How muscles work in different exercises. The most complete visual information!
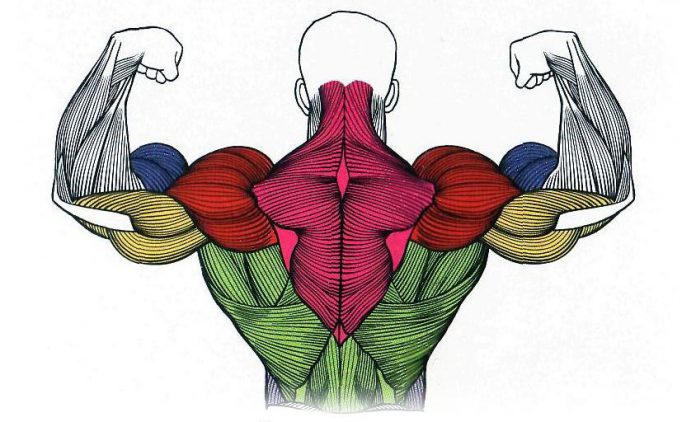
Muscles or muscles (from the Latin musculus - muscle (mus-mouse, small-mouse)) are organs of the body of animals and man, consisting of elastic, elastic muscle tissue, capable of contracting under the influence of nerve impulses. Designed to perform various actions: body movement, contraction of vocal cords, breathing.
Muscles allow you to move parts of the body and express in action the thoughts and feelings. A person performs any movements - from such simple ones as blinking or smiling, to the subtle and energetic that we see in jewelers or sportsmen - thanks to the ability of muscle tissues to shrink. The functioning of the muscles, consisting of three main groups, depends not only on the mobility of the organism, but also on the functioning of all physiological processes. And the work of all the muscle tissues is controlled by the nervous system, which ensures their connection with the brain and spinal cord and regulates the conversion of chemical energy into mechanical energy.
In the human body, 640 muscles (depending on the method of calculating the differentiated muscle groups, their total number is determined from 639 to 850). The smallest are attached to the smallest bones located in the ear. The largest are the large gluteus muscles, they set the legs in motion. The strongest muscles are gastrocnemius and chewing muscles. The man's longest muscle, tailor's, starts from the anterior superior ostium of the iliac wing (antero-superior parts of the hip bone), spirally swings forward through the thigh and is attached to the tuberosus of the tibia by the tendon (upper parts of the tibia).
The shape of the muscles is very diverse. Most often there are spindle-shaped muscles, characteristic for the limbs, and broad muscles - they form the walls of the trunk. If the muscles have a common tendon, and the heads have two or more heads, then they are called two-, three- or four-headed ones. The muscles and the skeleton determine the shape of the human body. Active lifestyle, balanced nutrition and exercise contribute to the development of muscles and reduce the amount of fat tissue.
All this knowledge will be an important milestone on the way to building a beautiful body relief. Well, we're starting ...
Why do muscles grow?
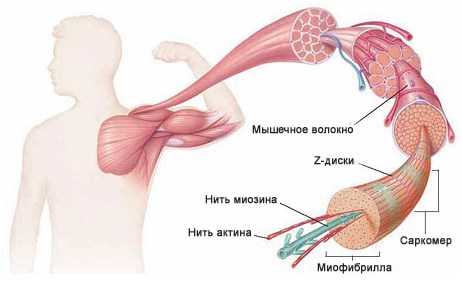
It is known that due to the reduction of muscle fibers (if more precisely myofibrils, which are responsible for it), the muscle itself also decreases. The signal comes from the motoneurons of the spinal cord and follows the axon and, branching, joins the muscle fibers. Myofibrils consist of sarcomeres, which contain the protein myosin and actin (see image).
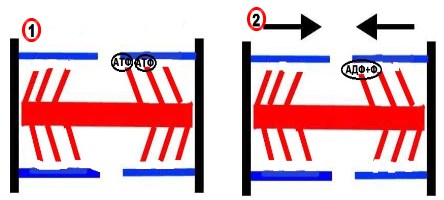
During the contraction of the muscle fiber, the myosin bands with the help of the processes pull the actin filaments towards each other. The shoots contain an ATP molecule, and they receive a signal to reduce (1). Then, under the action of the enzyme, ATP on the process passes into ADP + F (2).
