| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Inventions / Alternative energy / |
|
ETERNAL MAGNETIC-REDUCTION ENGINE
Dudyshev Valery Dmitrievich, Russia, Samara
Samara Technical University
Application for invention 2004129422 dated October 5, 2004
Valery Dmitrievich Dudyshev
abstract
A useful model of a magnetic motor using the energy and magnetic interaction forces of permanent magnets is proposed, and the prototype is simplified. This technical advantage is achieved by the fact that the motor stator is movable, for example, rotating on an independent shaft, the motor is supplemented with a device for fixing and adjusting the spatial angle of shear of the stator and rotor magnets relative to each other, specifically by turning their magnetization axes to a fixed spatial angle different from Zero degrees, which is mechanically connected to the magnets and shafts of rotation of the stator and the rotor, and is made in the form of a speed variator, using, as transmission elements, ring-shaped engaging rings in the form of cylinders with a rough surface, or a gear unit Magnets, for example, through two or more mechanical non-magnetic gears in meshing with a diameter of gears, which allows free rotation of the magnets on their shafts relative to each other, and along the length of the stator and rotor shafts, several magnets symmetrically deployed with respect to each other Each other with their axes of magnetization with their mutual fixed spatial shift different from the angle of displacement from the previous pair of magnets, with this spatial angle changing, for example, with a step-by-step change of this spatial angle between the magnetization axes of the next pair of magnets by a fixed angle, for example, The law of the helical helix, the motor is supplemented with a device for regulating the speed and direction of rotation of the engine, which can be performed, for example, in the form of a device for controlling the spatial rotation of magnets with a change in the angle of shear between their magnetization axes.
Magnetic-geared motor
MKI H 02 N 1/00
The utility model refers to magnetic motors with permanent magnets using the energy of permanent magnets and their magnetic forces for rotation.
The closest device of the same designation to the claimed utility model for a plurality of features is a magnetic motor comprising a stator and a rotor, a rotor rotation shaft, permanent magnets rigidly placed on the stator and the rotor at certain spatial angles to each other (prototype-RF patent 2145764) .
The prototype has a complex design and, as a result, reduced reliability in operation.
The technical result of this useful model is the simplification of the design of the magnetic motor-prototype and the increase of its reliability.
This technical result is achieved in the proposed utility model in that, in a magnetic motor, comprising a stator and a rotor, a rotor rotation shaft, permanent magnets rigidly placed on the stator and a rotor, the motor stator is movable, for example, rotating on an independent shaft, And adjusting the spatial angle of shear of the stator and rotor magnets relative to each other, specifically by rotating their magnetization axes to a fixed non-zero spatial angle that is mechanically connected to the magnets and rotor shafts of the stator and rotor, and configured as a speed variator, with Using as ring-transmitters the ring-shaped magnets themselves in engagement, made in the form of cylinders with a rough surface, or a reducer type device transmitting the moment of rotation of the magnets, for example, through two or more mechanical non-magnetic gears in meshing with a gear diameter providing free rotation of the magnets On their shafts relative to each other; moreover, along the length of the shafts of the stator and the rotor, several magnets symmetrically deployed relative to one another with their magnetization axes with their mutual fixed spatial displacement different from the angle of shear from the previous pair of magnets can be placed with a certain step, A change in this spatial angle, for example, with a step-by-step change of this spatial angle between the magnetization axes of the next pair of magnets by a fixed angle according to a certain regularity, for example, according to the law of a helical spiral, the motor is supplemented with a device for regulating the speed and direction of rotation of the engine, A device for controlling the spatial rotation of magnets with a change in the angle of shear between their magnetization axes.
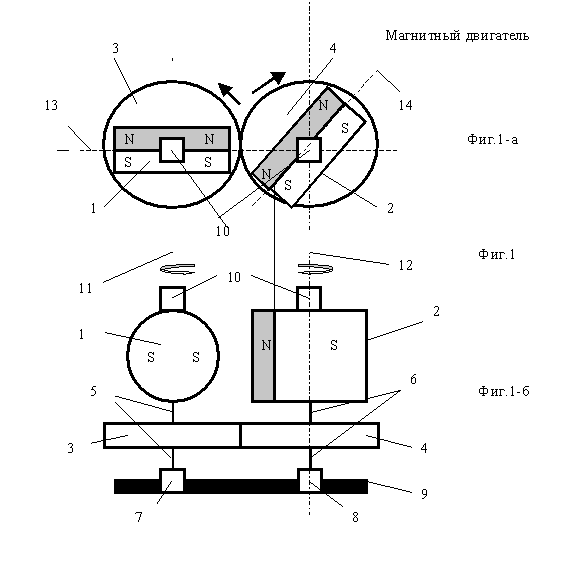
The magnetic motor on magnets with axial magnetization (FIG. 1)
The simplest magnetic motor with two permanent magnets 1, 2 with axial magnetization with magnetization axes 13, 14 located at a spatial angle of less than 90 degrees.
And fixed fixedly to rotate them, on the shafts of rotation 5, 6 rigidly fixed to the gears 3, 4 in meshing and movably fixed in the bearings 7, 8 on the common massive base 9 . Gears 3, 4 , form a mechanical gearbox providing an invariable spatial angle of shear of the planes of magnets 1, 2 relative to each other. On magnets 1, 2, the symbols N, S are the north and south magnetic poles.
The device works as follows.
Magnets 1, 2 , continuously unfold due to the presence of a rotating magnetic moment on the gears 3,4 , which transfer the rotation to the shafts 5, 6 . The rotational torque of the magnetic motor is due to the magnetic forces of the magnet rotation, which depend on the dimensions and properties of the permanent magnets 1,2 , on the distance between their rotation axes 11, 12 and the spatial angle between the magnetization axes 13, 14 of the magnets 1, 2 . The total magnetic moment of a turn of magnets 1, 2 should exceed the moment of resistance of gears 3, 4 . The adjustment of the torque, direction and angular rotation of the shafts 5, 6 of the magnets 1, 2 is achieved by varying the spatial angle of displacement of the magnetization axes 13, 14 of these magnets relative to each other.
The utility model formula
A magnetic motor comprising a stator and a rotor, permanent magnets mechanically fixed thereon in a certain order, a rotor rotational shaft, characterized in that the motor stator is movable, for example, rotating on an independent shaft, the motor is supplemented with a device for fixing and adjusting the spatial angle of shear of the stator magnets And the rotor relative to each other, specifically by rotating their magnetization axes to a fixed spatial angle other than zero degrees, the device is mechanically connected to the magnets and the shafts of rotation of the stator and the rotor and is executed, for example, as a speed variator, using as its transmission Links of the magnets themselves, meshed, or devices such as a mechanical gearbox, for example in the form of two or more non-magnetic gears meshed with a diameter of gears, allowing free rotation of the magnets on their shafts relative to each other, along the length of the stator and rotor shafts Be placed with a certain pitch several pairs of magnets symmetrically unfolded relative to each other by their magnetization axes with their mutual fixed spatial displacement different from the angle of shear from the previous pair of magnets, with a cyclic variation of this spatial angle, for example, with a step change in this spatial angle between the axes Magnetizing the next pair of magnets by a fixed angle according to a certain pattern, for example, according to the law of a helical helix, the motor is supplemented with a speed and direction control device for the motor, which can be executed, for example, as a device for controlling the spatial rotation of the magnets with a change in the angle of shear between their magnetization axes .
print version
Author: Valery Dudyshev
PS The material is protected.
Date of publication 25.10.2004гг




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.