| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2234477
![]()
CONCRETE FOR PROTECTION AGAINST RADIATION
Name of the inventor: Boltyshev SA (RU); Korolev EV (RU); Proshin AP (RU); Queen Olga
The name of the patentee: Penza State Academy of Architecture and Construction
Address for correspondence: 440028, Penza, ul. Titov, 28, PenGASA, patent department
Starting date of the patent: 2002.04.16
The invention relates to compositions of radiation-protective concrete used in the construction of facilities intended to protect against radiation exposure of nuclear facilities, nuclear power plants, companies develop isotopes and other special facilities that use radioactive sources. The technical result - increasing the tensile strength and the reduction in the average density of the concrete. Concrete for protection against ionizing radiation includes, in weight%: sulfur - 28,7-33,2;. soot - 3,4-5,2; sand from the coal particle diameter, respectively 0,315-0,63 mm - 19,3-22,8; rubble of coal with a particle diameter of 5-10 mm - 38,1-48,2; kerosene - 0.4-0.7.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to compositions of radiation-protective concrete used in the construction of facilities intended to protect against radiation exposure of nuclear facilities, nuclear power plants, companies develop isotopes and other special facilities that use radioactive sources.
A composition of concrete (RU №2153714 C1, published 27.07.2000.) For protection against ionizing radiation, including sulfur, filler - active fine additive, fine aggregate - sand, coarse aggregate - crushed stone.
A disadvantage of the composition of the concrete mix is the high labor and energy cooking, long setting time and hardening, but not enough and high strength of the hardened concrete.
The purpose of the present invention - increase the tensile strength and the reduction in the average density of the concrete.
This goal is achieved by the concrete for protection against ionizing radiation, including sulfur, mill ground additive fine aggregate - sand and coarse aggregate - crushed stone, as the mill ground supplements contain soot, sand and rubble of crushed coal with a particle diameter of 0,315-0, 63 and 5-10 mm, respectively, and further builder - kerosene in the following ratio, wt.%:
Sulfur 28,7-33,2
Soot 3,4-5,2
This sand 19,3-22,8
This rubble 48,2-38,1
Kerosene 0.4-0.7
For the preparation of the concrete used technical sulfur, corresponding to GOST 127-76 requirements. Sulfur is a thermoplastic binder having a high coefficient of removal of neutron radiation with neutrons more than 2 MeV. In addition, products made on the basis of sulfur, characterized by rapid curing, related only to the period of cooling the material to a temperature below 80-120ºS.
Application as from fine carbon black additive, and as coarse and fine aggregate - crushed coal, which is the main non-deficient and neutron moderator in nuclear reactors, can significantly increase the radiation-protective properties of concrete. Furthermore, the introduction of carbon black promotes strength concrete.
Introduction The kerosene improves the technological properties of the concrete mix.
Concrete is prepared as follows. The molten sulfur at a temperature 150-160ºS introduced otdozirovannye amounts of kerosene and soot, the mixture is stirred until smooth. Then introduced heated to a temperature 150-160ºS fine and coarse aggregate and mix again thoroughly mixed, incubated for 5-10 minutes at a temperature 150-160ºS, placed in heated metal molds and vibrate on shaking table for 0.5-1 minutes. After cooling, the mold is subjected to stripping.
The compositions of the proposed concrete given in Table 1 and the properties - in Table 2.
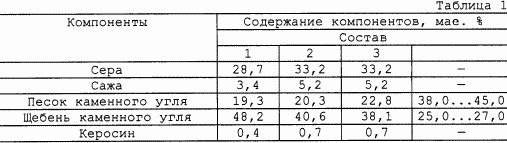
As can be seen from Table 2, the proposed concrete has a high (at 1,17-1,67 times) compressive strength and a lower (up to 1.11 times) the average density.
CLAIM
Concrete for protection against ionizing radiation, comprising a binder - sulfur from fine additive, fine aggregate - sand and coarse aggregate - rubble, characterized in that the additive it contains from fine soot, sand and gravel from the crushed coal particles having particle diameters respectively 0,315- 0.63 mm and 5.10 mm, and an additional builder - kerosene in the following ratio, wt.%:
Sulphur 28.7 ... 33.2
Soot 3.4 ... 5.2
This sand ... 19.3 22.8
This rubble 38.1 ... 48.2
Kerosene 0.4 ... 0.7
print version
Publication date 18.01.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.