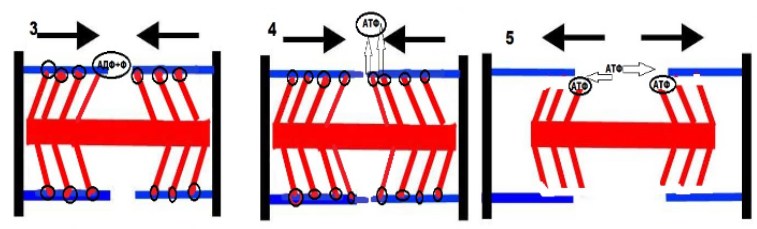
The outgrowth of myosin combines with the actin filament (3) and the actin filaments are pulled up to each other, thanks to the release of energy from the ATP molecule (4). However, the process is still linked to the actin filament, but without molecules of energy. Then a new molecule of ATP arrives, and the outgrowth of myosin is already detached from the actin filament (5).
This is how the process of muscle contraction looks. Understanding the process of muscle contraction will make it easier to understand how muscles grow. So, in every cell there is a nucleus (the same muscle fiber contains many nuclei), which contains DNA - information about the structure of the cell. In the case of muscle damage (their microtraumas with a heavy load), thanks to this "memory disc," a new tissue is built at the site of damage. Moreover, the process of recovery takes place in the supercompensation mode, i.e. Additional material is being built over the injured structures.
