| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2248381
![]()
BITUMENOUS-POLYMER MATERIAL AND METHOD OF ITS OBTAINING
The name of the inventor: Zaripov R.K.
(RU); Makhmutov AA (RU); Mahmutov MA (RU); Kuzmichev S.P. (RU); Khazipov RZ (RU); Gorbachev N.G. (RU); Kosorenkov DI (RU); Lebedev IN
The name of the patent holder: OOO "Dorplastservice" (RU); OOO "Izobit" (RU)
Address for correspondence: 423827, Republic of Tatarstan, Nizhnekamsk, ul. Shinnikov, 61, ap.119, D.I. Kosorenkov
Date of commencement of the patent: 2003.04.09
The bitumen-polymer material and the method of its preparation are related to the field of industrial preparation of modified bituminous mastics, sealing and waterproofing materials with improved technical characteristics for use in road and industrial civil construction. The bitumen-polymeric material consists of petroleum bitumen, synthetic rubber, petroleum solvent and / or fuel oil, sulfur-containing compounds and optionally containing a hydroxyethylated alkylphenol as a surfactant, as sulfur-containing compounds containing a sulfonated mixture of petroleum bitumen, synthetic rubber, petroleum solvent and / Or fuel oil, treated before airborne sulfonation at a temperature of 140-230 ° C, with the following ratio of components, mass parts: bitumen 60-70; Rubber 2-10; Sulfonated mixture of petroleum bitumen, synthetic rubber, petroleum solvent and / or fuel oil, 0.5-5.0; Oil solvent and / or fuel oil 18-30; Ethoxylated alkylphenol 0.1-5.0. And a method for preparing the above material is described. Improved quality and productivity of polymer modified bitumen mastics and sealants for waterproofing are achieved, using inexpensive materials available with energy savings.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the field of industrial preparation of modified bitumen compositions for road, industrial and civil construction, production of waterproofing and roofing materials, sealants and mastics with improved technical characteristics. The materials obtained have a wide range of applications in different climatic zones, are resistant to moisture, high and low temperatures, and have manufacturability in production and application.
Known are various bitumen-containing materials, in which additionally various additives are added: rubbers, thermoplastics, mineral fillers, plasticizers, antioxidants, adhesives, etc. Depending on the purpose and the required characteristics, their ratios may be different. However, the ways of introducing components, distributing them in bitumen, homogenizing and bringing to the required parameters determine the time of the production process, manufacturability, energy consumption and quality, which affects the cost of the materials obtained. Therefore, because of the above difficulties, only a limited number of developments have been distributed. Good enough in this respect can be called: polymer-bitumen mastics of hot application "IZHORA", MBR-G-90, MBR-G / Schm-75, TU 5775-002-11149403-97; Rubber-bituminous composite mastics MRBK-I / D, TU2384-003-40010445-2000; Mastic and sealing materials "BITREK-DI", patents RU №2167898, №2178434, TU5718-004-05204776.
The most closely related in technical essence is the bituminous polymer composition RU 2132857, comprising rubber, bitumen, sulfur and an organic vulcanization accelerator that contains as a rubber a terpolymer of ethylene, propylene and dicyclopentadiene and further contains fuel oil or industrial oil or toluene in the following ratio Components, parts by mass:
Bitumen 41-94
Fuel oil, or industrial
Oil, or toluene 3-48
Rubber 3-8
Sulfur 0.06-2.4
Organic vulcanization accelerator 0.06-0.24
According to the production method of claim 2, RU 2132857, characterized in that preliminarily rubber is mixed with fuel oil or industrial oil or toluene at 100-180 ° C to a homogeneous mass, bitumen, sulfur and an organic vulcanization accelerator are added to the resulting mass.
