How the ECG is conducted and how to prepare for the patient

Electrocardiography is a technique for recording and examining the electric fields produced by the heart. Electrocardiography is a relatively inexpensive, but valuable method of electrophysiological instrumental diagnostics in cardiology. The direct result of electrocardiography is the production of an electrocardiogram (ECG).
Electrocardiography underlies many diagnostic studies - Holter monitoring, bicycle ergometry, esophagus ECG recording, ECG with the use of medications, remote ECG, monitor monitoring in intensive care units or during surgeries. The cardiogram is a record of the electrical activity of the heart, which is produced from the patient's body surface - from the upper and lower extremities and the chest. To record the ECG (depending on the type of apparatus), electrodes, special suction cups and cuffs are used. ECG removal takes 5-10 minutes. The ECG is recorded at a different rate. Usually the paper speed is 25 mm / sec. The 1 mm of the curve is 0.04 sec. Sometimes for more detailed record use speed of 50 and even 100 mm / s use. With a long recording ECG for saving paper use a lower speed - from 2.5 to 10 mm / sec.
In a new cycle of articles, we will tell you about the specifics of the ECG procedure, as well as how to properly prepare for it and be able to independently decipher the results obtained by comparing your own indicators with the norm.
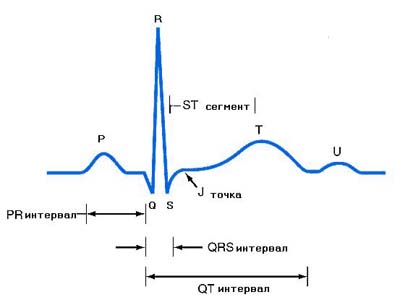
Electrocardiography (ECG) is a non-invasive test, which provides valuable information on the condition of the heart. The essence of this method consists in recording the electrical potentials that arise during the operation of the heart and in their graphic display on a display or paper.
A bit of history. Interest in the electrical activity of the heart appeared in the XIX century. German scientists R. Kelliker and I. Muller in 1856 found electrical phenomena in the contracting heart muscle. English physiologist R. Waller in 1873 produced the first record of the electrical activity of the human heart. In the early twentieth century Dutch physiologist Willem Einthoven introduced the ECG into clinical practice. In fairness, it should be said that Einthoven recorded only three standard leads - I, II and III (the "triangle of Einthoven"). Three more leads (amplified leads from the extremities - aVR, aVL, aVF) were proposed in the 1920s by Goldberger. A little later Wilson suggested recording the thoracic leads (V1-V6). So the current classical ECG of 12 leads was formed. In order to understand what revolution electrocardiography produced in medicine, it is enough to say that in 1924 the ancestor of the ECG Willem Einthoven received the Nobel Prize.
ECG How to Prepare
Contrary to the opinion of cardiologists, it is accepted that the ECG does not require special preparation. Examination of the work of the heart muscle requires avoidance of stress, fatigue, and requires complete rest. On the day of the procedure, you need a good night's sleep, and ignore the morning exercises. If the procedure is scheduled for the morning, you should avoid a hearty breakfast, and it is better to give it up altogether. With the upcoming day treatment, you should limit yourself to an easy snack 2 hours before the session.
Do not forget to reduce the amount of fluid intake that affects the work of the muscle. Give up coffee, tea and other energy drinks. They will contribute to stimulating cardiac activity, and the results will be distorted.
It is advisable to take a shower. The body does not need to apply care products, because the components of creams and lotions, will contribute to the formation of a greasy film on the surface, which will adversely affect the contact of the electrodes with the skin.
Just before you hold the ECG, try to relax as much as possible. Sit with your eyes closed, regain your breath - this will ensure a smooth pulse and objective readings of the device.
Is ECG harmful?
On a logical question about whether ECG is harmful, you can answer based on the advantages of this diagnostic method:
- Reliability of information
- Safety and comfort of the session
- Efficiency (10min)
- No restrictions on health or pregnancy
As you already understood, it is impossible to damage the health of the ECG, since this method is based on the removal of cardiac rhythm parameters and does not produce any radiations or effects on the body. Moreover, people whose work is associated with constant physical exertion, electrocardiography is done almost daily, which once again confirms its absolute harmlessness.
Procedure Procedure
How is the ECG performed if the time is right?
You will be asked to remove the outer clothing so that nothing interferes with access to the chest, and release the lower leg. Places where the electrodes will be fastened, treated with alcohol, which will apply a special gel.
The next step is to fasten the cuffs and suckers. They are fixed on the hands, in the ankles and chest. Ten electrodes will follow the rhythm of the heart, and give out an encrypted result.
The heart plays the role of an electric generator. The tissues of the body have a high degree of electrical conductivity, which allows one to note the electrical impulses of the heart, applying electrodes to the parts of the body. Indications of biopotentials are processed by the electrocardiograph, and provides data in the form of a summary picture - the propagation of excitation signals along the muscle in a graphic image. Specifically, the difference in electrical voltage.
Propagation of the pulse along the heart leads to the depolarization of myocardial cells, during which a part of the cells acquires a positive charge, the other part - a negative one. So there is a potential difference. In the case of complete depolarization (contraction) or repolarization (relaxation) of cells, the voltage difference is not marked. The device records EMF - electromotive force of the heart.
After the ECG is performed, the doctor gets an idea of the organ's functioning and the available deviations.
An electrocardiogram can reveal:
- Arrhythmia
- Ischemia
- Myocardial infarction
How often ECG to do
As we have already explained, this method is absolutely harmless to the body. So you can forget about the risk of getting any complications from frequent monitoring of the heart muscle. On the contrary, the portal "All about hypertension" recommends conducting an electrocardiography in the event of the first disturbing symptoms and discomfort.
The reason for ECG are:
- Discomfort in the chest
- Dyspnea
- excess weight
- Chronic stress
- tachycardia
- Rapid rhythm
- Suspicion of hypertension
Of course, one should not be checked daily - it's simply pointless. However, the decision about the frequency of the ECG should be made by the attending physician, based on an anamnesis.
Doctors recommend people after the age of 40 to examine the heart every year, and representatives of a more mature age - 1 time per quarter.
The resulting cardiogram will be interpreted and, if necessary, treated. Remember that the disease is better to warn in advance.
In the following articles, we will look at the example of a ready-made cardiogram for its interpretation and compliance.
Via vse-o-gipertonii.ru


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.