Microtraumas in muscles occur when there is no necessary ATP molecule to detach the myosin processes from actin filaments. It turns out that microtrauma - this is nothing like the detachment of the above process. After such a separation (and there are quite a lot of them, because there are thousands of processes in the muscle):
- The organism restores its original structure, recreating the damaged processes;
- Thanks to a good protective reaction (and survival mechanism) to stress, the body seeks funds to build additional outgrowths of myosin. Thus, the next time this weight of burdening is hardly "shocking", which means that the working weight will increase and the muscle will increase in volume.
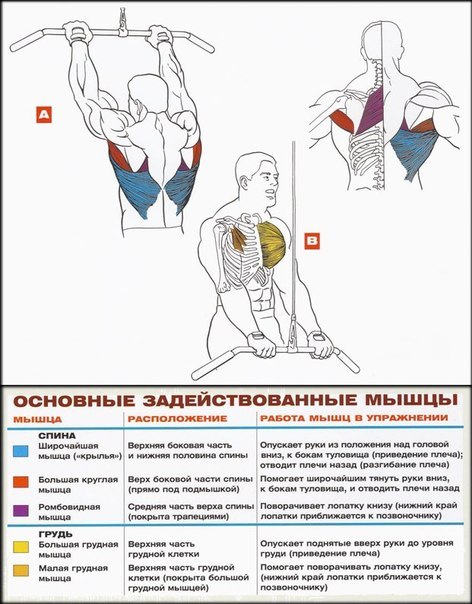
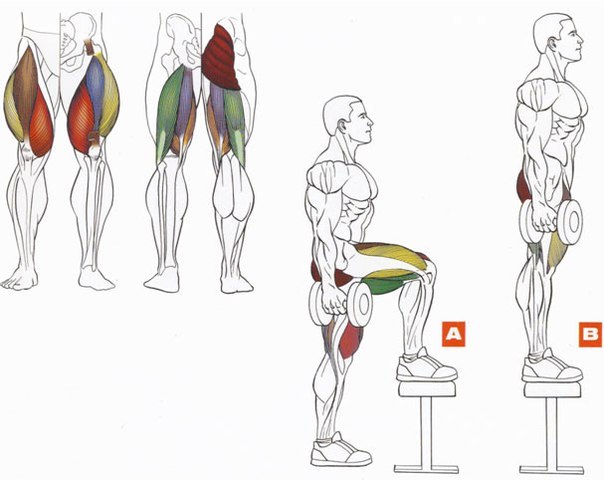
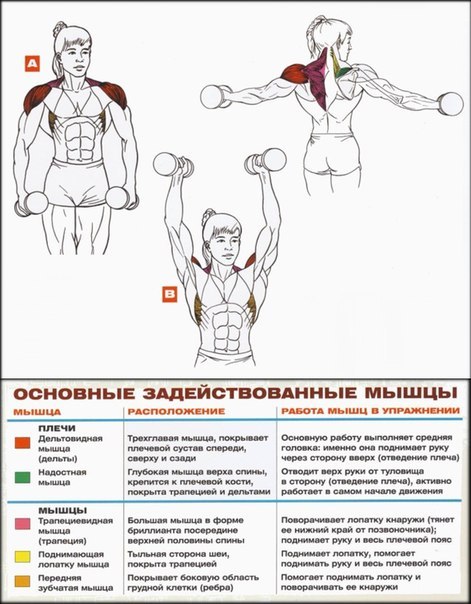
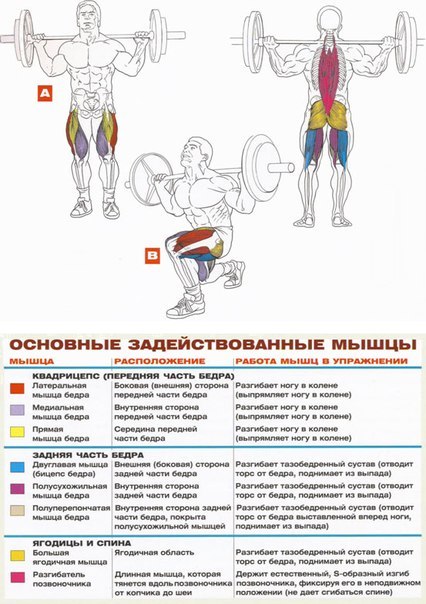
Muscle Atlas and Muscle Groups
And to start a few words about the very concept - the atlas of muscles. This is a generalized picture of the muscle groups that belong to all parts of the human body. In accordance with the latter, the muscles are divided into:
