| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2278848
![]()
THERMAL INSULATING CONCRETE
The name of the inventor: Svatovskaya Larissa Borisovna (RU); Solovyeva Valentina Yakovlevna (RU); Rusanova Ekaterina Vladimirovna (RU); Sychev Anastasia Maksimovna (RU); Anatoly Khitrov (RU); Titova Tamila Semyonovna
The name of the patent holder: State Educational Establishment of Higher Professional Education "St. Petersburg State Transport University of the Ministry of Railways of the Russian Federation" (RU)
Address for correspondence: 190031, St. Petersburg, Moscow Ave, 9, PGUPS of the Ministry of Railways of Russia, the Patent Department
Date of commencement of the patent: 2005.01.17
The invention relates to the field of building materials and can be used for manufacturing products in industrial and civil construction.
The technical result of the invention is the production of heat insulating concrete with improved protective properties for thermal insulation and for environmental performance by improving the ability of the material to adsorb heavy metal ions. Thermal insulating concrete, including cement, lime, aggregate - sand, water, complex foam-forming additive containing, in mass% : sodium abietate 30,34-33,67 , potassium alkali 6,88-7,64 , mezdra adhesive 10,67- 11,83 , water 34,11-37,86 and fatty acid salts 9,0-18,0 , contains additionally the aggregate-ash from the incineration of sewage sludge, at the following ratio of components, mass% : cement 28,7-33 , 5 , lime 4,6-7,6 , sand 8,8-9,1 , indicated ash 26,5-27,1 , specified additive 0,32-0,33 , water - the rest.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the field of building materials and can be used for manufacturing products in industrial and civil construction.
Heat-insulating concrete is known, containing, by weight : cement: 44.0-47.00 ; Foam-forming additive "NIKA" (based on hydrolysed blood of cattle, where aluminum sulfate Al 2 (SO 4 ) 3 ) is used as a stabilizer -0.5-0.7, montmorillonite clay (including at least 60% of mineral (Al, Mg) 2 (OH) 2 [Si 4 O 10 ] · H 2 O and with specific surface area 1500-2000 cm 2 / g ) - 11.0-13.8 and water 40.0-42.8 ( RF patent No. 2145586, C 04 В 38/10, 02/03/1999 ).
Heat-insulating concrete is known, containing, in mass% : cement - 43,0-46,2 ; Thin-ground slag of metallurgical production (with Fe (II) content not more than 4% ) - 12,0-14,4; Sand - 18,0-15,0 ; Foaming additive (based on sodium stearate density of 1.15-1.7 g / cm 3 ) - 9.5-10.3 ; Chemical additive "DEA" (includes a post-burnt bard and modifier - expanded porous product with a bulk density of 0.5 g / cm 3 in an amount of 3.0% ± 0.5 by weight , represented by calcium magnesium silicates) - 0.4- 0.5 ; Aluminum powder - 0,5-0,6 ; Fibreboard fiber - 1.4-1.8 and water - 12.0-14.4 ( RF patent No. 2145315, C 04 V 38/10, 02.03.1999 ).
The closest to the claimed heat-insulating concrete, chosen for the prototype, is a cellular autoclave foam concrete containing cement - 38.0-42.0; Sand - 28,0-30,0 ; Lime - 4,2-4,6 ; Complex foam-forming additive (sodium abietate C 19 H 29 COONa · 3C 15 H 29 COOH - 30,30-33,67 , potassium alkali KOH - 6,88-7,64 , mezdrovy glue - 10,67-11,83 , water - 34.11-37.86 and fatty acid salts - 9.0-18.0 ) - 0.4-0.7 and water - 25.4-26.7 ( RF patent No. 2205814, C 04B 38 / 10, 06.05.2002 ).
The shortcomings of these analogues and the prototype include insufficient thermal insulation properties of the material (increased coefficient of thermal conductivity) and low properties of environmental protection (in terms of protection against ions of heavy metals).
The object of the invention is to provide a new heat insulating concrete with improved protective properties for thermal insulation and for environmental performance by improving the ability of the material to adsorb heavy metal ions.
The object is achieved in that the heat-insulating concrete comprising cement, lime, aggregate is sand, water, a complex foaming additive containing, in mass% : sodium abietate 30,34-33,67 , potassium alkali 6,88-7,64 , Mezdr glue 10,67-11,83 , water 34,11-37,86 and fatty acid salts 9,0-18,0 , it contains an additional aggregate-ash from the incineration of sewage sludge, at the following ratio of components, mass% :

