| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2199499
![]()
METHOD OF OBTAINING PLASTIFIING ADDITIVES FOR CONCRETE MIXTURES
The name of the inventor: Khairudinov IR; Khabirov DM; Imashev B.U .; Khrushchev OV; Telyashev E.G.
The name of the patentee: Institute of Petroleum Refining Problems of the Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Bashkortostan
Address for correspondence: 450065, Ufa, ul. Initiative, 12, IPNHP of the Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Belarus, OIS, S.A. Zajcevoj
Date of commencement of the patent: 2001.06.26
The invention relates to building materials, in particular to methods for producing plasticizing additives used in the preparation of concrete and reinforced concrete products. The method for producing a plasticizing additive for a concrete mixture includes sulfonation of aromatic hydrocarbons, such as concentrates of bicyclic aromatic hydrocarbons derived from liquid pyrolysis or reforming products of gasoline, sulfuric acid, condensation of the resulting sulfonic acids with formaldehyde, mixing the condensation product with a technical lignosulfonate and neutralizing the resulting mixture with alkali . The preferred ratio of the components when the condensation product is mixed with the technical lignosulfonate is the following,%: the condensation product of the sulfonic acids of aromatic hydrocarbons with formaldehyde 78-94, a 50% aqueous solution of technical lignosulfonate 6-22. Simplification of the technology of obtaining a plasticizing additive with simultaneous increase of its quality is achieved.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to building materials, in particular to methods for producing plasticizing additives used in the manufacture of concrete and reinforced concrete products.
A method is known for preparing a plasticizing additive for concrete mixtures from a methylnaphthalene fraction of 240-265 ° C by sulfonating it with sulfuric acid at a temperature of 100-180 ° C, then condensing the resulting sulfomass with formaldehyde at a temperature of 100 ° C and neutralizing the condensation product with alkali ( Czechoslovakia Patent 236116, C 04 B 13/30, C 08 K 5/01, 1987 ).
The disadvantage of this method is its complicated instrumentation due to the high temperature at the stage of sulfonation and the intensive flow of corrosive processes.
The closest in terms of technical nature to the claimed object is the method for producing a plasticizing additive, which includes sulfonation of aromatic hydrocarbons with sulfuric acid, condensation of the resulting sulfonic acids with formaldehyde, neutralization of the condensation product of sulfonic acids with alkali, compounding of the condensation product with technical lignosulfonate ( RF patent 2100305 C1, class 04B 24/18, 27.12.1997) .
However, concrete mixtures obtained with the use of this additive have unsatisfactory parameters of delamination - high water separation and solution separation.
The invention is directed to improving the quality of a plasticizer.
This is achieved by the fact that in the process for producing a plasticizing additive for concrete, which includes sulfonation of aromatic hydrocarbons with sulfuric acid, condensation of the resulting sulfonic acids with formaldehyde, neutralizing the condensation product of sulfonic acids with alkali, compounding the condensation product with technical lignosulfonate, neutralizing the condensation product of the sulfonic acids with alkali, after mixing with the technical lignosulfonate , And as concentrates of bicyclic aromatic hydrocarbons extracted from liquid pyrolysis products or gasoline reforming are used as aromatic hydrocarbons. The preferred ratio of the components is,%:
Condensation product of sulfonic acids of aromatic hydrocarbons with formaldehyde - 78-94
50% aqueous solution of technical lignosulfonate - 6-22
The method is illustrated by the following examples.
Example 1
As a raw material for the production of sulphomass, a distillate fraction of a heavy pyrolysis resin was used, boiling in the range 230-260 ° C, density 993 kg / m 3 , refractive index 1.5520 and containing 72% methylnaphthalenes, 11.5% tetralin derivatives, 9% derivatives Acenaphthene, 4% of the derivatives of diphenyl.
Sulfurization of the raw material was carried out at a temperature of 40-60 ° C by treating concentrated sulfuric acid (92-98% monohydrate content). The sulphonation product was diluted with water, treated at 70-80 ° C with an aqueous solution of formaldehyde (concentration 35-37%). 6 g of a 50% aqueous solution of lignosulfonate were added to a condensation product in an amount of 94 g, stirred with a conventional stirrer and the resulting mixture was neutralized with an aqueous solution of NaOH to a solution pH of 8-10.
