| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2278229
![]()
LOW-STORAGE BUILDING WITH VENTILATED FACADE AND METHOD OF ITS EFFECTIVENESS (VARIANTS)
The name of the inventor: Salamatov Yuri Petrovich (RU); Salomatov Vladimir Petrovich
The name of the patent owner: Salamatov Yuri Petrovich (RU); Salomatov Vladimir Petrovich
Address for correspondence: 660122, г.Красноярск, ул. Pavlova, 69, ap. 2, V.P. Salomatov
Date of commencement of the patent: 2004.01.09
The invention relates to the field of construction, namely the erection of low-rise buildings. The low-rise building includes foundations, a framework consisting of metal columns arranged in two directions of metal crossbars forming the frame cells, metal connections located in the column line, slabs, external fencing consisting of a heat-insulating layer and a shell in the form of a ventilated facade layer made From tile elements, pitched roof and stairs. The foundations are dotted with ribbon inserts between them, at least along the outer contour of the building. Columns and crossbars are made of bent and / or curved profiles. Each floor slab is formed of a metal frame, a lower cement-chip board, a heat and sound insulating layer and an upper cement-particle board. Clearances between bolts and cement-chipboards are filled with heat and sound insulation material. Columns, crossbars and connections are provided with an anti-corrosion coating. Columns and crossbars have a T- or U-shaped profile. The outer guard comprises an inner finishing layer attached to the metal columns, bolts and connections from their inner side, an outer metal frame attached to the metal columns and bolts from their outer side. The thermal barrier layer is vapor-permeable, consisting of mesh bags of a length multiple of d, where d is the dimension of one of the sides of the plate element, with a heat-insulating granular non-combustible closed porous material or mineral wool plates, a length multiple of d, and fasteners, located inside the outer metal frame. The outer metal frame has horizontal and / or vertical bars of the T or H profile, located in steps of d. The tiles of the ventilated facade layer have L-shaped fasteners, by means of which they are connected to T-shaped or H-shaped bars. And the ways of erecting a low-rise building are given. The invention provides for improving the economic performance of the erected building by reducing the material consumption and labor costs by using lightweight elements of the structural framework of the building, light and quickly installed elements that make up the walls and the facade layer, and by eliminating the use of cement-sand mortars for the installation of walls and a ventilated facade layer .
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the field of construction and can be used for the erection of low-rise buildings, cottages of urban, rural and country buildings, public buildings for recreational, social, cultural, domestic purposes, industrial and storage facilities.
A building is known that includes a foundation, metal columns and crossbars forming a supporting frame (see RF patent 17550, MKI 7 E 04 B 1/00., Prefabricated frame-panel building / published 2001.04.10).
The disadvantage of this technical solution is the increased material consumption in the construction of walls.
The closest technical solution (prototype) to the claimed is a low-rise building comprising foundations, a framework consisting of metal columns arranged in two directions of metal crossbars forming the frame cells, metal bonds located in the column line, slabs, an outer guard consisting of A heat-insulating layer and a shell in the form of a ventilated facade layer made of tile elements, a pitched roof and stairs, the foundations being dotted with ribbon inserts between them at least along the outer contour of the building, the columns and crossbars being made of bent and / or bent-welded Profiles, and each overlap plate is formed of a metal frame, a lower cement chipboard, a heat and sound insulating layer and an upper cement-chip board, and the gaps between the crossbars and cement-chipboards are filled with heat and sound insulation material, the columns, crossbars and links are provided with an anti-corrosion coating (cm. Patent of the Russian Federation 2052615, МКИ 6 Е 04 Н 1/00. Low-rise building and skeleton of low-rise building / published 1996.01.20).
The disadvantages of this technical solution in comparison with the claimed are the increased material consumption and labor costs for the construction of walls and a ventilated facade layer.
A method for constructing a low-rise building is known, including the installation of a foundation, walls and roofing (see RF patent 2062841, MKI 6 E 04 B 1/00. Building and method of its erection / published 1996.06.27). The disadvantage of this method is the increased labor costs for the construction of walls.
Building of buildings using wall panels requires the use of sufficiently powerful lifting mechanisms, which increases the laboriousness, and hence the cost of erecting buildings. Therefore, the construction of, for example, residential cottages in the private sector with the use of wall panels is uneconomical. The use of cement-sand or adhesive solutions, when building walls, also increases the cost of erecting buildings.
