| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2130912
![]()
RAW MIXTURE AND METHOD OF MANUFACTURING WALL CERAMICS
The name of the inventor: M. Sadovich ; Lokhova NA; Volkova O.E .; Yakovlev EI
The name of the patent holder: Bratsk Industrial Institute
Address for correspondence: 665728, Irkutsk region, Bratsk, Makarenko street 40, Bratsk industrial institute, patent department
Date of commencement of the patent: 1997.10.07
The invention relates to the production of building materials and can be used for the manufacture of wall ceramic products. The raw material contains components with the following ratio, by weight: Gliages 23-41, microsilica 77-59. The method for manufacturing wall ceramic products from the above raw meal includes the preparation of the charge, shaping, drying, calcining at 900-950 ° C, and additional moistening of the products after firing. The technical result of the invention is to increase the strength of burned articles.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the production of building materials and can be used for the manufacture of wall products.
A raw mix for the manufacture of ceramic products is known, including the ferro-silicon production lines, loam and chemical additive [1]. However, products from the proposed mass are characterized by a high average density, and consequently, deteriorated heat-shielding properties.
The raw material mixture closest to the proposed raw material in terms of its technical essence and achieved effect is 60-85% of the ash of dry sampling at the Tom-Usinskaya GRES and 40 ... 15% of fine ferrosilicon wastes [2]. A disadvantage of this mixture is the relatively low strength of the fired products.
The invention solves the problem of increasing the strength of fired products.
The technical result is achieved by using microsilica of the production of crystalline silicon in the raw mixture as siliceous dust, and as the aluminosilicate component, gliobes with the following component ratio, by weight:
Gliages - 23-41
Microsilica production of crystalline silicon - 77-59
Microsilica production of crystalline silicon is a multi-tonnage waste, most of which currently does not find any rational use. Specific surface microsilica - more than 25 thousand cm 2 / g.
The preferred particle size of this waste is 0.1 ... 3 μm. According to the existing technological scheme, microsilica is precipitated in electrostatic precipitators of the gas cleaning system of melting furnaces of crystalline silicon production, after which it is removed in the form of an aqueous suspension into the sludge dump.
Microsilica of production of crystalline silicon is an amorphous material and has the following chemical composition, mass%:
SiO 2 90 - 95
Al 2 O 3 - Up to 0.8
Fe 2 O 3 - Up to 0.8
CaO - Up to 1.6
MgO - Up to 1,2
K + - Up to 0,25
Na + - Up to 0.06
SiC - Up to 5
Msg. - Up to 9
Pp. - Up to 20
The high specific surface and amorphous state of microsilica causes its high chemical activity and a decrease in the temperatures of the reactions occurring during roasting. Burning carbon contained in the waste provides additional porcelain porridge and reduced fuel consumption for firing.
Gliakes are natural burnt rocks formed as a result of self-ignition of carbonaceous rocks under natural conditions for a long time. Gliages, having a high content of dehydrated clayey constituents, almost do not have a vitreous phase and carbonaceous impurities.
Chemical composition of glazes of the Kodinskoye deposit, mass%
SiO 2 63.6
Al 2 O 3 - 18.4
Fe 2 O 3 - 7.2
CaO - 2,3
MgO 1.9
SO 3 - 0.13
TiO 2 - 0.84
Na 2 O 1.43
K 2 O - 3.7
Pp. - 0.5
S -100
Soluble Al 2 O 3 - 3.7
The partially decomposed and disordered structure of the glue, and the high content of soluble alkalis, aluminum oxides, iron in them, cause the active interaction of glia and microsilica with the formation of a silicate melt and the formation of a strong ceramic shard.
A method for the manufacture of ceramic articles is known, which includes the preparation of a mixture, molding, drying and firing of articles [1]. However, products manufactured by this method have a relatively high average density and deteriorated heat shield characteristics.
The method closest to the proposed method for the technical essence and the effect achieved is the method [2], which involves preparing the mixture, molding, drying and roasting the products at 1000 ° C. Disadvantages of this method are the increased costs of firing and low strength of the baked products.
The technical result is achieved by the fact that the products made from the proposed mixture are burned at 900 ... 950 ° C and placed in a moist environment.
Example 1
To prepare the raw mix, microsilica is used for the production of crystalline silicon from the Bratsk Aluminum Smelter and glazes of the Kodinskoye deposit.
Crushed grains to a particle size of less than 1 mm are mixed with microsilica, after which water is introduced in the amount necessary to produce a charge of humidity of 16%. The content of the ingredients (in% by weight) in the proposed formulations is given in Table. 1 (formulations N 1, 2, 3, see at the end of the description). From the received charge by the method of semi-dry pressing at a pressing pressure of 25 MPa, sample-cylinders with a diameter of 40 mm are formed, which are dried at 100 ... 110 ° C. to constant weight and calcined at 1000 ° C.
For calcined articles, the average density, water absorption, compressive strength and the design quality coefficient are calculated.
The use of the proposed raw mixture allows to increase the strength of the burned articles by 2.1 ... 2.7 times while maintaining the values of the average density.
The specific values of the parameters to be evaluated according to item 1. are shown in Table. 1
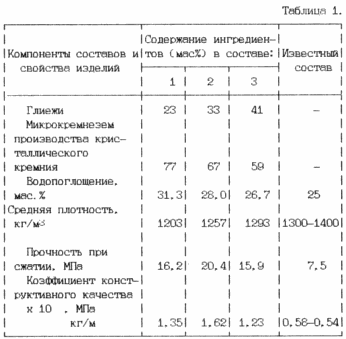
Example 2
Products made according to paragraph 1, dried at 100 ... 110 o C to constant weight and burn at 900 ... 950 o C. After roasting, the samples are moistened by standing in water for 24 hours.
For fired products, the average density, water absorption, compressive strength of dry and aged products within a day are determined.
Moistening of the calcined material leads to hydration of low-basic minerals formed during the firing process along with the traditional ceramic component, which in turn provides an additional increase in the strength of the products when moistened.
The specific values of the parameters to be evaluated as per item 2 are given in Table. 2 (see at the end of the description).
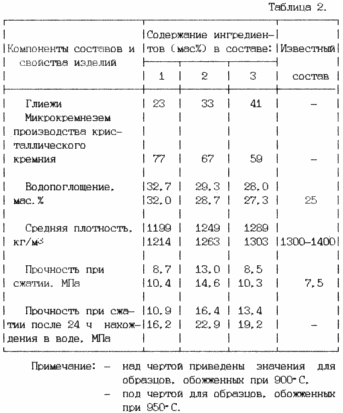
The proposed method provides an increase in the strength of products in 1,5 ... 3,1 times.
INFORMATION SOURCES
1. Ac. 1310366, MKI C 04 B 33/100 - 1987. - N 18.
2. Pak NV, Artemova LM, Makarov V.Ya., Shkolnikov P.V. Production of gold-ceramic stone and ash blocks of Tom-Usinskaya GRES // Power engineering. - 1990. - 3. - p. 38.
CLAIM
1. A raw material mixture for the manufacture of wall ceramic products, including siliceous and aluminosilicate components, characterized in that it contains microsilica as a silica component in the form of dusty wastes of production of crystalline silicon, and as an aluminosilicate component, glia, with the following component ratio, wt% :
Gliakes - 23 - 41
Microsilica - 77 - 59
2. A method of manufacturing walled ceramic articles from a raw meal mixture according to claim 1, comprising preparing the charge, shaping, drying and calcining, characterized in that the articles are burned at 900 ° -950 ° C. and after roasting are placed in a moist medium.
print version
Date of publication 06.04.2007гг




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.