Example 2
The same raw material was sulfonated and condensed under the same conditions. 14 g of a 50% aqueous solution of lingosulfonate were added to the condensation product taken in an amount of 86 g, then the mixture was stirred and neutralized with alkali, as described in Example 1.
Example 3
The same raw material was sulfonated, condensed under the same conditions. To the condensation product taken in an amount of 78 g. Was added 22 g. 50% aqueous solution of lignosulfonate, then the mixture was stirred and neutralized with alkali, as described in Example 1.
Example 4
As a raw material, a distillate fraction of the gasoline reforming product (230-360 ° C), density 975 kg / m 3 , refractive index 1.5675, containing 59% methylnaphthalene, 17.5% diphenyl derivatives, 7.7% anthracene derivatives was used.
The sulfonation of the raw material, condensation of the sulphomass with formaldehyde was carried out under the same conditions. To the condensation product, taken in an amount of 94 g, 6 g of a 50% aqueous solution of lignosulfonate was added, the mixture was stirred and neutralized with alkali, as described in Example 1.
Example 5
The raw material taken in Example 4 was sulfonated, condensed under the same conditions. 14 g of a 50% aqueous solution of lignosulfonate were added to a condensation product in an amount of 86 g, then the mixture was stirred, neutralized as described in Example 1.
Example 6
The raw material taken in Example 4 was sulfonated, condensed under the same conditions, 22 g of a 50% aqueous solution of lignosulfonate was added to a condensation product in an amount of 78 g, then the mixture was stirred as described in Example 1.
Tests of products obtained in Examples 1-6 were carried out by using them for the preparation of concrete mixtures in accordance with GOST 30459 "Additives for concrete: methods for determining the effectiveness"; GOST 10184.4 "Concrete mixtures: methods for determining delamination"; GOST 10181.1 "Concrete mixtures: methods for determining workability"; GOST 10180 "Concretes: methods for determining the strength of control samples." The composition of concrete mixtures is given in Table. 1. The composition of the control mixture containing no additive is also given there. Table 2 shows the characteristics of concretes obtained from concrete mixtures containing additives and from a control mixture.
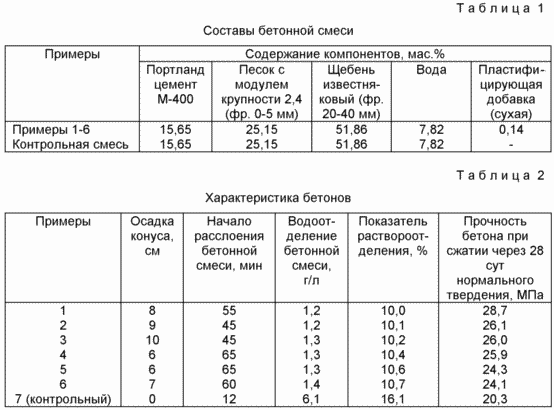
The results of the tests showed that for equal values of the mixing-cement-cement ratio of 0.5 and the same dosage of dry matter additives, the qualitative indices of concrete and concrete mixtures using the proposed additive (Examples 1-6) are much higher, Than in the additive obtained by the method described in the prior art.
In particular, the value of the sender of the cone sediment increased in comparison with the prototype by 1.5-2.5 times, the strength of concrete during compression increased by 15.7-38.0%.
In addition, the indicators characterizing the degree of delamination of concrete mixtures, and improved in our examples compared with the prototype.
Thus, the use of the proposed method will make it possible to obtain more effective plasticizing additives that greatly improve the quality of concrete products than the plasticizing additives obtained by the method described in the prior art.
CLAIM
1. A method for producing a plasticizer for a concrete mixture, which comprises sulfonating aromatic hydrocarbons with sulfuric acid, condensing the resulting sulfonic acids with formaldehyde, neutralizing the condensation product of the sulfonic acids with alkali, compounding the condensation product with lignosulfonate, characterized in that the neutralization of the condensation product of the sulfonic acids with alkali is carried out after mixing with the technical Lignosulfonate, and as concentrates of bicyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, isolated from liquid pyrolysis products or gasoline reforming.
2. A process according to claim 1, characterized in that mixing of components is preferably carried out with the following ratio of components,%:
Condensation product of sulfonic acids of aromatic hydrocarbons with formaldehyde - 78-94
50% aqueous solution of technical lignosulfonate - 6-22 tons
print version
Date of publication 19.12.2006гг




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.