Disadvantages of the bitumen-polymer composition RU 2132857 are the presence of fuel oil or oil as a solvent or plasticizer in an unbound form, diluting the material, increasing penetration and reducing the softening point, and as a result, in the future, oxidized and sun-radiated oxidation and oxidation under the influence of acid-ozone depletion and solar radiation Dries up and thereby loses its original physico-chemical properties and performance characteristics (claimed advantages). The composition is characterized by a lack of metals or insufficient cohesive strength, a tendency to aging under the influence of solar radiation and oxygen. Among other things, the authors state that the lower limit of the plasticizer content of fuel oil or industrial oil can be 3 parts by weight, which implies according to the formula the minimum concentration of rubber in a mixture of any possible solvents to 50%, which under no circumstances can not be achieved. In reality, the minimum amount of fuel oil, or industrial oil, or toluene should be at least 9 wt. H, while maintaining the composition of the remaining components of the composition, according to the formula and description RU 2132857. The increase in the softening temperature of the prototype is possible only with an increase in the content of sulfur-containing or vulcanization time, which leads to a too viscous, heterogeneous and thus unsuitable material . The use of aromatic hydrocarbons (toluene) in the composition worsens the environmental situation at the manufacturing plant and at the construction site, among other things does not improve the technical characteristics of the material, lowers the flash point, which increases the risk of fire, explosion, accident, accident, etc. .
The purpose of the present invention is to increase adhesion, resistance to weathering (moisture, oxygen) and solar radiation, reduce production costs, simplify the process, and bring the characteristics of the resulting materials to the requirements of Russian regulatory documents: SniP 2.05.03-84, SniP 3.06. 04-91 "Bridges and pipes", SniP 2.03.11-85 "Protection of building structures against corrosion, VSN 32-81" Instruction on the installation of waterproofing of bridges and pipes on iron, road and city roads. "
Cost reductions are achieved by using mass-produced rubbers such as SKI-3, SKS-30ARKM, SKMS-30ARKM, SKD-2, BK-1675H (T), (C), ethylene-propylene and ethylene-propylene diene SEP- (T), shortening the technological Process using sulphonation and oxidation with a sulfo-oxidant to produce a sulfonated mixture of petroleum bitumen, synthetic rubber, an oil solvent with the presence of alkanesulfonic acids R-SO 2 -OH, where R is a hydrocarbon radical, the effect and influence of which simultaneously contributes to the expansion of the range of heat resistance and strengthening of cohesive bonds in Obtained bitumen-polymer material, hereinafter referred to as BOP. In addition, the use of a sulfo-oxidant allows for controlled aging, which avoids aging during operation and loss of quality of technical properties. The use of alkali, caustic soda, allows to obtain in the composition of bitumen-polymeric materials mixtures in which salts of higher alkanesulfonic acids are the alkyl sulfonates R-SO 3 Me, where Me is a metal. In particular, the presence of alkyl sulfonates in the BPM composition further affects the surface-active properties, which increases the ability of the material to wet the surface to be treated and enhance adhesion.
Preliminary preparation of a rubber solution in an oil solvent and / or black oil allows the elastomer to be combined easily, which is the main modifying component affecting the physical and mechanical properties of the resulting bitumen-polymer materials with bitumen, which ensures uniform distribution of components in the mixture. The use of various organic and mineral fillers allows to obtain a wide range of manifestations of mechanical properties, such as deformation strength, toughness, ductility, etc.
According to the composition of the material, the technical problem of the present invention is realized by the production of a bitumen-polymer material consisting of petroleum bitumen, synthetic rubber, petroleum solvent and / or fuel oil, sulfur compounds and further containing as a surfactant oxyethylated alkylphenol, as sulfur-containing compounds it contains sulfonated Mixture of petroleum bitumen, synthetic rubber, petroleum solvent and / or fuel oil, treated prior to air-sulfonation at a temperature of 140-230 ° C, with the following ratio of components, mass parts:
Bitumen 60-70;
Rubber 2-10;
Sulfonated mixture of petroleum bitumen, synthetic rubber, petroleum solvent and / or fuel oil, 0.5-5.0;
Oil solvent and / or fuel oil 18-30;
Ethoxylated alkylphenol 0.1-5.0.
In the bituminous polymer material, an alkanesulfonic acid is present as one of the sulfur-containing components. After introduction of the sulphoxidant into the mixture, alkanesulfonic acids appear as a result of the sulfonation reaction, which increase the technical characteristics of the BPM.