The objective of the claimed invention is to improve the economic performance of the erected building by: reducing the material consumption and labor costs, by using lightweight elements of the load-bearing framework of the building, light and quickly installed elements that make up the walls and the facade layer; Exclusion of the use of cement-sand mortars for the installation of walls and facade layer; And by reducing the repair work, by increasing the durability of the building.
The task is achieved by the fact that a low-rise building comprising foundations, metal columns, two-way metal crossbars forming the frame cells, metal links located in the column alignment, slabs, external fencing consisting of a heat-insulating layer and a shell in the form of a ventilated facade Layer, made of tile elements, pitched roof and stairs, while the foundations are dotted with ribbon inserts between them at least along the outer contour of the building, the columns and crossbars are made of bent and / or bent profiles, each floor plate is formed From the metal frame, the lower cement-chipboard, the heat-sound-insulating layer and the upper cement-particle board, and the gaps between the crossbars and the cement-chipboards are filled with heat and sound insulation material, the columns, crossbars and links are provided with an anticorrosive coating, the columns and crossbars have T- or The U-shaped profile, the outer guard, contains an inner finishing layer attached to the metal columns, crossbars and connections from their inner side, an outer metal frame attached to the metal columns and bolts from their outer side, and the heat-insulating layer is a vapor-permeable consisting of mesh bags Length, multiple d, where d is the dimension of one of the sides of the plate element, with a heat-insulating granular non-flammable closed porous material or of mineral wool slabs of a length multiple of d and fasteners, is located inside the outer metal frame, the outer metal frame has horizontal and / or vertical crossbeams T-shaped or H-shaped profile, located in steps of d, arranged in steps of d, the tiled elements of the ventilated facade layer have L-shaped fasteners by means of which they are connected to the cross-bars of the T- or H-shaped profile.
The task is achieved by the fact that: the metal bonds located in the column alignment are made with an H-shaped profile; The inner finishing layer is made of gypsum fiber sheets or cement-particle boards; The fastening element for fixing the heat-insulating layer is made of an elastic plate in the form of an element with a stiffener and an F-shaped profile or a U-shaped bend at one end; The fastening element for fixing the heat-insulating layer consists of a threaded pin at both ends and a spline at one end, a disk nut and nut; Heat-insulating non-flammable closed porous material is made of foam silicate or foam glass granules or expanded clay or foam; Tile elements contain at least three L-shaped fasteners; Between the inner finishing layer and the heat-insulating layer there is a hydro-protective air gap.
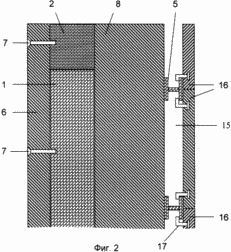
Making the thermal barrier layer 8 vapor-permeable is necessary in order that the vapor penetrating from the house through the inner finishing layer 6 to the heat-insulating layer 8 does not condense therein and the condensate does not freeze during periods of negative outside temperature. When the condensate freezes, ice breaks the pores of the heat-insulating layer and, thereby, its strength and heat-insulating properties decrease.
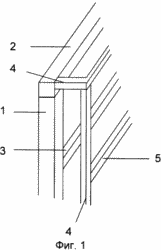
The execution of columns and crossbars, not with a closed profile, but in the form of a T- or U-shaped profile, makes it possible to reduce their material consumption, and consequently, their weight.
The presence of a waterproof air gap 9 between the inner finish layer 6 and the heat insulating layer 8 is caused by the fact that the condensate formed in the heat-insulating layer at a positive temperature close to zero does not drain onto the inner finishing layer and therefore does not damage it. The possible formation of moisture on the wall leads to the appearance of mold and other fungal microorganisms that adversely affect the living conditions in the room.
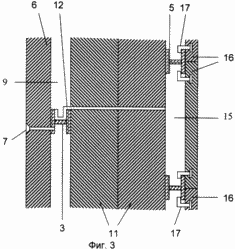
The presence of an air gap 15 between the heat-insulating layer 8 and the facade layer is necessary so that the vapor penetrating from the house through the inner finishing layer 6 to the heat-insulating layer 8 does not condense in it but exits to the outside atmosphere.
The technical feasibility of fasteners, columns, crossbars, links and crossbeams does not require justification.
