| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2278214
![]()
METHOD OF ESTABLISHMENT OF LOCAL FOUNDATIONS AND WALLS OF BUILDINGS, STRUCTURES AND DEVICE (ELEMENT) FOR ITS IMPLEMENTATION
The name of the inventor: Barkhatov Sergey Nikolaevich
The name of the patent owner: Barkhatov Sergey Nikolaevich
Address for correspondence: 105064, Moscow, ul. Ground shaft, 42/20, ap. 54, L.N. Ryzhkov for S.N. Barkhatova
Date of commencement of the patent: 2003.05.05
The invention relates to the field of construction, in particular for the erection of curvilinear foundations and walls of buildings and structures. New in the method of erecting foundations and walls from prefabricated prefabricated elements is that in the manufacture of curvilinear foundations and walls along the line of their location with a step determined by the dimensions of the precast element, there are mounting and frame guides for placing prefabricated elements on them with rounding and Holes at the ends for their interfacing at different angles, with rounding done up to half the height of the collecting element, the second half of the height of which is made with a ledge for the entire length of the rounding, and in the apertures of the prefabricated elements there are mounting frames to ensure the spatial stability and strength of the curvilinear foundations And walls. New in the element for the construction of curvilinear foundations and walls is that the element is made in the form of a block beam with rounded ends and holes at these ends to accommodate the mounting frame and support reinforcement, the rounded ends being made up to half the height of the beam and the second half Height is executed with a ledge on the entire length of the rounding. The technical result consists in the universality of the execution of curvilinear foundations and walls.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to construction and structural building elements providing various construction methods. It is intended for the erection (construction) of the local (planocervical) foundations and walls of buildings, structures, cellars, garages and storages from piece serial modular elements (block devices).
The construction of foundations and curvilinear supporting walls has always been one of the most responsible construction operations with increased requirements for the strength and sealing properties of block elements. In this regard, these typical elements, as a rule, had to meet the stringent requirements of state standards and be maximally uniform in form and manufacturing conditions.
An example (analog 1) can serve as GOST 13579-78 "Concrete blocks for cellar walls". In this GOST strict regulation is subject to both the type (three types of FBS, FWB and FBP), and the form (dimensions) of a standard set of elements in the form of a bar of fixed length and height and a step-by-step series of widths, which is caused by the requirements of productive production and minimization of construction costs . This approach fully meets the requirements for the construction of rectangular rooms and linear foundations. It is especially important that the VBV series has cutouts at the ends for skipping communications and laying the jumpers. The advantage of the analogue 1 is the possibility of preliminarily ensuring the unification of properties, the production of these types of timbers by industrial methods, the possibility of laying walls and foundations (linear) large surfaces by laying (the method of erection 1), increasing the strength and stability of structures.
The disadvantage of the method, determined by the lack of the basic element of laying, is the possibility and rationality of realization only for linear (rectilinear sections) of the foundations and walls. In the case of attempts to perform this method and this set of structural elements of more complex foundations, for example, the local ones, the above advantages become disadvantages. There appear unfilled or hard-to-fill seams, the method of dressing loses the advantages of a reinforcing construction, curved sections instead of strengthening the overall strength of the structure become weak points. In some cases, this creates advantages for competitive methods of making curved sections of foundations and walls by the method of individual shut-off filling with the formation of building material (for example, reinforced concrete) directly on the construction site or methods associated with non-serial single-configuration fabrication of precast elements (for example, RU 2024715) .
Analogous solutions (analog 1) exist for banded foundations (see GOST 13580-85. "Reinforced concrete slabs of band-like foundations) (analogue 2, prototype 1).
However, all the advantages mentioned above, just as in the case of analog 1, go to nothing when erecting foundation foundations and walls, since voids form in the joints of the blocks, which either substantially weaken the construction of the building, structure, or foundation, or substantially increase the consumption of materials and Labor costs, effectively nullifying the advantages of a mechanized factory technology for the production of elements (blocks) ensuring stability and high values of the strength and performance characteristics of elements (blocks).
There are two alternatives to the implementation of the curvilinear foundations and walls in complex buildings and structures not covered by the analog 1:
A) The implementation of all construction works, including the formation of local foundations and walls, directly on the construction site, most often a sequential method of sliding formwork - the method of erecting an expensive and labor-consuming manual labor, therefore suitable for the construction of only unique, one-off and difficult-to-form objects.
B) Creation of independent private ways of performing support structures for type classes of objects. For example, RU 2024715 (analog 3) is known for buildings and structures of a vaulted structure in which a vault made of prefabricated flat elements of the same size is installed on foundation blocks that differ in shape from the bar, and having an inclination angle corresponding to the angle of the support structure foundation. The patent also provides for the introduction of a stand-alone foundation foundation for the support of diaphragms and rigid metal connecting rods. The disadvantage of the method is its suitability for a rather narrow class of vaulted structures, therefore, despite the standardity of the element - the foundation block, it is not suitable for other constructions of buildings that do not have an easy vaulted solution. By the method of analogue 3, the main advantage of block methods of laying food and walls is lost - a large-scale industrial production of structural elements that make construction low-cost due to the information of the process of erecting a structure for installation work and making the process of creating structural elements outside the construction site
The object of the present invention is to create a universal method for the implementation of curved (foundation) foundations and walls on the basis of unified building elements (blocks), which, having the advantages of industrial production of structural elements (as analog 1), would allow performing arbitrary, Foundations and walls of complex structures of arbitrary shape. Such a problem is solvable only when creating a special block element, which by its simplicity is suitable for mass industrial production, its construction would allow for laying the foundation and walls of arbitrary curvature while maintaining the strength of the block laying and with a minimum consumption of laying construction materials.