Additional introduction to the mixture after sulfonation of caustic soda allows to obtain salts of higher alkanesulfonic acids - alkyl sulfonates in the composition of BPM.
The amount of alkali introduction is controlled by the neutralization of alkanesulfonic acids and, accordingly, the content of alkyl sulfonates, the sulfur-containing ones additionally being alkanesulfonic acid, alkyl sulfonate or an alkanesulfonic acid mixture with alkyl sulfonates and other sulfur-containing compounds obtained by sulfonating bitumen, rubber, petroleum solvent and / or fuel oil.
In addition, BOP may contain, as filler, mineral powders, organic crumbs or a multicomponent mixture thereof with the following component ratio, mass parts:
Bitumen 60-70;
Rubber 2-10;
Sulfonated mixture of petroleum bitumen, synthetic rubber, petroleum solvent and / or fuel oil, 0.5-5.0;
Oil solvent and / or fuel oil 18-30;
Ethoxylated alkylphenol 0.1-5.0;
Filler of 1.0-15.0.
According to the method, a technical problem is solved by producing a bitumen-polymeric material comprising the preparation of a mixture by mixing oil bitumen with a synthetic rubber solution in an oil solvent and / or fuel oil at a temperature, followed by sulfonation, where oil bitumen is blended with 6.25-30% rubber solution in an oil Solvent and / or fuel oil is stirred at a temperature of 140-230 ° C with air treatment until a uniform mixture is obtained, followed by sulfonation by the addition of a sulfooxidant for 10-60 minutes to obtain a mixture of sulfur-containing compounds in the mixture, followed by the introduction of an ethoxylated alkyl phenol with the following component ratio , Wt. H .:
Bitumen 60-70;
A solution of rubber in an oil solvent and / or black oil 20-40;
Sulfur-containing compound 0.5-5.0;
Ethoxylated alkylphenol 0.1-5.0.
And by the method of preparation, the technical problem is solved by introducing, after sulfonation, a mixture of bitumen, rubber solution and sulfur-containing compounds into the mixture, before the introduction of the ethoxylated alkylphenol, alkali, at the following component ratio, H .:
Bitumen 60-70;
A solution of rubber in an oil solvent and / or black oil 20-40;
Sulfur-containing compound 0.5-5.0;
Ethoxylated alkylphenol 0.1-5.0;
Alkali (caustic soda) 0.5-5.0.
Thus, a complete or partial neutralization reaction of the alkanesulfonic acid is carried out to produce alkyl sulfonates in the BPM, the degree of neutralization is controlled by the amount of alkali introduced, depending on the required technical characteristics of the BPM.
If necessary, in order to obtain a BPM with more viscous parameters, greater rigidity, increased softening temperature and heat resistance, an additional filler is added in an amount of 1.0-15.0 parts by weight.
The technology of obtaining the BOP is as follows.
Preliminarily crush synthetic rubber, then it is mixed with fuel oil and petroleum solvent, or with one of them, with the petroleum solvent being kerosene, naphtha or an oil solvent, white spirit, nefras and the like.
After obtaining a homogeneous solution with the required concentration within the range of 6.25-30%, it is introduced into the oil bitumen preheated to 100 ° C, which can be, for example, BND90 / 130 or BN-90/10, the temperature is raised to 140- 230 ° C. and mixed with air-treatment by self-suction into the mixture by means of a mechanical stirring device or forced from the compressor, or any other air blowing device.
After the components are completely mixed into the mixture of bitumen and the solution, a sulphoxidant is introduced, which can be, for example, sulfuric acid H 2 SO 4 , in batches, discretely or with a calibrated per unit time dispenser for 10-60 minutes, Experimentally, depending on the raw materials used and the necessary requirements for the technical parameters of the finished product, for example, the softening and brittle temperature.