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
|
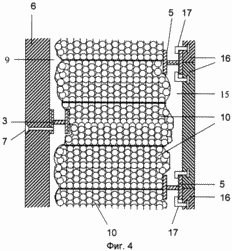
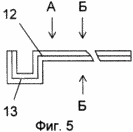
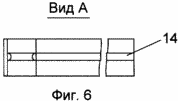
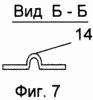
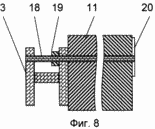
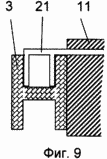
FIG. 1 shows a fragment of a vertical section of the supporting frame of a building with an outer frame; FIG. 2 shows a fragment of a vertical section of an outer fence of a building with columns, bolts and a heat-insulating layer; FIG. FIG. 3 is a fragment of a vertical section of an outer fence of a building with a heat-insulating layer consisting of mineral wool boards and a fixing member with a U-shaped profile; FIG. 4 is a fragment of a vertical section of an outer fence of a building with a heat-insulating layer consisting of mesh bags with a heat-insulating layer Granular non-flammable, closed porous material; FIG. 5 shows a fastening element with a U-shaped bend; FIG. 6 shows a view A of FIG. 5; FIG. 7 shows a view of BB, the stiffener of FIG. 8 - vertical section of a fragment of an option of fastening mineral wool boards; FIG. 9 is a vertical sectional view of a fragment of an embodiment of fastening mineral wool boards by a fastening element with an F-shaped profile. In this case, the relative dimensions of the constituent parts of the building fragments are conditional.
In this case: 1 - column, 2 - bolt, 3 - metal connection, in the form of H-shaped profile, in the column of the frame of the building, 4 - outer frame, 5 - horizontal crossbar H-shaped profile of the outer frame, 6 - inner finishing layer ; 7 - self-tapping screw; 8 - heat-insulating layer; 9 - waterproof air gap; 10 - bags with heat-insulating granular non-combustible closed-porous material; 11 - mineral wool plates; 12 - fastening element, with a U-shaped bend, for fixing the heat-insulating layer; 13 - U-shaped bend; 14 - stiffener; 15 - ventilated air gap; 16 - tiled elements of the facade layer; 17 - L-shaped fastening elements of tile elements; 18 - a rod with a thread at the ends; 19 - nut; 20 - disk nut; 21 - fixing element, with an F-shaped profile, for fixing the heat-insulating layer.
A low-rise building with a ventilated facade contains: metal columns 1 connected to bolts 2; Metal bonds 3 connected to columns and / or crossbars; An outer metal frame 4 connected to columns and bolts and having cross-bars 5; An inner finishing layer 6 attached to the columns, bolts and connections between them by means of self-tapping screws 7; A heat insulating layer 8 having a waterproof air gap 9 with an inner finishing layer 6 and consisting of bags with a heat-insulating granular non-combustible closed porous material 10 or mineral wool boards 11 attached to the metal bonds 3 by means of fasteners 12 having an U-shaped bend 13 and a stiffening rib 14 ; Ventilated air gap 15; The tiled elements of the facade layer 16 connected to the bars 5 by means of the L-shaped fastening elements 17.
In this connection, the connection of the mineral wool slabs 11 to the metal bonds 3 has the following embodiments: by means of the fastening elements 18, 19 and 20 of FIG. 8, by the F-shaped fastening element 21 for fixing the heat-insulating layer, FIG. In this case, the fastening element with the F-shaped profile has a stiffening rib that is the same as that of the fastening element with a U-shaped bend (see Fig. 7).
The initial general part of the three ways of erecting the building is as follows: they build foundations, mount metal columns 1, metal crossbars 2, metal ties 3 in the alignment of columns, an outer metal frame 4 with horizontal and / or vertical bars 5 T- or H- Located in steps of d, the slabs fill the gaps between the crossbars and the cement-chipboards with heat and sound insulation material, mount the pitched roof, the stairs, make the tile elements 16 with the size of one side equal to d, having, on the inside, L-shaped fasteners 17 .
Further, according to the first method of erecting a building, the following is done: the installation of the inner finishing layer 6 is carried out by attaching it to metal columns, crossbars and metal bonds located in the string of columns by means of screws 7, the plate elements 16 are mounted from the bottom upwards, Installation of each row of plate elements, produce a dense packing of mesh bags 10 with a length of a multiple of d, with a heat-insulating non-flammable closed porous material between the metal bonds 3 in the column alignment and the bars of the 5 T or H-shaped profile.
