When are antibiotics needed?

Antibiotics (from other Greek anti-against + bio-life) are substances of natural or semi-synthetic origin that suppress the growth of living cells, most often prokaryotic or protozoans.
Antibiotics of natural origin are most often produced by actinomycetes, less often by non-micellar bacteria. Some antibiotics exert a strong inhibitory effect on the growth and reproduction of bacteria and, at the same time, damage or not at all damage the cells of the macroorganism, and are therefore used as medicines. Some antibiotics are used as cytostatic (antitumor) drugs in the treatment of cancer. Antibiotics usually do not affect viruses and are therefore useless in the treatment of diseases caused by viruses (eg, influenza, hepatitis A, B, C, chicken pox, herpes, rubella, measles). However, a number of antibiotics, primarily tetracyclines, also act on large viruses.
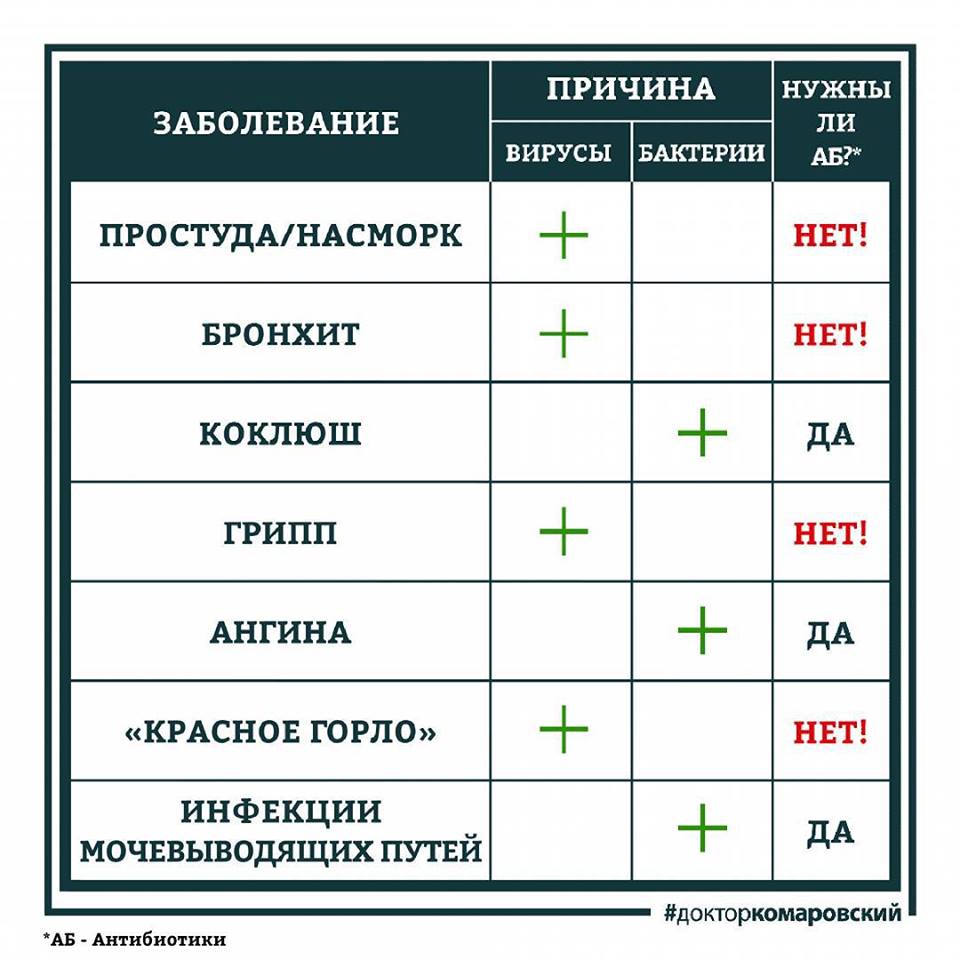
Dr. Komarovsky compiled a terrific table: When and when antibiotics are not needed.
Every disease has a reason, it's either a virus or a bacterium. The virus passes by itself in 5-7 days. But the bacterium is already the reason to seek help with antibiotics.
The first antibiotic, penicillin, was discovered back in 1928 by Alexander Fleming. This medicine has been used to treat many diseases. But with the development of medicine, new types of antibacterial drugs began to appear. Moreover, each time they became better.
Despite their dignity, antibiotics have side effects. Therefore, one should be very cautious when using them, especially in the treatment of children with antibiotics. After all, the baby's body can not always cope with the consequences of using strong medications.
Although you should not be afraid of antibiotics, in some situations they are the only way out. If necessary, the doctor will prescribe the right drug and dosage. And you will only have to follow the recommendations.
When antibiotics are needed
Bacteria can adapt to the effects of drugs. To cope with them, you need to use modern drugs. Therefore, in any case, do not give the child antibiotics for prophylaxis, this can cause harm to his health. But there are situations when you can not do without them.
1. Acute form of the disease. To treat follicular sore throat, pneumonia, purulent otitis, pyelonephritis and sinusitis, antibiotics should be used. In the acute period of the disease, the doctor will prescribe them. When the effect is achieved, you can go to homeopathy or physiotherapy. Only with the appointment of a doctor.
2. Postoperative period. The course of antibiotics will help prevent inflammation.
3. Poisoning the body with toxins from bacteria. In the treatment of diphtheria, tetanus, botulism without potent means can not do.
4. Chronic course of the disease. For some diseases (for example, cystitis in girls) antibiotics are necessary, otherwise the problem will only worsen.
Principle of antibiotics
Antibiotics are in the form of tablets, syrup, suspension. For the treatment of children with antibiotics, fruit syrup is usually prescribed, although sometimes you have to inject. Of course, the procedure is painful, but very effective.
In whatever form the drug was, the blood carries it throughout the body. Gradually, it accumulates in a specific organ (depending on the antibiotic). For example, some drugs penetrate the bones, and treat inflammation of the bone system, others accumulate in the middle ear area and treat otitis. There are also substances that attach to immune cells and, together with them, get into the source of infection, where they begin to act.
Limited action
Antibiotics cope well with bacteria, but if the disease is caused by other pathogens, they are useless.
- Flu, colds, a slight runny nose and cough, ARD. These diseases are caused by viruses, and they need to be treated, respectively, with antiviral drugs.
- Fungal diseases (eg thrush). It is treated only by antifungal agents. And the use of antibiotics will only exacerbate the infection.
- Heat. Antibiotics help to eliminate the cause of fever, and not to knock it down. Please note that pediatricians often recommend not using antibacterial drugs in conjunction with antipyretic drugs to see how effective the drug is (but this is provided that the temperature does not rise above 38 ° C).
For antibiotic treatment of children to be as effective as possible and do no harm, follow the instructions!


Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.