3. RCD - effective fire and electrical protective means
3.2. PRINCIPLE OF ACTION OF RCD
Functionally, the RCD can be defined as a high-speed safety switch that reacts to the differential current in the conductors supplying electricity to the protected electrical installation .
The main functional blocks of the RCD are shown in Fig. 3.2.
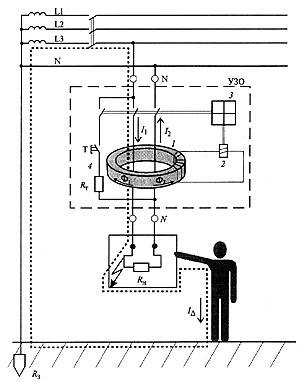
Fig. 3.2. Structure of the RCD
The most important functional unit of the RCD is the differential current transformer 1. In the absolute majority of RCDs that are produced and operated nowadays throughout the world, the current transformer is used as the differential current sensor. In the literature on the design and application of RCDs, this transformer is sometimes referred to as a residual current transformer - TTNP, although the term "zero sequence" is applicable only to three-phase circuits and is used in calculations of asymmetric modes of multiphase circuits.
The starting element (threshold element) 2 is usually performed on sensitive direct-acting magnetoelectric relays or electronic components. The actuator 3 includes a power contact group with a drive mechanism.
In the normal mode, in the absence of a differential current - leakage current, in the power circuit through the conductors passing through the window of the magnetic circuit of the current transformer 1 the operating load current flows. The conductors passing through the window of the magnetic circuit form the interconnected primary windings of the differential current transformer. If we denote the current flowing towards the load as I 1 , and from the load as I 2 , then we can write the equation:
I 1 = I 2 .
Equal currents in counter-wound windings induce in the magnetic core of the current transformer equal, but vector-counter-directed magnetic fluxes Ф 1 and Ф 2 . The resulting magnetic flux is zero, the current in the secondary winding of the differential transformer is also zero.
The starting organ 2 is in this case at rest.
When a person touches open conductive parts or the case of an electrical receiver that has been subjected to an insulation breakdown, an additional current flows through the phase conductor through the RCD, in addition to the load current I 1 , the leakage current (I D ), which is differential (differential) for the current transformer.
The inequality of the currents in the primary windings (I 1 + I D in the phase conductor) and (I 2 , equal to I 1 , in the neutral conductor) causes the inequality of the magnetic fluxes and, as a consequence, the appearance in the secondary winding of the transformed differential current. If this current exceeds the setting value of the threshold element of the trigger 2, the latter operates and affects the actuator 3.
An actuator, usually consisting of a spring actuator, a trigger mechanism and a group of power contacts, opens the electrical circuit. As a result, the protected electrical installation is de-energized.
To perform periodic monitoring of the serviceability of the RCD, a testing circuit is provided. 4. By pressing the "Test" button, a breaking differential current is artificially created. The operation of the RCD means that it is generally good.


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.