At the time of application, in the opinion of the authors and the applicant, the claimed insulating concrete is not known and has a world-wide novelty.
The claimed set of essential features shows a new property that allows to obtain the specified technical result, namely, the heat-insulating properties of the material are improved (the coefficient of thermal conductivity decreases) and the ability to adsorb heavy-metal ions with equal other physical-mechanical properties is improved in comparison with known technical solutions.
From the state of the art, the use of ash from the incineration of sewage sludge for the production of heavy concrete, lightweight concrete and in ceramics (the production of ceramic bricks) is known. The indicated technical result is obtained due to a new combination of components, hardening which is carried out under hydrothermal conditions at a temperature of 175 ° C and a pressure of 8 atm , which provides an increase in hydration processes with the formation of low-basic calcium hydrosilicates (such as tobermorite), which, characterized by a low coefficient of thermal conductivity, and Provide a tomermorite bond in the gel state, which gives the resulting foam concrete a reduced value of the thermal conductivity coefficient and an increased protective ability for heavy metal ions.
The claimed invention is industrially applicable and can be used in industrial and civil construction for the manufacture of products characterized by improved thermal conductivity and environmental protection.
In addition, the use of ash from the incineration of sewage sludge as a filler for the manufacture of thermal insulating concrete will allow the utilization of ashes from incineration of sewage sludge, expand the raw material base of construction, simplify the technology of making foam autoclave hardening.
The feasibility of the invention is confirmed by examples of specific implementation.
EXAMPLE OF CONCRETE EXECUTION
Manufacturing of heat-insulating concrete
Dosage the cement with a dispenser.
Dosage lime with a dispenser.
The sand is grinded by a continuous-action wet-grinding mill up to a specific surface area Sd = 200 m 2 / kg .
Dosage the sand slurry with a dispenser.
Dosage ash (specific surface area Sd = 200-300 m 2 / kg ) from the incineration of sewage sludge from the general sewage system in St. Petersburg with the aid of a dispenser.
Dosage the water through the flowmeter into the sand grinding mill, into the preparation tank of the working solution of the foaming agent, into the weighing hopper in front of the mixer.
-
Prepare a complex foam-forming additive from foam concentrate ( Makhambetova UK, Soltambekov TK, Estemesov ZA "Modern foam concrete", St. Petersburg, 1997 )
Dosage the complex foam-forming additive.
The dosed foaming additive is mixed with water in a 1:25 combination and a working solution of the foaming additive is obtained.
The resulting working solution of the foam-forming additive is converted into a foam with a bulk density of 80 g / l by means of a foam generator.
The detached sands of sand and ash, water, cement, lime enter the mixer, where the mixing is carried out for 2 minutes.
The resulting solution is added with the resulting foam and mixed thoroughly for 1 minute until a uniform foam-concrete mixture is obtained.
-
The resulting foam concrete mixture is used to prepare articles and samples that are subjected to autoclave treatment:
Pre-aging in pre-holding chambers with t = 30-40 ° C for 4-6 hours ;
Hardening of concrete in an autoclave according to the scheme 2.5-12 - 4 (hours) , where 2.5 hours - temperature rise from 20 ° C to 175 ° C ; 12 hours - isothermal heating at t = 175 ° C and pressure p = 8 atm ; 4 hours - cooling at normal pressure.
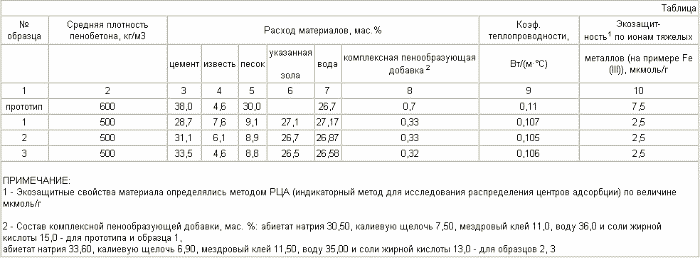
Foam concrete samples after autoclave treatment are subjected to tests in accordance with the requirements of TU 5741-004-51556791-2002 "Small wall blocks of cellular concrete (foam concrete)". The results of tests of heat-insulating concrete are presented in the table.
The analysis of the obtained results shows that the heat-insulating concrete on the basis of the proposed composition is characterized by reduced thermal conductivity and an increased ecological index, by improving the ability of the material to adsorb heavy metal ions.
This material can be recommended for the manufacture of products characterized by improved thermal conductivity and eco-protection for housing and civil construction.
CLAIM
Thermal insulating concrete, including cement, lime, aggregate - sand, water, complex foam-forming additive containing, in mass%: sodium abietate 30,34-33,67 , potassium alkali 6,88-7,64 , mezdra adhesive 10,67- 11.83 , water 34.11-37.86 and a fatty acid salt 9.0-18.0 , characterized in that it contains an additional aggregate-ash from the incineration of the sewage sludge with the following component ratio, by weight :

print version
Date of publication 11/21/2006




Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.