Antioxidants in food
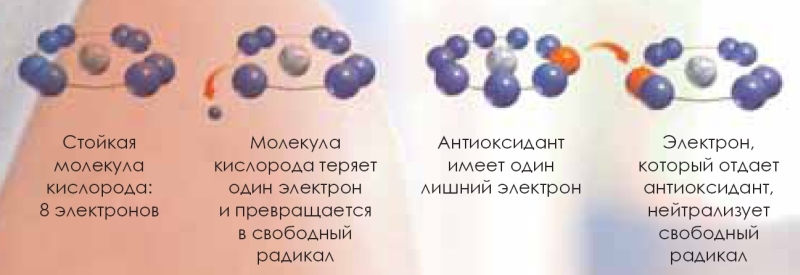
Antioxidants (antioxidants, preservatives) are oxidation inhibitors, natural or synthetic substances that can slow down oxidation. They are considered mainly in the context of the oxidation of organic compounds.
The most well-known antioxidants are ascorbic acid (vitamin C), tocopherol (vitamin E), B-carotene (provitamin A) and lycopene (in tomatoes). They also include polyphenols: flavin and flavonoids (often found in vegetables), tannins (in cocoa, coffee, tea), anthocyanins (in red berries).
SV Okovity (2009) offers the following classification of antioxidants:
- Antiradical drugs
- Endogenous compounds: a-Tocopherol (vitamin E), B-carotene (provitamin A), retinol (vitamin A), ascorbic acid (vitamin C), reduced glutathione (tothionyl), a-lipoic acid (tiocycid), carnosine, ubiquinone Kudesan)
- Synthetic drugs: ionol (dibunol), thiophene, acetylcysteine (ACTS), probucol (fenbutol), succinobukol (AGI-1067), dimethyl sulfoxide (dimime), tirilazad mesylate (fidox), emoxypin, olifene (hypoxenum), echinochrome A ), Preserving (NXY-059)
- Antioxidant enzymes and their activators
- Preparations of superoxide dismutase: eroside, orgothein (peroxinorm)
- Feruloxidase preparations of ceruloplasmin: ceruloplasmin
- Activators of antioxidant enzymes: Sodium selenite (selenase)
- Free radical scavengers: allopurinol / milurite, oxypurinol, antihypoxants
Antioxidants are found in large quantities in prunes, fresh berries and fruits, as well as freshly squeezed juices, fruit drinks and mashed potatoes. Antioxidants rich in berries and fruits include sea-buckthorn, blueberries, grapes, cranberries, mountain ash, chokeberry, currants, garnets, mangosteen, acai.
Antioxidants are rich in nuts and some vegetables (beans, feces, artichokes), and in the second case, excessive antioxidants can interfere with the body's absorption of iron, zinc, calcium and other trace elements.
Other products containing antioxidants include cocoa, red wine, green tea and, to a lesser extent, black tea.
Oxidation of hydrocarbons, alcohols, acids, fats and other substances by free oxygen is a chain process. Chain reactions of transformations are carried out with participation of active free radicals - peroxide (RO2 *), alkoxy (RO *), alkyl (R *), and also active oxygen species (superoxide anion, singlet oxygen). Chain branched oxidation reactions are characterized by an increase in the rate during the transformation (autocatalysis). This is due to the formation of free radicals in the decay of intermediate products - hydroperoxides, etc.
The mechanism of action of the most common antioxidants (aromatic amines, phenols, naphthols, etc.) is the breakage of the reaction chains: the antioxidant molecules interact with the active radicals to form low-activity radicals. Oxidation is also slowed down in the presence of substances that destroy hydroperoxides (dialkyl sulfides, etc.). In this case, the rate of formation of free radicals decreases. Even in a small amount (0.01-0.001%), antioxidants reduce the oxidation rate, therefore, oxidation products are not detected during a certain period of time (inhibition, induction). In the practice of inhibition of oxidative processes, the phenomenon of synergism - mutual enhancement of the effectiveness of antioxidants in the mixture or in the presence of other substances - is of great importance.
Below we present the summary tables of the content of antioxidants in food.
Recall antioxidants neutralize free radicals, which, in turn, are one of the main causes of aging and many degenerative diseases.
Plants are forced to exist in such environmental conditions from which they need to be protected.
For protection, they produce different protective substances, including antioxidants, antioxidants.
Using these plants for food, we also protect our body from free radicals and souring them to the called.
Studies of the presence of antioxidants in food were conducted at the Boston University in the United States.
Two tables are given, because different methods were used to measure antioxidants in products.
We need to pay attention to the fact that with equal amounts of antioxidants we usually eat different amounts of each product.
For example, in some spice there can be as many antioxidants as in beans, but it is obvious that we can eat much more beans, so we should give it an advantage.
In addition, it is important to look at the calorie content of foods.
For example, the amount of antioxidants in prunes is one of the largest, but its caloric value is high - it's better not to abuse it and there is not in addition to the rest of the products, but instead of sweets, rolls, etc.
Summary table of the content of antioxidants in food
| PRODUCT | ANTIOXIDANT ABILITY / GRAMMAR | |
| FIVE BEST BERRIES AND FRUITS: | ||
| Cranberry | 94.56 | |
| Blueberries (wild plants) | 92.60 | |
| Black plum | 73.39 | |
| Plum (type not specified) | 62.39 | |
| Bilberry (cultivated) | 62.20 | |
| FIVE BEST VEGETABLES: | ||
| Small red beans | 149.21 | |
| Conventional red beans | 144.13 | |
| Beans (color is not defined) | 123.59 | |
| Artichokes | 94.09 | |
| Black beans | 80.40 | |
| FIVE BEST NUTS: | ||
| Pecans | 179.40 | |
| Walnut | 135.41 | |
| Hazelnut, hazelnut | 135.41 | |
| Pistachios | 79.83 | |
| Almond | 44.54 | |
| FIVE BEST SPICES: | ||
| Carnation | 3144.46 | |
| Ground cinnamon | 2675.36 | |
| Oregano leaf | 2001.29 | |
| Turmeric | 1592.77 | |
| Dried parsley | 743.49 | |
| AND FURTHER: | ||
| Cacao Grated | 1031.90 | |
Antioxidants in the top 10 antioxidant products per 100 grams
| Fruit: | Vegetables: | ||
| Prunes | 5,770 | Cabbage | 1,770 |
| Raisins | 2,830 | Spinach | 1.260 |
| Blueberries | 2,400 | Brussels sprouts | 980 |
| Blackberry | 2,036 | Alfalfa sprouts | 930 |
| Strawberries | 1.540 | Broccoli (flowers) | 890 |
| Raspberries | 1.220 | Beet | 840 |
| Plum | 949 | Red pepper | 710 |
| Oranges | 750 | Bow | 450 |
| Red grapes | 739 | Corn | 400 |
| Cherry | 670 | Eggplant | 390 |


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.