We read through the teeth about diseases ... Doctors are surprised by the accuracy of this method!
The tooth consists mainly of dentin with a cavity, covered with enamel and cement on the outside. The tooth has a characteristic shape and structure, occupies a definite position in the dentition, is constructed of special tissues, has its own nervous apparatus, blood and lymphatic vessels. Normally, a person has 28 to 32 teeth. The absence of third molars, called the wisdom tooth, is the norm, while the third molars themselves are considered by an increasing number of scientists to be atavism, but this is currently a controversial issue.
Inside the tooth is a loose connective tissue, permeated with nerves and blood vessels (pulp). Distinguished milk and permanent teeth - a temporary and permanent bite. In the temporary bite there are 8 incisors, 4 canines and 8 molars - only 20 teeth. The permanent bite consists of 8 incisors, 4 canines, 8 premolars and 8-12 molars. In children, baby teeth begin to erupt at the age of 3 months. In the period from 6 to 13 years, the milk teeth are gradually replaced by permanent teeth. In rare cases, additional, supercomplete teeth (both dairy and permanent) are observed.
About illnesses of internal organs can tell not only analyzes, but also ... teeth. An experienced dentist needs to look into the patient's mouth to understand the state of the heart or gastrointestinal tract.
How does this method work and is it possible to predict the ailments by simply looking at the teeth?
Many of us have first-hand knowledge of the feeling of unbearable toothache when, it seems, one head, heart and stomach suffer from one ruthless incisor. There are a lot of "lucky people" who are not saved by the appearance of caries and other dental pathology, either high-quality toothpaste, a medical brush, rinsing, or even a timely visit to the dentist. Perhaps, it is necessary to treat not the teeth, but other organs? For doctors who practice methods of traditional treatment, there are no contradictions here - they know which tooth is responsible for which organ.
How does this method work and is it possible to predict the ailments by simply looking into the mouth?
A tooth for an eye
Many of us have first-hand knowledge of the feeling of unbearable toothache when, it seems, one head, heart and stomach suffer from one ruthless incisor. There are a lot of "lucky people" who are not saved by the appearance of caries and other dental pathology, either high-quality toothpaste, a medical brush, rinsing, or even a timely visit to the dentist. Perhaps, it is necessary to treat not the teeth, but other organs? For doctors who practice non-traditional methods of treatment, there are no contradictions here - they know which tooth is responsible for which organ.
So, problems with the gall bladder can result in the loss of one of the molars (seventh back teeth), and constantly aching fangs will tell about cholecystitis or the threat of hepatitis. If the relationship between the teeth and the rest of the organs exists, then it is almost impossible to prove it, says academic medicine. "Any tooth, being problematic, can give complications to other organs," Valery Kaminsky, a periodontist surgeon, believes. "But we can not talk about a direct relationship between each individual tooth and a specific organ." To whom to believe - the official medicine or the conclusions of the "populists" - decide for yourself, but knowing the position of both sides will never interfere.
Keep the diagnosis behind your teeth
Even a slight damage to the structure of the tooth can tell a lot. Of course, only an expert and a detailed examination will give a complete picture of which tooth is connected with which organ and what kind of problem it signals. But you can independently conduct a preliminary examination and compare the symptoms (see table). For this you need to consider the following:
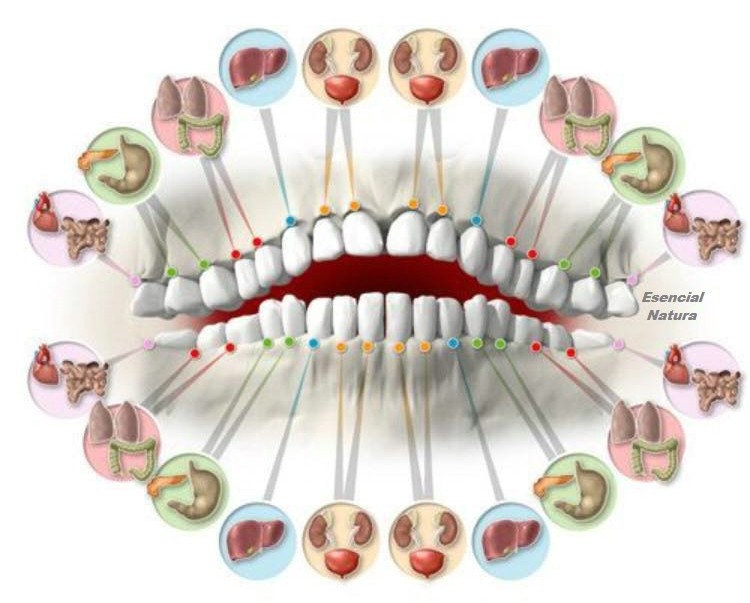
- 1 On the upper and lower incisors judge the state of the kidneys, bladder, ears and organs of the reproductive system. And their poor condition may indicate chronic pyelonephritis, cystitis, otitis, tonsillitis, osteochondrosis and even prostatitis.
- 2 Fangs are responsible for the liver and gallbladder, signaling for cholecystitis and hepatitis.
- 3 Small molars (premolars) are the lungs and large intestine. Problems with them can be caused by dysbacteriosis, colitis, allergy, chronic bronchitis or pneumonia.
- 4 Large molars (molars) are associated with the stomach, spleen and pancreas. Accordingly, the list of possible diseases-provocators is as follows: gastritis, ulcer, pancreatitis, anemia, sinusitis, tonsillitis, disorders of the endocrine system, atherosclerosis, varicose veins and others.