Explanations about gluing together on the contour of tiled elements of the facade layer in the course of their installation:
1) Rain streams capture a large number of gaseous industrial emissions from the atmosphere, such as oxides of carbon, sulfur, nitrogen and phosphorus, ammonia, chlorine and hydrogen chloride. Dissolving in part in the water, they turn the rain into an acid solution, destroying the concrete, marble and other materials. This increases the number of pores, capillaries and microcracks, which are all new foci of aggression, and the degree of destruction of the material is significantly increased. In addition, the content of acid oxides of sulfur and nitrogen as well as hydrogen chloride in the air can cause a shift in the ecological parameter of the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide equilibrium. In this case, the content of free carbon dioxide in the air, which is called "aggressive" in this case, is essentially increased. Aggressive carbon dioxide is in relation to mineral building materials (lime, marble and concrete), converting insoluble calcite CaCO 3 to water soluble calcium hydrogen carbonate Ca (HCO 3 ) 2 : CaCO 3 + CO 2 + H 2 O = Ca (HCO 3 ) 2 .
2) In the process of rain (chemically aggressive according to item 1)), at a certain head of wind, raindrops will penetrate between the tiled elements of the facade layer, destroyingly acting on the building elements of the building.
3) Bonding (sealing joints) around the perimeter of the plate elements can be made, for example, with EMPI polyurethane sealant, resistant to UV radiation, salts, acids and alkalis in concentrations up to 10%. The sealant does not change its volume during vulcanization, it does not flow down the wall, it is easily colored, polymerization occurs under the influence of air humidity, thus creating a strong and elastic sealed seam. It was developed by the French firm EMFI SA. (France, 67501 Haguenau Cedex, Rue Ettore Bugatti +33 (3) 88906044 + 33 (3) 88734838 http://www.emfi.com). Sealant Emfimastics PU-15 is certified by Russian certification bodies and has corresponding conclusions. Certificate of Conformity ROSS FR.CL16.H00172 №0148852 Gosstroy of Russia, Hygienic Conclusion №77.01.03.570.П.02012.01.2 State Sanitary and Epidemiological Service of the Russian Federation.
According to the second method of erecting the building, the following is done: in the metal bonds of the 3 H-shaped profile, holes are drilled through both opposing ribs; inside the outer metal frame 4, a number of mineral wool boards 11 are placed; they are inserted into the holes 3 drilled in metal bonds 3 and pierced through The proximal ends of the pins are located inside the cross-section of the metal bonds 3 of the H-shaped profile, screwed onto the nuts of the nut 19 and the pins are inserted into both sides of the metal bonds of the H-shaped profile, the disk nuts 20 are screwed onto the opposite ends of the pins by pressing the mineral wool plates , The assembly of the tile elements 16 is carried out, the inner finishing layer 6 is assembled by attaching it to the metal columns, bolts and metal bonds with self-tapping screws 7.
According to the third method of erecting the building, further the following is done: inside the outer metal frame 4 there are a number of mineral wool slabs 11, each mineral wool board is raised several centimeters in turn and pierced through it by the flat ends of fasteners with a U-shaped bend or F-shaped profile, Parts of the fastening elements into the upper groove of the metal bonds of the 3 H-shaped profile and lower the mineral wool board into place, make installation of the tile elements 16, install the inner finishing layer 6 by attaching it to the metal columns, bolts and metal bonds by means of screws 7.
The proposed low-rise building allows: to reduce the material consumption and labor costs, by using lightweight elements of the structural framework of the building, light and quickly installed elements that make up the walls and the facade layer; Exclude the use of cement-sand mortars for the installation of walls and facade layer, and reduce the amount of repair work, by increasing the durability of the building. At the same time, the building is completely made of non-combustible materials.
CLAIM
1. A low-rise building comprising foundations, a frame consisting of metal columns arranged in two directions of metal crossbars forming the frame cells, metal links located in the column line, slabs, an outer enclosure consisting of a heat-insulating layer and a shell in the form of a ventilated facade A layer made of tile elements, pitched roof and stairs, while the foundations are dotted with ribbon inserts between them, at least along the outer contour of the building, the columns and crossbars being made of bent and / or curved profiles, each plate Overlapping is formed of a metal frame, a lower cementite plate, a heat and sound insulating layer and an upper cement board, and the gaps between the crossbars and cement-slabs are filled with heat and sound insulation material, the columns, crossbars and links are provided with an anticorrosive coating, characterized in that the columns and crossbars have T or P Shaped profile, the outer guard comprises an inner finishing layer attached to the metal columns, bolts and connections from their inner side, an outer metal frame attached to the metal columns and bolts from their outer side, and the heat-insulating layer is a vapor-permeable consisting of mesh bags of a length , A multiple of d, where d is the dimension of one of the sides of the plate element, with a heat-insulating granular non-flammable closed porous material or of mineral wool slabs of a multiple of d and fasteners, is located inside the outer metal frame, the outer metal frame has horizontal and / or vertical cross bars T Or H-shaped profile, located in steps of d, the tiled elements of the ventilated facade layer have L-shaped fasteners by means of which they are connected to T or H-shaped bars.
