
History of the discovery
It was discovered and named "caffeine" in 1819 by the German chemist Ferdinand Runge.
In 1827, Oudry isolated a new alkaloid from tea leaves and called it thein. Caffeine in its pure form was first obtained in 1828 (Pelletier and Cavant). In 1832, its composition was established by Weller and Pfaff with Liebig. In 1838, Iobst and G. Ya. Mulder proved the identity of theine and caffeine.
The structure of caffeine was clarified by the end of the XIX century by Hermann Emil Fischer, who was also the first person who artificially synthesized caffeine. He won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1902, which he received partly because of this work.
Chemical structure and properties
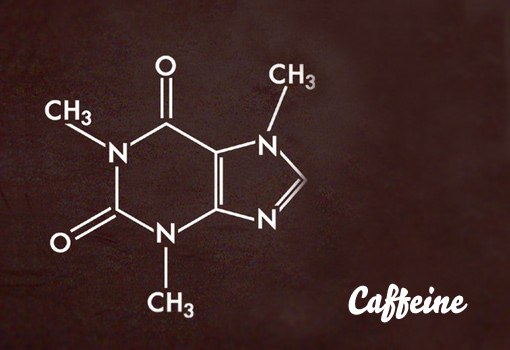
The chemical name of caffeine is 1,3,7-trimethyl-xanthine. In an alkaline medium (at pH> 9), it turns into caffeine C7H12N4O. By its structure and pharmacological properties, caffeine is close to theobromine and theophylline; All three alkaloids belong to the group of methylxanthines. Caffeine acts better on the central nervous system, and theophylline and theobromine - as stimulants of cardiac activity and mild diuretics.
Caffeine, like other purine alkaloids, gives a positive murexide reaction, when heated with Nessler's reagent, caffeine forms a red-brown precipitate, unlike theobromine, giving under such conditions a light brown color.
Physical properties
White needles are bitter taste, odorless. It is soluble in chloroform, poorly soluble in cold water (1:60), easily - in hot (1: 2), it is difficult to be soluble in ethanol (1:50). Solutions have a neutral reaction; Sterilized at + 100 ° C for 30 minutes. ??? m.p. 234C
As soon as caffeine enters the blood, our body receives a signal of attack. He introduces a state of emergency and conducts general mobilization for his defense. Pupils dilate to better see the threat, the pulse is increasing and blood pressure is increasing to better supply blood to the muscles. Mobilizing all forces to protect themselves and striving to increase the blood supply of muscles, the body takes the digestive system a secondary role and translates it into a "dependent ration". Therefore, coffee lovers often have digestive problems.
The liver, switching to the "fight or run" mode (the body's response to stress), saturates the blood with sugar and fats. Caffeine stimulates the work of the nervous system of the adrenal glands, leading the body to a state of full "combat readiness".
And you thought that coffee gives you strength! The human body can not often be in such a high degree of stress without serious health consequences, such as heart attacks and hypertensive crisis. For such a caffeine "explosion" your body pays too much. In the morning you feel a retardation and lethargy. You need to drink again a cup of coffee, and the vicious circle closes again.
"Using stimulants is like pushing a horse. They act for a short time, but with constant application lead to catastrophic consequences. " Stephen Chernysky, "Coffee Blues".
Many people use coffee to stimulate bowel evacuation. On an empty stomach, coffee acts as a laxative. However, it is not coffee that stimulates defecation. A cup of hot water with lemon and natural honey will have exactly the same effect. In fact, coffee consumption, on the contrary, often leads to constipation. Caffeine draws water from the digestive tract, which makes the stools harder.
And any food, eaten after a cup of coffee, will not be fully digested and digested, because the blood supply to the digestive tract is weakened.
Caffeine exacerbates many problems, such as dry skin, itching and tremor of hands. Like nicotine and alcohol, caffeine is a vasoconstrictor that worsens the supply of moisture and blood to the skin. Strengthening dehydration, caffeine accelerates the aging process. And this means premature appearance of wrinkles and folds on the skin and a decrease in the efficiency of metabolism.
There is also much evidence that after drinking a cup of coffee from the body with urine, nutrients are excreted.
Caffeine leads to the loss of thiamine and other B vitamins, which provokes disturbances in the body's nutrition. It reduces the absorption of iron and can cause its deficiency in the body. The phosphoric acid contained in coffee makes it hard to absorb calcium. The data of the carried out researches testify to the raised risk of fractures at the women using caffeine. And if caffeine is mixed with sugar, then the body's losses of mineral substances even increase.
You drink a cup of coffee, and after two hours so necessary for the body of calcium, magnesium and potassium are in your urine! Where did they come from? Of course, not from the coffee you drank!
The detoxification of caffeine is made by the liver, which creates for it an extra overload.
Caffeine is a psychotropic drug, the same as morphine, nicotine and cocaine. The lift you experience during its reception has a cumulative effect and quickly becomes addictive.
Caffeine can provoke errors in replication of DNA and RNA, which in turn leads to a failure in the transfer of biological information.
Coffee interferes with a sound sleep, and that's why, in order to come back in the morning, you need another dose of this drink. Coffee contains not only caffeine, but also a large number of toxic chemicals. Some of them are carcinogens.


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.