Next, a surfactant, a hydroxyethylated alkylphenol, may be introduced, which may be polyethylene glycol ether of mono- and dialkylphenols R-C6H4O- (CH2CH2) n-CH2CH2OH, for example OP-10 or oxyethylated monoalkylphenol based on Trimers of propylene neonol brand AF9-10 in the right amount and mix. If necessary, depending on the specific purpose of the resulting material, a filler, which may be dolomite flour, silica or carbon black, rubber crumb, mineral powder or a multicomponent mixture thereof, is added to the resulting material. After mixing the incoming components and achieving homogeneity, the finished product is drained and packed.
Recommended substances for bitumen-polymer material:
A) rubber - SCEP- (T), TU2294-035-05766801-95;
BK-1675N, TU2294-034-05766801-95;
SKI-3, GOST 14925-79; SKDK (N), TU2294-073-05766801-98
B) fuel oil - M-100, GOST 10585-75;
C) bitumen - BND 90/130, GOST 22245-90; BN-90/10, GOST 6617-76;
D) surfactant - AF 9-10, TU 2483-077-05766801-98; OP-10, GOST 8433-81;
E) solvent - naphtha K-6, TU-0250-001-04855329-94; Oil solvent GOST 10214-78; White spirit C4-155 / 200;
F) filler - carbon black P-514, TU38-41558-97; Rubber crumb of fraction 1.0-1.5mm, TU 38.00149438-48-92; Mineral powder, GOST 16557-78;
G) sulfooxidant - sulfuric acid, GOST 2184-77;
H) alkali - caustic soda NaOH.
The invention is illustrated by the following examples.
Example 1
1.1 A crumb of EPDM-40 in an amount of 15 kg is mixed and dissolved in 85 kg of M-100 fuel oil at a temperature of 100 ° C.
1.2 The resulting solution is introduced into 300 kg of pre-heated BND 90/130 bitumen and the temperature is raised to 180 ° C with simultaneous stirring and air treatment provided by self-suction into the mixture while the agitator is operating.
1.3 After obtaining a homogeneous mixture with continued mixing, a sulfooxidant, 15 kg of concentrated sulfuric acid H 2 SO 4 , is uniformly introduced within 20 minutes. Thirty minutes after the acid supply is cut off, the analysis of the obtained material is made to match the softening temperature T kiso ° C with the required characteristics and, in case of a positive result, 15 kg of ethoxylated monoalkylphenol of neonol AF9-10 brand are introduced into the mixture and mixed for 30 minutes, the temperature is maintained within 160 -180 ° C.
1.4 At the end of cooking, the product is drained. The ratio of the incoming components and the composition of the resulting bitumen-polymer material is shown in Table 1.
Example 2
2.1. A crumb of SKY-3 rubber in an amount of 15 kg is mixed and dissolved in 80 kg of M-100 fuel oil and 5 kg of C4-155 / 200 at a temperature of 100 ° C until a homogeneous mass is obtained.
2.2. The resulting solution is introduced into 350 kg of pre-heated bitumen BND 90/130, the temperature is raised to 180 ° C and mixed with the treatment of the mixture with air.
2.3 After the homogeneous mixture is obtained, 15 kg of sulfuric acid is introduced for 20 minutes with continued agitation.
2.4. After 30 minutes, after the acid supply has ceased, after oxidation and sulfonation with simultaneous stripping of the light ends of the solvent C4, a sample is taken for analysis of the softening point. In case of inconsistency of Tkish ° C, the necessary mixing process is continued until the required result is achieved and then 5 kg of OP-10 substance are introduced into the mixture and mixed for 10 min at T = 160-180 ° C.
2.5 At the end of the process, a mixture of mineral powder with rubber chips of 25 kg each is introduced into the resulting mixture and mixed for 45 minutes until complete distribution and uniformity.
2.6 The finished product is drained and packaged. The ratio of the incoming components and the composition of the produced BPM are presented in Table 2.
Example 3
3.1 Crumb rubber SKDK (H) in an amount of 15 kg is mixed with 80 kg of fuel oil M-100 at T = 100 ° C and dissolved until a homogeneous mass is obtained.
3.2 The resulting solution is introduced into 350 kg of liquid bitumen BND 90/130, the temperature is raised to 180 ° C and mixed with the air mixture treatment.