2. A building according to claim 1, characterized in that the metal bonds located in the column alignment are made with an H-shaped profile.
3. A building according to claim 1, characterized in that the inner finishing layer is made of gypsum-fiber sheets or cement-slabs.
4. A building according to claim 1, characterized in that the fastening element for fixing the heat-insulating layer is made of an elastic plate in the form of an element with a stiffening rib and an F-shaped profile.
5. A building according to claim 1, characterized in that the fastening element for fixing the heat-insulating layer is made of an elastic plate with a stiffener and a U-shaped bend at one end.
6. A building according to claim 1, characterized in that the fastening element for fixing the heat-insulating layer consists of a threaded rod at both ends and a spline at one end, a disk nut and nut.
7. A building according to claim 1, characterized in that the heat-insulating non-flammable, closed-cell material is made of foam silicate or foam glass granules, or expanded clay, or foam isole.
8. The building of claim 1, wherein the tile elements comprise at least three L-shaped fastening members.
9. A building according to claim 1, characterized in that there is a hydro-protective air gap between the inner finishing layer and the heat-insulating layer.
10. The method of erecting a low-rise building, including the construction of foundations, the installation of metal columns, metal crossbars, forming the frame cells, metal bonds located in the string of columns, slabs, filling gaps between the crossbars and cement-slabs with heat-insulating material, installing a heat-insulating layer, ventilated facade layer , Teplogidroizolyacii closed-porous material pitched roof, stairs, characterized by the fact that before the installation of the outer fence to build an external metal frame with horizontal and / or vertical bars T or H-shaped profile, located in steps of d, where d - the size of one side of the tile Element, produce tile elements with the size of one of the sides equal to d, having L-shaped fixing elements on the inside, make the installation of the inner finishing layer by attaching it to metal columns, crossbars and metal bonds located in the column alignment, mounting from the bottom upwards Tile elements, after installing each row of tile elements, a dense packing of mesh bags of a length multiple of d is produced with a heat-insulating non-flammable closed porous material between the metal bonds in the column alignment and the T or H profile bars, providing a waterproof air gap between the inner finishing layer and Mesh bags.
11. The method of claim 10, wherein the tile elements are glued together around the contour during their installation.
12. The method of erecting a low-rise building, including the construction of foundations, the installation of metal columns, metal crossbars, forming the frame cells, metal bonds located in the string of columns, slabs, filling the gaps between the crossbars and cement-slab heat-insulating material, mounting the heat-insulating layer, ventilated facade layer , Teplogidroizolyacii closed-porous material pitched roof, stairs, characterized by the fact that before the installation of the outer fence to build an external metal frame with horizontal and / or vertical crossbar H-shaped profile, located in steps of d, where d is the size of one side of the tile element, Make tile elements that have L-shaped fasteners on the inside, in the H-profile bars, holes are drilled through both opposing ribs, a number of mineral wool slabs are placed inside the outer metal frame, the pins are pierced into holes drilled in the crossbeams and through them pierce mineral wool plates , The proximal ends of the pins are located inside the cross section of the bars of the H-shaped profile, they are screwed onto the nuts of the nut and the pins are inserted into both sides of the H-shaped crossbeams, the disk nuts are screwed onto the opposite ends of the pins, pressing the mineral wool plates, Inner finishing layer, by attaching it to metal columns, crossbars and metal bonds.
13. The method of erecting a low-rise building, including the construction of foundations, the installation of metal columns, metal crossbars, forming the frame cells, metal bonds located in the string of columns, slabs, filling gaps between bolts and cement-slab heat-insulating material, installing a heat-insulating layer, ventilated facade layer , Teplogidroizolyacii closed-porous material pitched roof, stairs, characterized by the fact that before the installation of the outer fence to build an external metal frame with horizontal and / or vertical crossbar H-shaped profile, located in steps of d, where d is the size of one side of the tile element, Make tile elements that have L-shaped fixing elements on the inside, a number of mineral wool slabs are placed inside the outer metal frame, each mineral wool board is raised several centimeters in turn and pierced through it with flat ends of fasteners with an F-shaped profile or a U-shaped bend, Insert the curved parts of the fastening elements into the upper groove of the cross-bar of the H-shaped profile and lower the mineral wool board into place, make the assembly of the tile elements, and install the inner finishing layer by attaching it to the metal columns, crossbars and metal bonds.
print version
Date of publication 01/21/2007




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.