- 5 Wisdom teeth "manage" the state of the heart, vessels and small intestine. Therefore, a dentist can help in the treatment of coronary disease and even congenital heart disease. Pain in the joints is reflected in the condition of the front teeth of the upper and lower jaws.
"After thirty," says dentist Igor Molozhanov, "many patients have problems with gums. If a person regularly takes care of the oral cavity, and thus the bleeding gums do not pass - you can confidently say that the problem lies in other organs. In women, for example, one of the signs of breast pathology is the so-called causeless gingivitis (inflammation of the gums). In children, gingivitis on the gums may be manifested by leukemia. A dentist session after treatment treats periodontal disease, whereas a child needs at least a blood test. "
To be ill - so together
If the teeth often deteriorate due to diseases of the internal organs, there is also feedback: problems with the teeth lead to various disorders and diseases.
It is known that toothache can cause terrible headaches. And the aching fangs and incisors of the upper jaw auknutsya in the forehead and whiskey, and inflammation of the molars will give a dull pain in the back of the head.
Even the most common caries can cause permanent migraines. Problems of periodontal (gum) promote the development of cardiovascular diseases, and pulpitis (inflammation of the dental nerve) provokes gastritis, colitis and cholecystitis.
As officialdom
From the point of view of official (academic) medicine, any inflamed tooth, which is the focus of infection, the so-called chroniosepsis, is a danger to the whole organism. "Problem teeth (with caries, destroyed or dilapidated) entail a general decrease in immunity or outbreaks of infection in other organs," explains the dentist Elena Legeza. But the connection between teeth and diseases is far from always provable. With confidence, we can say that with the inflammation of the tooth in the gastrointestinal tract products come along with toxins. This causes a variety of diseases (depending on the state of human immunity), starting from the usual indigestion of the stomach and ending with gastritis. But no dentist will take a parallel between incisors and osteochondrosis.
"Pain symptomatology affects the whole body," says Candidate of Medical Sciences Valery Kaminsky. - When a person has a toothache, then the head starts to hurt, the stomach or intestines, liver, bile ducts and even the heart suffers. The fact that the dental nerve sends a signal to the brain regions of the central nervous system and is connected to the nuclei of neighboring nerve cells that respond to pain and transmit the signal to other organs. And the ways of transmission of pain in each person are individual. But at the risk group, first of all, problematic, that is, unhealthy organs. " Therefore, if you have chronic bronchitis, do not be surprised that, having started your teeth, you suddenly started to get pneumonia.
A comment
Igor Molozhanov, head of the Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of the Kiev Institute of Traditional Medicine.
According to statistics about 95% of people suffer from caries. By what tooth is affected, at what age and to what extent, a specialist can diagnose a serious disease in a patient. For example, diabetes in the initial stages can also manifest as gum disease. A dentist may be the first doctor who diagnosed a person with diabetes for a sharp deterioration of the gum condition.
A classic example of the connection of teeth with internal organs is the so-called hepatic tooth, when teeth are destroyed from gastric or liver pathologies (the same gastritis, pancreatitis, etc.). But other interrelations are known to dentists.
There are three periods of dental life. Therefore, the correctly diagnosed diagnosis depends on the age of the patient.
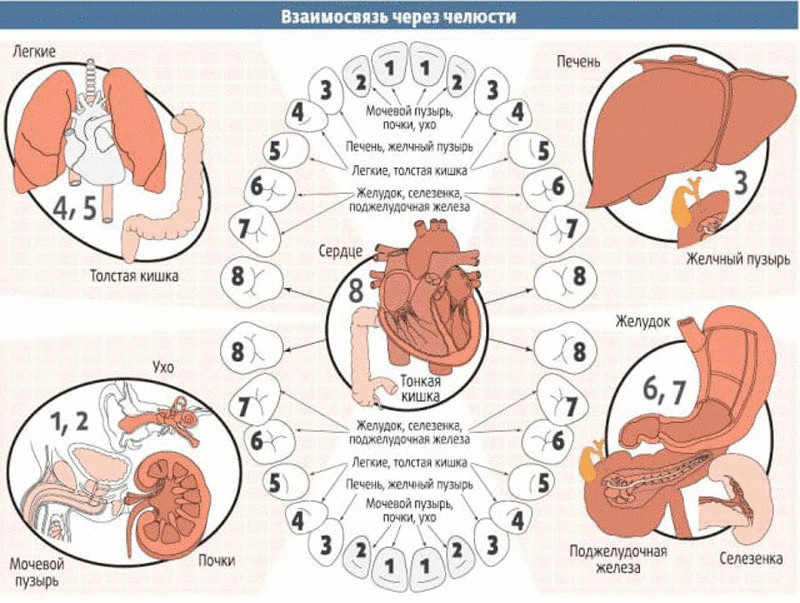
In the case of violations of the gastrointestinal tract and liver: in children 8-10 years old, the sixth and the frontal (first, second, third) suffer first, while in adults, the sixth and seventh teeth are first destroyed.
With the pathology of the respiratory system: in children with pathology of adenoids, tonsils and polyps, the first, second teeth of the upper and lower jaws suffer, and less often the fangs. In adults, bronchitis, pneumonia and even asthma affect the first and second teeth of both jaws.
Diseases of the urinary system: in adolescence and up to 25 years, they are responsible for the fourth, fifth teeth of the lower jaw. In adults, the diseases of the fifth and sixth teeth of both jaws begin.


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.