| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2289558
![]()
METHOD FOR PROCESSING porous building products and constructions
Name of the inventor: ebeldin Nikolai (RU); Gerasimov Vitaliy (RU); Efimova Valentina (RU); Gerasimov Vladimir V.
The name of the patentee: Kazan State Power Engineering University
Address for correspondence: 420066, Kazan, st. Krasnoselskaya 51 KSPEU, STIPs
Starting date of the patent: 2005.03.31
The invention relates to ceramic processing techniques, silica brick, concrete products and structures and other porous materials to improve their properties and process parameters. The technical result of the invention is to improve the surface wear resistance and durability of construction products and designs. In the method of treatment of porous building and construction products, comprising impregnating bases acidic compound followed by treatment with a film-forming kislotootverzhdaemym for impregnation as an aqueous acidic compound geksaftorkremnievoy acid salt solution and as film-forming kislotootverzhdaemogo - phenol-formaldehyde resole resin, taken in equimolar ratios.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to ceramic processing techniques, silica brick, concrete products and structures and other porous materials to improve their properties and process parameters.
Known method of impregnating a surface of building products flyuatami - geksaftorkremnievoy aqueous solutions of acid salts, for example ZnSiF 6, MgSiF 6, Al 2 (of SiF 6)3 (Instructions for reinforcement of concrete and stone surfaces VNIISMI - M .: TsBTI, 1959).
The disadvantage of this method is the water permeability of building products and low efficiency.
It is known and the method of treatment of porous construction according to the authors. St. USSR №279404, C 04 B 41/68 - prototype compound comprising impregnating acid (oxalic acid solution) followed by treatment with a film-forming kislotootverzhdaemym (urea resin mixed with oxalic acid).
A disadvantage of the second method is a low wear resistance, strength building structures, and a high cost and scarcity of oxalic acid and urea resin.
Also, oxalic acid does not completely cure the resin in the cracks and capillary constructions.
Object of the invention is to improve strength and wear resistance of the surface of building products and structures. To achieve technical result in the method of treatment of porous building and construction products, comprising impregnating bases acidic compound followed by treatment with a film-forming kislotootverzhdaemym for impregnation as an aqueous acidic compound geksaftorkremnievoy salt solution (pH ~3-4), and as the film-forming kislotootverzhdaemogo - phenol-formaldehyde resole resin, taken in equimolar ratios.
Impregnation is carried out once the components - carpal manner by spraying or dipping at room temperature. Warm-up time of the treated layer 1-3 days.
The mechanism of action geksaftorkremnievoy acid salts, in particular magnesium as a readily available and least expensive, is as follows.
On the one hand, the salt is a compound formed by a weak base and a strong acid, is subjected to a two-step hydrolysis and forms a proton in aqueous solution ions that provide the desired pH value and having a catalyzing effect on the curing of the binder.
On the other hand, salt, diffusing into the pores of the product and interact with the components of the capillary walls, particularly calcium compounds, forming insoluble fluorides of calcium, magnesium and silica gel.
Phenol-formaldehyde resole film forming, filling the pores of the product, cured, forming rezitnuyu structure creates together with the newly formed inorganic compounds organomineral skeleton, sealing and reinforcing the structure of the material.
Tests Compressive strength ( ![]() SJ. ) And bending strength (
SJ. ) And bending strength ( ![]() Number of Bending. ) Ceramic and silicate bricks were made in accordance with GOST 8462-85.
Number of Bending. ) Ceramic and silicate bricks were made in accordance with GOST 8462-85.
Test on durability of concrete samples were carried out on compression-cubes (100 × 100 × 100 mm) in accordance with GOST 10180-90.
Tests on concrete abrasion carried out on samples-cubes on the circle abrasion LCI-3 in accordance with GOST 13087-81.
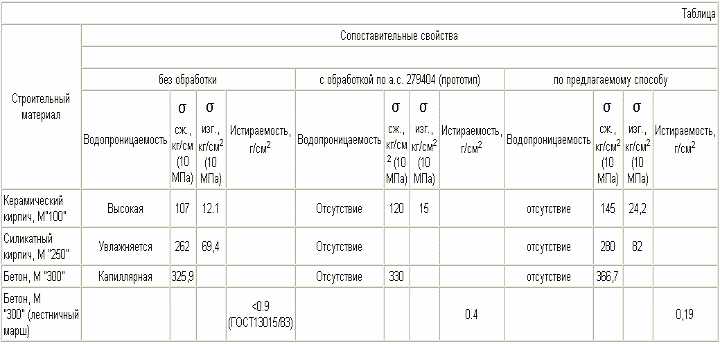
Comparative experimental data on water permeability, strength characteristics, abrasion porous building materials: ceramic bricks, sand-lime brick, concrete are given in the table.
The inventive method has advantages as the processing cost of acid component and the film-forming cost.
The method is being used by most often as acidic compound 10-40% aqueous salt solution geksaftorkremnievoy - kreineftorid magnesium, zinc or aluminum.
CLAIM
A process for treating porous building and construction products, comprising impregnating an acidic compound followed by treatment with a film-forming kislotootverzhdaemym, characterized in that for impregnation as an aqueous acidic compound geksaftorkremnievoy acid salt solution and as film-forming - phenol-formaldehyde resin was taken in equimolar ratios.
print version
Publication date 21.01.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.