3.3 After obtaining a homogeneous mixture, 15 kg of sulfuric acid is introduced with continued agitation for 20 minutes.
3.4. After 30-50 minutes after the acid supply is cut off and the sulfonation is carried out, the softening temperature of the material obtained is determined and, if a positive result is obtained, i.e. To achieve the required Trici ° C, 15 kg of crystalline caustic NaOH are introduced and mixed for 30 minutes to form a sulfonated mixture of alkyl sulfonates in the BPM composition.
3.6 Then 5 kg of neonol AF9-10 are added and mixed for 20 minutes at a temperature of 160-180 ° C.
3.7 At the end of the process of mixing with surfactants, carbon black P-514 is added to the resultant in an amount of 50 kg and mixed until uniform. The finished product is drained and packaged. The ratio of the incoming components and the composition of the obtained BPM in Example 3 are presented in Table 3. The characteristics of the obtained BPM are presented in Table 4.
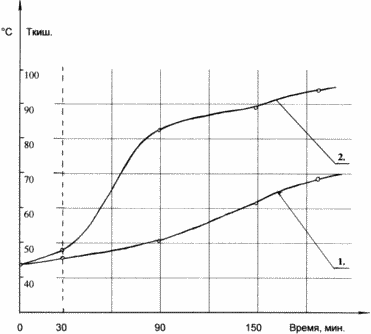 |
The kinetic dependence of the degree of preparation of bitumen-polymeric materials with the use of the sulfo-oxidant in the process, in comparison with the method for producing modified bitumens and bitumen-polymeric materials by air oxidation is shown in the graph of FIG. Curve 1 demonstrates the dynamics of the variation of the softening temperature T ° C according to Kishnan without the use of a sulfo-oxidant. Curve 2 demonstrates the dynamics of the variation of the softening temperature T ° C according to KiSH when using a sulfo-oxidant. Depending on the purpose of the bitumen-polymer material, the ratios of the incoming components may vary. The softening temperature is the determining factor for determining the degree of availability of the material and is controlled by the amount of the sulfooxidant fed, the mixing time, and the process temperature. The physical and mechanical properties of bitumen-polymer materials of BPM make it possible to use them as mastics for the repair of roads, sealants for sealing inter-panel joints, coating masses for waterproofing, corrosion protection of main pipelines and metal structures. Materials are resistant to low and high temperatures, which allows them to operate in the northern and southern regions of Russia. |
The ratio of the incoming components and the composition of the resulting bitumen-polymer materials of BPM.
Example 1
| Table 1 | |||
| Incoming components | Number of kg. | Composition of bodyshaft | Amount, wt. H |
| SKEPT-40 rubber | 15 | SKEPT-40 rubber | 3.5 |
| Fuel oil M-100 | 85 | Fuel oil M-100 | 20 |
| Bitumen BND90 / 130 | 300 | Bitumen BND90 / 130 | 66.5 |
| H 2 SO 4 | 15 | H 2 SO 4 | - |
| Sulfur compounds | 3.5 | ||
| Neonol AF9-10 | 15 | Neonol AF9-10 | 3.5 |
Example 2
| table 2 | |||
| Incoming components | Number of kg. | Composition of bodyshaft | Amount, wt. H. |
| Rubber SKI-3 | 15 | Rubber SKI-3 | 3 |
| Fuel oil M-100 | 80 | Fuel oil M-100 | 15.5 |
| Bitumen BND90 / 130 | 350 | Bitumen BND90 / 130 | 65 |
| H 2 SO 4 | 15 | H 2 SO 4 | - |
| Sulfur compounds | 3 | ||
| C4-155 / 200 | 5 | C4-155 / 200 | - |
| Substance OP-10 | 5 | Substance OP-10 | 1 |
| Mineral powder fr. 0.07 mm. | 25 | Mineral powder Fr. 0.07 mm. | 4.8 |
| Rubber crumb | 25 | Rubber crumb | 4.8 |
Example 3
| Table 3 | |||
| Incoming components | Number of kg. | Composition of bodyshaft | Amount, parts by weight |
| SKDK (N) rubber | 15 | SKDK (N) rubber | 2.8 |
| Fuel oil M-100 | 80 | Fuel oil M-100 | 15.1 |
| Bitumen BND90 / 130 | 350 | Bitumen BND90 / 130 | 63.2 |
| H 2 SO 4 | 15 | H 2 SO 4 | - |
| Caustic soda | 15 | Caustic soda | - |
