| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2060242
![]()
METHOD FOR PREPARATION OF WATER SUSPENSION
The name of the inventor: Caprielov SS; Sheynfeld AV; Rudomino MV; Gurevich MZ; N. Krutikova; Kopeiko EG
The name of the patent holder: Scientific Research, Design and Technological Institute of Concrete and Reinforced Concrete
Address for correspondence:
Date of commencement of the patent: 1993.09.06
Use: in the production of active mineral additives for concrete.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION: An aqueous suspension is prepared by mixing microsilica of water and complex salts based on nitrilotrimethylenephosphonic acid at a component ratio, by mass% : microsilica 50 to 70 ; Complex salts based on nitrilotrimethylenephosphonic acid 0.05-0.42; Water - the rest. The suspension has an improved stable consistency over time.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to methods for preparing fluid, concentrated and stable microsilica suspensions used as an active mineral additive for concrete.
A method for producing concentrated slurries from microsilica is known , comprising mixing an aqueous suspension of microsilica of 70-75% concentration with a stabilizing component with hydrochloric or sulfuric or acetic acids.
A disadvantage of this method is that the suspensions have low flowability, and the addition of these acids reduces the pH of the suspension from microsilica to 4.0-4.6 , which leads to a decrease in the inhibitory properties of concrete with respect to steel reinforcement.
The purpose of the invention is to increase the inhibitory properties of concrete in relation to steel reinforcement, and to improve the stability of the consistency of the suspension in time and its activity in concrete.
The aim is achieved in such a way that complex salts based on nitrilotrimethylene phosphonic acid are used in the process for preparing an aqueous suspension comprising mixing microsilica, water and a stabilizing component with the following component ratio, Microsilica 50-70 Complex salts based on nitrilotrimethylenephosphonic acid 0.05-0.42 Water remaining.
The proposed method differs from the prototype in that, with new component ratios, complex salts based on nitrilotrimethylenephosphonic acid are used as the stabilizer, which, due to their complex action (bind metal ions on the surface of microsilica particles to poorly soluble complexes, Modify the double electric layer of microsilica particles Dissolve the diffuse Layer around microsilica particles) prevent the formation of longitudinal and transverse bonds (cross-links) between microsilica particles and lead to the disintegration of molecular-dense aggregates. Increase the aggregative and sedimentation stability and reduce the viscosity of the suspensions, thereby increasing the stability of the suspension over time and increasing the activity of the microsilica slurry as an additive to the concrete.
Consequently, the claimed method meets the criteria of "novelty" and "inventive step".
The method of preparing aqueous suspensions is as follows. The calculated amount of components, Water 29.58-49.95 ; Stabilizer 0.05-0.42 ; Microsilica 50-70 , which are intensively mixed until a homogeneous suspension of 50-70% concentration is formed.
Example
The characteristics of the materials used for the preparation of suspensions are given below. As microsilica (MK), ultrafine production was used for the production of ferrosilicon at the Chelyabinsk Electrometallurgical Combine of the MK-85 grade according to TU 7-249533-01-90 . As stabilizing components, complex salts based on nitrilotrimethylene phosphonic acid were used:
Dihydrate trisodium salt of nitrilotrimethylenephosphonic acid "Corilate" (MF) N (CH 2 PO 3 H) 3 Na 3 2H 2 O , corresponding to TU 6-09-20-216-92 ;
Trisodium salt of the zinc complex of nitrilotrimethylene phosphonic acid (NFC) N (CH 2 PO 3 ) 3.
H.
Zn x xNa 3.
3H 2 O , corresponding to TU 6-09-01-642-83 (with notices N 1, 2) ;
Complex ammonium salt (AMFO) consisting of a mixture of ammonium salt of nitrilotrimethylenephosphonic acid (95%) "Amifol" N (CH 2 PO 3 ) 3 H 3 (NH 4 ) 3 corresponding to TU 6-09-20-195-91 and oxyethylidenediphosphonic acid (5%) of CH 3 C (OH) (PO 3 H 2 ) 2 corresponding to TU 6-09-5372-87 (with Notification No. 1) .