In addition, in order to create competitiveness for methods with elemental dressings, the assembly and frame part of the foundation and walls must take on the spreading-strengthening functions of the dressing.
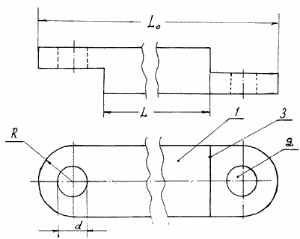 |
In order to achieve the stated objectives of the inventive method of laying, the invention provides for the block element to have rounded endings of half the height of the beam with an opening for passage of the support and mounting / guiding reinforcement of the foundation and walls. The second half of the height in this case is carried out by stepping on the entire length of the rounding. An example of the implementation of the foundation beam of the described construction is shown in the drawing, where 1 is the main body of the foundation element, 2 is the hole for the passage of the assembly frame framework, 3 is the end rounding, which allows to match the structural elements at different angles, which makes it possible to perform the foundation fundamentally, Number and variable curvature without loss of structural strength. The analog of the special configuration protrusions for the purpose of increasing the airtightness is AC SU 1131990 A, but in it the configuration protrusions are in the form of ribs. |
The set of sequential procedures outlined above leads to the following distinctive features of the claimed method.
1. A method for erecting a foundation foundation, including the pre-production of standard multimounted prefabricated elements (as in prototype 1 and analog 1), containing structural features that facilitate alignment during assembly and installation of structural elements, delivery and installation along rails, characterized in that the assembly and frame Guides that can simultaneously serve as communication routes are pre-positioned along the line of the foundation with a step determined by the size of the structural elements - foundation slabs made of various building materials of natural and artificial origin with roundings at the ends that allow the plates to be mated at various angles and holes allowing passage Through the system of slabs by frame-mounting guides, ensuring the spatial strength and stability of the foundation and walls. Special forms of the frame for the purpose of ensuring the strength of various forms of the building are proposed in different patents, but among them there is no skeleton playing the role of guiding during installation for the purpose of holding the form of the local configuration of the foundation.
2. The device (element) for carrying out the method according to claim 1 in the form of a system of reinforcing (for example, a system of rigidly coupled pipes) and mounting and restraining elements in combination with stackable elements of various materials. The block element has rounded endings of half the height of the beam with a hole for the passage of the support and mounting and directing reinforcement of the foundation and walls. The second half of the height in this case is carried out by stepping on the entire length of the rounding. An example of the implementation of the foundation beam of the described construction is shown in the drawing, where 1 is the body (the main body of the foundation element), 2 is the hole for the passage of the assembly frame, 3 is the end rounding (the coupling step), which allows to match the structural elements at different angles, Perform the local foundation of arbitrary, including variable curvature without loss of structural strength.
An additional comparison of the set of features of known methods and devices shows that
- the claimed method, having advantages of analogue 1 and prototype 1, associated with the possibility of high-speed and economical construction due to the adoption of the procedure for manufacturing standardized blocks on an external industrial basis, does not have their disadvantages, manifested in the implementation of the foundation and walls;
- the claimed method allows, without resorting to individual construction technological processes on the construction site, to perform complex configurations of foundations and walls while maintaining the spatial strength and stability of the structures.
The system of multiply connected block elements that are mounted and laid along the guides of the frame elements through the holes of the ears of the structural blocks, allows to arbitrarily place in the space hardening the main (for example, the tubular frame) of communication, which gives a solid monolithic structure together with the system of basic mounted blocks. Thus, the proposed method of erecting foundation foundations, consistently realizing the operations of pre-production of blocks on industrial sites, the operation of preparing the assembly and strength complex frame and the operation of junction of the system of assembly blocks with frame elements. Possesses the advantages of all patents and author's certificates, including GOSTs, described earlier, eliminating their shortcomings with regard to the foundation and walls.
CLAIM
1. A method for erecting foundations and walls from prefabricated prefabricated elements, characterized in that in the manufacture of curvilinear foundations and walls along the line of their location with a step defined by the dimensions of the precast element, mounting and frame guides are provided for placing prefabricated elements on them with rounded edges And holes at the ends for their interfacing at different angles, with rounding done up to half the height of the collecting element, the second half of the height of which is made with a ledge for the entire length of the rounding, and in the holes of the prefabricated elements there are mounting frames to ensure the spatial stability and strength of curvilinear Foundations and walls.
2. A method according to claim 1, characterized in that the communication paths are used as mounting rails.
3. An element for erecting curved foundations and walls according to claim 1, characterized in that the element is in the form of a block beam with rounded ends and holes at these ends for positioning the frame and frame reinforcement, the rounded ends being made up to half the height Beams, and the second half of the height is made with a ledge for the entire length of the rounding.
print version
Date of publication 01/21/2007




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.