- Muscles of the back
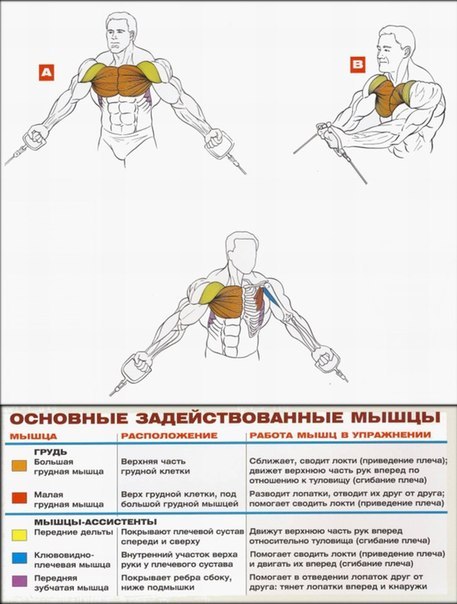
- Muscles of the breast
- Muscles of the shoulder girdle
- Muscles of hands
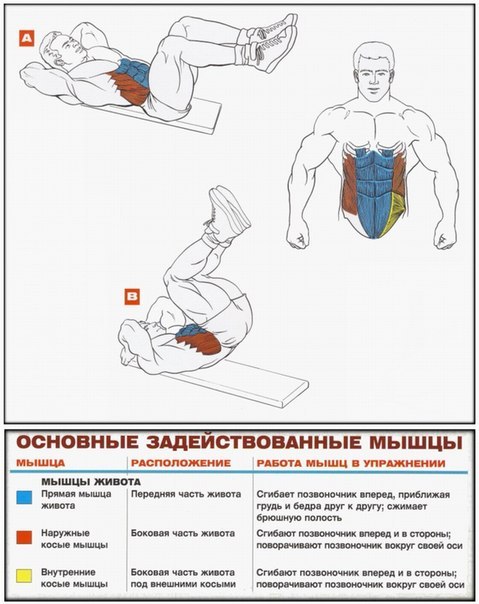
- Abdominal muscles
- Muscles of the legs
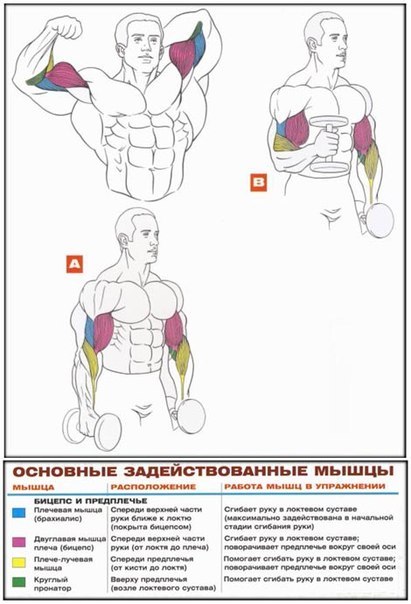
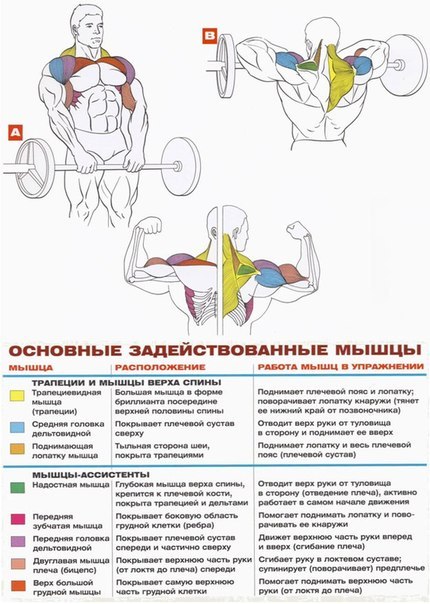
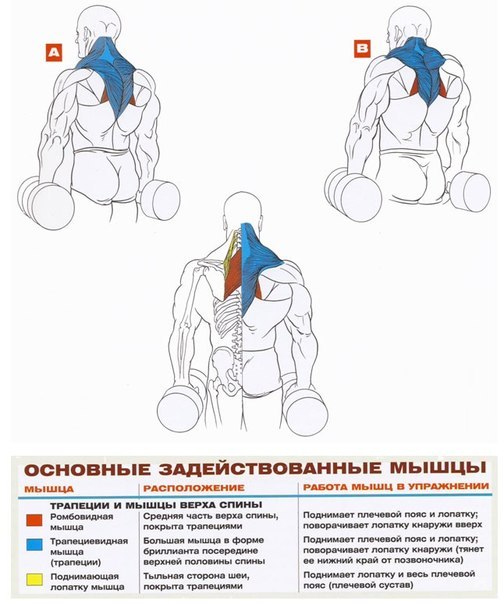
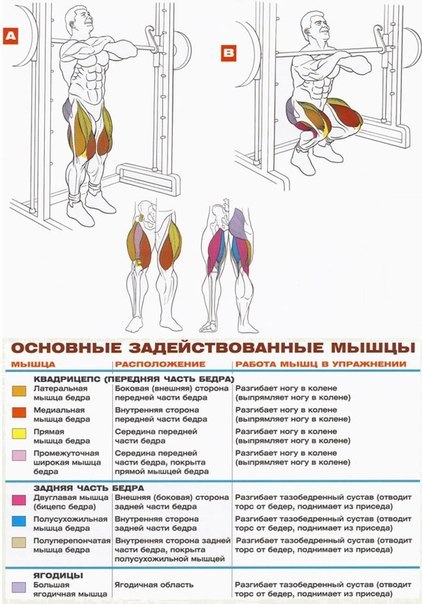
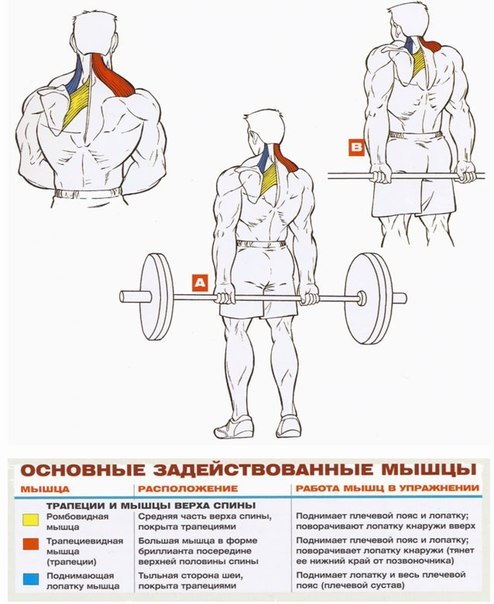
In each part of the body, they separate their muscle groups - a complex consisting of several muscles that perform the same motor function. Very often, with the same movement in exercises, almost all muscles from one muscle group are involved, therefore they operate with the names of muscle groups. Although, the latter can sometimes be omitted and replaced by the name of the largest muscle of this group, for example, the anterior surface of the thigh is often "called" quadriceps (quadriceps).