The stability of the suspension was evaluated by the presence of stratification and water separation, which were determined according to the following procedure. A suspension of microsilica in a volume of 200 cm 3 was placed in a graduated cylinder 35 mm in diameter and over time (up to 90 days ) the volume of water released on the surface of the suspension was determined as a percentage of the total volume. With a water separation of more than 1% , it was considered that the suspension is stratified and its stability is lost. The fluidity of the suspension was estimated from the time of the suspension of the suspension from the VZ-4 device in accordance with GOST 9070 (with a hole diameter of 8 mm ). The pH of the suspension was determined on a pH meter of grade I-120M .
The results of the studies of suspensions are given in Table. 1 .
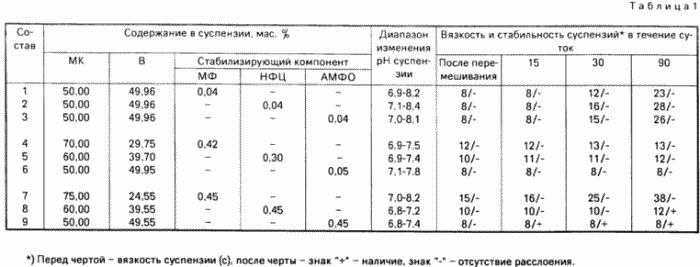
To determine the activity of suspensions from microsilica as an additive to concrete, concretes with the addition of superplasticizer C-3 and suspensions prepared according to the compositions 4, 5 and 6 of Table 1 were studied. 1 . The concretes had the same composition of the components, and the suspensions stored for 90 days were added in an amount in which the dosage of microsilica (on dry matter) was 20 wt. Cement. The water included in the suspension was accounted for as mixing water. The activity of suspensions was estimated from the mobility of concrete mixtures (OK) and the strength of concrete at 28 days of normal hardening, which was determined on samples of cubes 10 x 10 x 10 cm by standard technique.
Materials used:
- Portland cement M400 of the Voskresensky plant, corresponding to GOST 10178 ;
- Superplasticizer S-3 NPO Orgsintez , corresponding to TU 6-36-0204229-625-90 ;
- Sand quartz with Mkr = 2,1 ;
- Rubble granite fraction 5-20 mm .
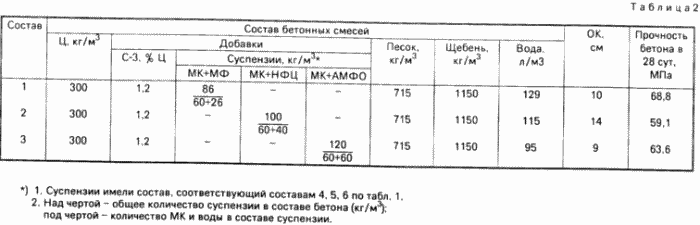
Compositions of concrete mixtures and the results of tests of concrete are given in Table. 2 .
As can be seen from the results, the pH of all suspensions is in the range 6.9-8.4 , which indicates the neutral character of the suspension medium and their non-aggressive nature with respect to metals ( Table 1 ).
The proposed stable microsilica suspensions have great fluidity and stability, which practically do not change until 90 days of storage. Making suspensions of a higher concentration, and lowering the dosages of the stabilizer lead to a sharp increase in the viscosity of the system. When the stabilizer is introduced in quantities higher than those proposed for practically unchanged slurry viscosities, the sedimentation stability of the system decreases and its stability is lost.
As can be seen from the results of the concrete test ( Table 2 ), the use of complex salts based on nitrilotrimethylenephosphonic acid as stabilizers of a suspension of microsilica results in a certain increase in the mobility of concrete mixtures and in the strength of concrete, which indicates an increased pucolanic activity of these suspensions.
Thus, the proposed microsilica suspensions are non-corrosive to metals, have great fluidity and lasting (up to 90 days ) stability.
CLAIM
A process for the preparation of an aqueous suspension comprising mixing microsilica, water and a stabilizing component, characterized in that the complexing salts based on nitrilotrimethylene phosphonic acid are used as the stabilizing component at the following component ratio,
- Microsilica 50-70
- Complex salts based on nitrilotrimethylenephosphonic acid 0.05-0.42
- Water Other
print version
Date of publication 25.11.2006гг




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.