| Sulfur compounds, including: Alkanesulfonic acids, Alkylsulfonates | 2.8 | ||
| Neonol AF9-10 | 15 | Neonol AF-9-10 | 15 |
| Carbon black P-514 | 50 | Carbon black P-514 | 10 |
Table of the main technical indicators of bitumen-polymer material
| Table 4 | ||||
| The name of the indicator | Example 1 | Example 2 | Example 3 | Prototype |
| Softening temperature, T ° C, according to Kish, not lower than | 80 | 95 | 90 | 54 |
| Depth of needle penetration, 0,1 mm., At + 25 ° С, not less than | 25 | 25 | 33 | 103 |
| Flexibility on a beam of radius R = 25 mm, ° C, not higher than | -25 | -25 | - | - |
| Temperature of brittleness according to Fraas, ° C, not higher | -thirty | -25 | -25 | -33 |
| Heat resistance, not lower than, ° С | 70 | 85 | 80 | - |
| Extensibility, cm, at + 25 ° С, not less than | 6th | 7th | 5 | - |
| Strength of adhesion to concrete, MPa, not less, at + 20 ° С | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.5 | - |
| Type of separation | Cohesion The |
Cohesion The |
Cohesion The |
- |
| Strength of adhesion to steel, MPa, not less, at T = + 20 ° С | 0.7 | - | - | Absences. |
| Water absorption for 24 hours,% by weight, no more than | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0,15 | - |
| Elasticity at + 25 ° С,%, not less than | 50 | 70 | 50 | - |
| Flash point, ° С, not lower than | 220 | 230 | 220 | 170-180 |
CLAIM
1. A bitumen-polymeric material consisting of a mixture of petroleum bitumen, synthetic rubber, petroleum solvent and / or fuel oil, sulfur-containing compounds, characterized in that it further includes a hydroxyethylated alkylphenol as a surfactant, as a sulfur-containing compound it contains a sulfonated mixture From petroleum bitumen, synthetic rubber, petroleum solvent and / or fuel oil, to airborne sulfonation at a temperature of 140-230 ° C with the following ratio of components, mass parts:
Bitumen 60-70;
Rubber 2-10;
The aforementioned sulfur-containing compounds are 0.5-5.0;
Oil solvent and / or fuel oil 18-30;
Ethoxylated alkylphenol 0.1-5.0.
2. A bitumen-polymer material according to claim 1, characterized in that the sulfonated mixture is further treated with caustic soda.
3. Bitumen-polymer material according to claims 1 and 2, characterized in that it further comprises a filler in an amount of 1.0-15.0 parts by weight.
4. A process for producing a bitumen-polymer material, comprising: providing a mixture by mixing oil bitumen with a solution of EPDM rubber in an oil solvent and / or fuel oil at a temperature, followed by sulfonation, characterized in that oil bitumen is blended with 6.25-30% rubber solution in Oil solvent and / or fuel oil is stirred at a temperature of 140-230 ° C with air treatment until a uniform mixture is obtained, followed by sulfonation by the addition of a sulfoxidant for 10-60 minutes to form a sulfur-containing compound in the mixture, followed by the introduction of a hydroxyethylated alkylphenol at the following ratios Components, parts by mass:
Bitumen 60-70;
The above rubber solution is 20-40;
Sulfur-containing compound 0.5-5.0;
Ethoxylated alkylphenol 0.1-5.0.
5. The production method according to claim 4, characterized in that, before the introduction of the ethoxylated alkylphenol, after the sulfonation, an alkali is introduced in an amount of 0.5-5.0 parts by weight.
6. The production method according to claim 4 and 5, characterized in that after addition of the ethoxylated alkyl phenol, a filler is added in an amount of 1.0-15.0 parts by weight. And stirred.
print version
Date of publication 01/18/2007




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.