| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2090580
![]()
Adhesive additives to the bitumen TO INCREASE CLUTCH
With acidic rocks
Name of the inventor: Krut VV .; Solomentsev AB .; Sump VP .; Repin ND .; Zinchenko VF .; L. Bedin
The name of the patentee: Joint Stock Company "Oreldorstroy"
Address for correspondence:
Starting date of the patent: 1994.07.28
Usage: for construction materials.
The inventive use penozolina containing a mixture of imidazolines structure pointed out in the claims, where R - hydrocarbon radical of C 17-20, as adhesion additives to the bitumen to improve adhesion with acidic rocks.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the field of construction materials, namely the use of surface-active agents (surfactants) to improve adhesion to the bitumen an acidic rocks.
SAW "Penazolin 17-20" TU 38-40753-75 is a non-aqueous foam stabilizer in the production process and the foams obtained from synthetic fatty acid with a hydrocarbon radical from C 16 to C 26, and polyethylene polyamine mark B. On physicochemical parameters correspond to the table 1.
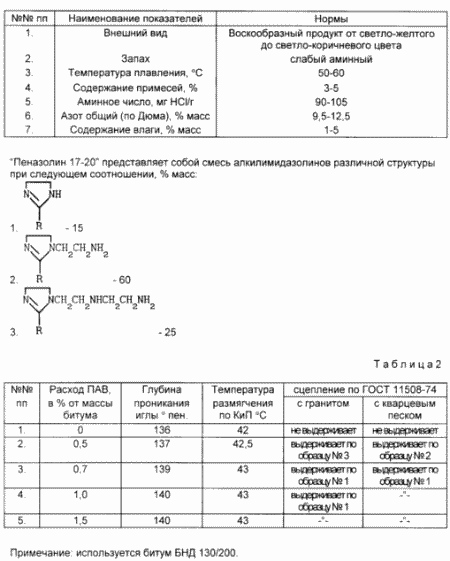
Imidazolines surfactants are a class of compounds which, depending on the composition and structure have different surface activity and colloid respectively different chemical and application properties.
"Penazoliny" is targeted composite products, representing a mixture of imidazolines of different structures in certain proportions. We have found that not all mixtures of imidazolines and individual imidazolines show ability to improve the adhesion of bitumen to acidic rocks. For example, Penazoliny 7-9, 10-13, 10-16, 21-25, having a close structure and component ratio of a mixture of imidazolines, but different length hydrocarbyl radicals R (R 7 September Penazolinov for 7-9, R 13 October Penazolinov to 10-13, and so on. d.) are not effective additives to improve adhesion of bitumen to acidic rocks (they improve the adhesion of bitumen to sample N 3 according to GOST 11508-74).
Individual imidazolines structures I, II, III, cited in the application, individually and do not give the desired effect on adhesion (adhesion bitumen and N corresponds to sample 3 in accordance with GOST 11508-74).
In the process of foam production (particularly, of polyvinyl chloride) "Penazolin 17-20" is used as follows. The molten resin is introduced under agitation surfactant in an amount of 0.5-1.5% Freon saturate the melt and the resulting mixture is passed through an oven heated to 140 150 o C.
Foam by allocating Freon resin increases in volume due to the formation of structured cells in a volume of resin. Uniformly distributed at the interface between the liquid phase (resin) gas phase (freon) surfactants provides gas distribution uniformity of the resin volume, significantly reducing its average density and increasing strength. The effectiveness of surfactant action is provided both by physical adsorption at the interface, and the chemical through the formation of complexes with amino surfactants chlorine polyvinyl chloride.
It is known that asphalts have poor adhesion (adhesion) with acidic rocks (granite, quartz, etc.), which is the reason for the lack of durability, cold resistance, weather resistance and other operational characteristics of bitumen and mineral materials. The claimed invention solves the technical problem: improving the adhesion of bitumen to acidic rocks.
"Penazolin 17-20" non-aqueous foam stabilizer synthesized as a target composite system with a certain ratio of components. We have found that when using this product as an adhesion additive for bitumen, a synergistic effect occurs which manifests itself in improving the adhesion to bitumen sample 1 N GOST11508-74. Flow surfactant is 0.5-1.5% by weight of bitumen. The molten surfactant is introduced into the bitumen heated to operating temperature (100-150 o C) and stirred 10-20. Evaluation of adhesion strength of the bitumen was carried out by comparing the adhesion of bitumen with acidic rocks in accordance with GOST 11508-74 with different amount of surfactants in the bitumen. Data for adhesion and physicomechanical properties of the bitumen with the surfactant shown in Table 2.
Bitumen film for bitumen without surfactant is peeled from the mineral material after 30 minutes of boiling almost entirely. When introduced into the bitumen 0,5% surfactant retained by its mass on the quartz sand more than 3/4 pad bitumen film after boiling, and at least 4.3 square granite. At a flow rate of surfactant 1.0% or more by weight of bitumen retained almost the entire surface of the bitumen film on the mineral material.
The mechanism of action of surfactants in bitumen may be represented as follows. When introduced into the bitumen surfactant surfactant molecules are adsorbed on the disperse particles in bitumen, ie. E. On asphaltene units, lowering the interfacial tension at the interface units asphaltene (dispersed phase) liquid hydrocarbons (dispersion medium). In the formation of the bituminous film on the surface of mineral grains acidic rocks occurs bituminous particulate adsorption on their surface. Present on the surface of the bitumen particles of surfactant molecules leads to significantly better grip bitumen film with stone material surface and increases the adhesion strength.
CLAIM
Application penazolina containing a mixture of imidazolines of the following structure, by weight.
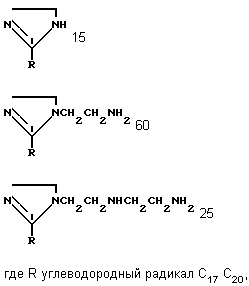
as adhesion additives to the bitumen to improve adhesion with acidic rocks.
print version
Publication date 31.10.2006gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.