Interesting Facts:
- A person has more than 680 different muscles
- Muscles of the jaw develop an effort of 80 kg
- The fastest muscle is the muscle of the eyelid, responsible for blinking
- The largest muscle is gluteal (in some, just a very large
- The smallest muscle is a staped (3 mm), adjusts the sensitivity of the ear to the sound
- The strongest muscle - calf, can hold weight up to 150 kg
- Functionality of the thumb muscles is 75% of the functionality of all the muscles of the hand

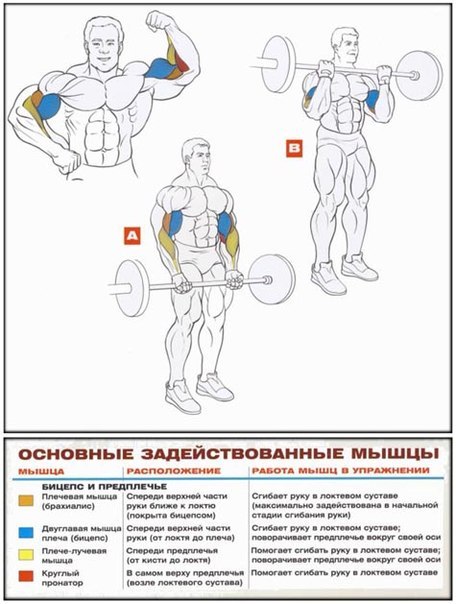
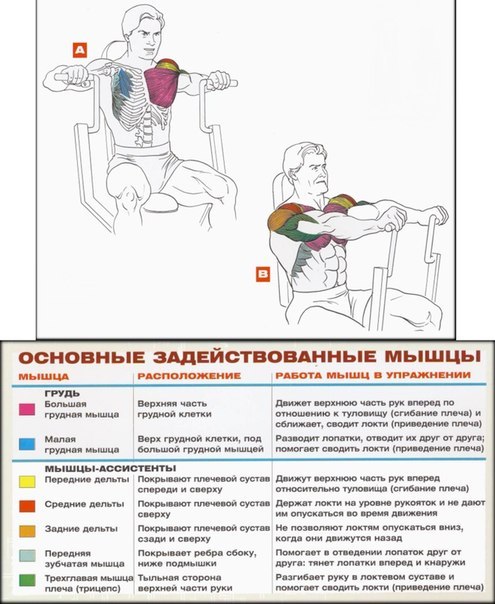
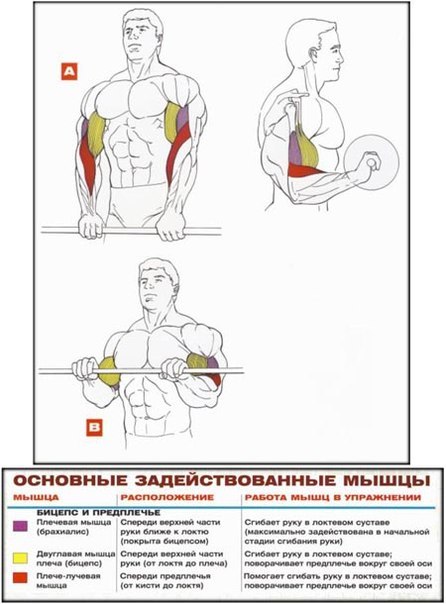
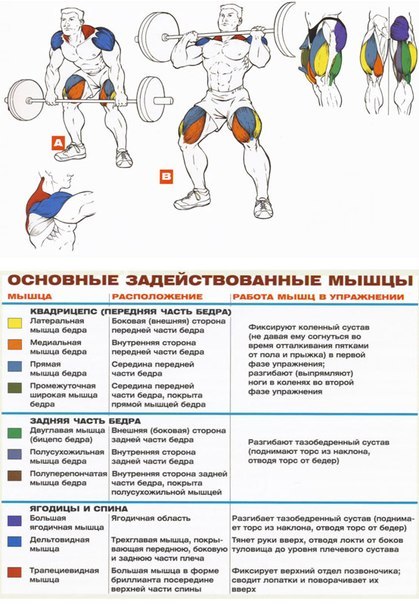

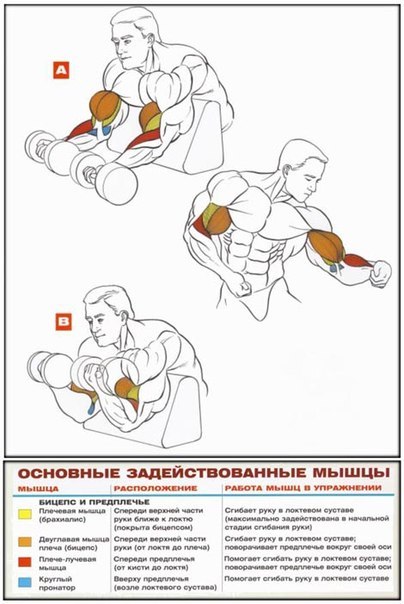
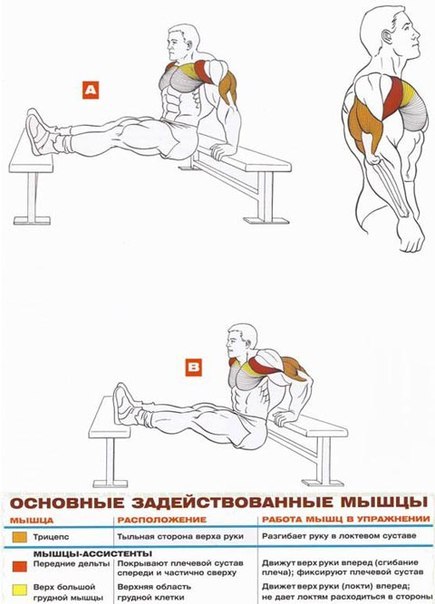
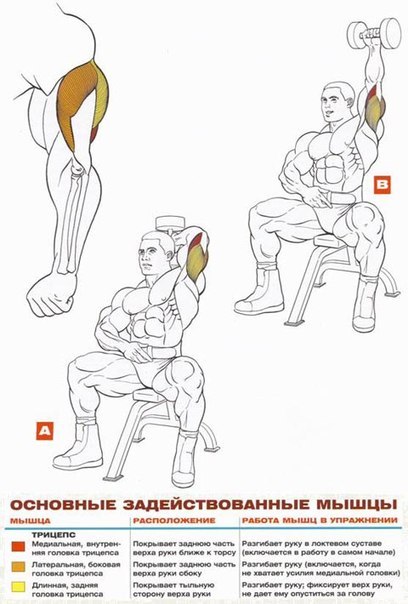
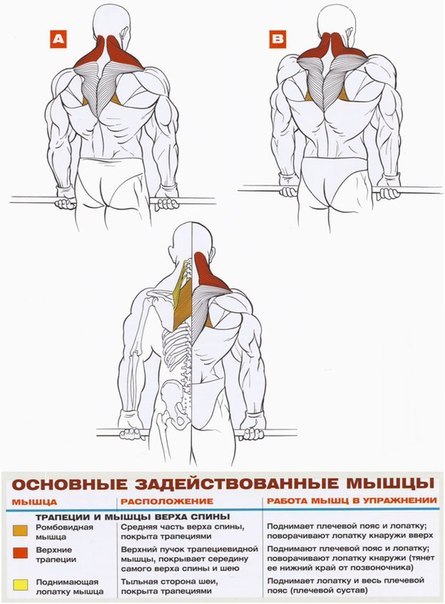

Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.